预约演示
更新于:2026-03-07
Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide
更新于:2026-03-07
概要
基本信息
在研机构- |
最高研发阶段终止临床前 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
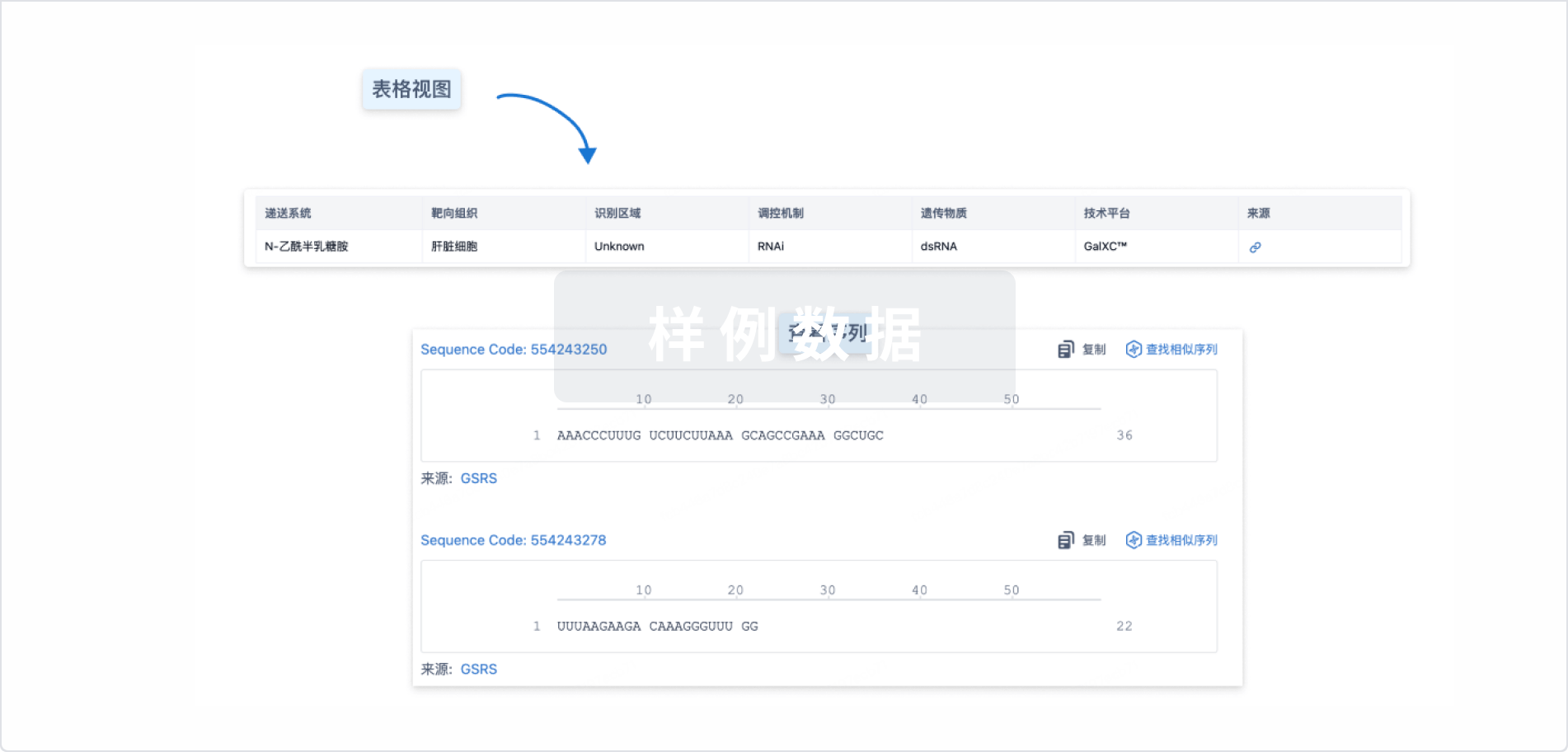
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
关联
100 项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1
项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的文献(医药)2017-03-01·International journal of obesity (2005)2区 · 医学
Pharmacological modulation of LMNA SRSF1-dependent splicing abrogates diet-induced obesity in mice
2区 · 医学
Article
作者: D Scherrer ; B Pau ; F Mahuteau-Betzer ; S Capozi ; C Lopez-Herrera ; J Santo ; F Casas ; Y Bareche ; L Lapasset ; R Najman ; C Apolit ; E-Z Amri ; G Béranger ; I C Lopez-Mejía ; P Fornarelli ; C Chavey ; J Tazi
SUBJECTS/METHODS:
Small molecules modulating SR protein activity and splicing were tested for their abilities to interact with SRSF1 and to modulate LMNA (AS). Using an LMNA luciferase reporter we selected molecules that were tested in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice. Transcriptomic analyses were performed in the white adipose tissues from untreated and treated DIO mice and mice fed a chow diet.
RESULTS:
We identified a small molecule that specifically interacted with the RS domain of SRSF1. ABX300 abolished DIO in mice, leading to restoration of adipose tissue homeostasis. In contrast, ABX300 had no effect on mice fed a standard chow diet. A global transcriptomic analysis revealed similar profiles of white adipose tissue from DIO mice treated with ABX300 and from untreated mice fed a chow diet. Mice treated with ABX300 exhibited an increase in O2 consumption and a switch in fuel preference toward lipids.
CONCLUSIONS:
Targeting SRSF1 with ABX300 compensates for changes in RNA biogenesis induced by fat accumulation and consequently represents a novel unexplored approach for the treatment of obesity.
2
项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的新闻(医药)2024-07-15
·药智网
偶联技术有多火?仅ADC(抗体偶联药物)领域,2017年之后就有超过10款新药获FDA批准上市,时至今日,全球进入临床阶段的ADC药物更是超过500余款,而万物偶联趋势下,这个数字还在无限扩大。
偶联药物有多卷?随着DS-8201获批上市,其突出的优势为ADC药物开发提出了更高的标准,也让“差异化偶联创新药”成为主要趋势,部分入局较晚的企业产品还在研就已丧失优势,不得不思考“偶联药物未来又将如何发展”?
其实,与最初“魔术子弹概念”时代并没有太大的变化,尽管蛋白质基因工程、化学偶联等技术的持续进步,但偶联药物的发展方向仍主要围绕新的靶抗原、新作用机制的有效载荷、新的抗体和载体形式等方面进行,而最大的不同就在于,偶联药物方向更偏向于了靶向性,即更多具有特异定向作用的结构被用作了小分子毒素等有效载荷的载体。
数据来源:公开数据整理
在此环境之下,组合用药、精确递药的理念和应用场景进一步扩大,多种新兴偶联技术概念相继涌现,业界也掀起了新兴偶联技术药物研发热潮。
差异化之路
非抗体蛋白偶联的出现
原则上来讲,偶联药物或许并不存在最优组合。
“万物皆可偶联”的核心理念之下,对最优组合的不断探索反而促进了更多创新技术的出现,继ADC爆火之后,PDC、FDC、SMDC、ISAC、RDC、ARC等多种技术如雨后春笋般不断冒出。
多样化策略之下,各种创新偶联技术相较传统ADC技术,或多或少都存在自身的核心优势,如PDC较强肿瘤穿透性、更低的免疫原性与更低的生产成本;SMDC工艺简单、安全性较好与安全性较高。而除了抗体、多肽与小分子等常规的靶向分子,近来出现的“非抗体蛋白”也逐渐全新的研究领域。
非抗体蛋白偶联药物,即将靶向性蛋白分子与发挥药效的效应分子(比如细胞毒分子,siRNA等)连接在一起,递送效应分子到特定疾病部位发挥作用。其原理上与ADC的机理类似,最大区别就是靶向分子的不同,但相较前者却有着核心的四大优势:
免疫副作用更小:蛋白偶联药物的蛋白部分大都来源于人类蛋白,例如重组人甲胎蛋白、重组人转铁蛋白等,相较于抗体、多肽能对人产生较小的免疫副作用。
靶点灵活:对靶点的选择相对灵活,很多企业在蛋白部分做了很多创新,例如Aro Biotherapeutics的Centyrins蛋白经过设计后可以与不同肿瘤抗原相结合。原则上可以避开偶联药物较集中的hear2等领域,去尝试更新、更小众的靶点方向。
高效:如外泌体偶联药物,可控的、模块化的药物装载与递送,突破了抗体偶联药物(ADC)载药率低、安全性有限的瓶颈,实现了更高效的提升效率。
稳定:蛋白偶联药物的结构稳定性一般较高,且具有高效、可控的制药载荷数量。
依从性高:可以通过在蛋白中引入半胱氨酸来提高药物的结合率,提高了药物的依从性和便利性。
不过,由于蛋白偶联技术总体上处于研究早期阶段,某种程度上其优势性与局限性都尚未研究透彻,后续或可能存在系列变化,但无论如何,从目前市面上相继出现的非抗体蛋白偶联技术来看,其临床优势也可初见端倪。
外泌体+转铁蛋白
蛋白偶联的两大典型技术路线
外泌体偶联药物(EDC)
2021年7月26日,Nature子刊Nature Biomedical Engineering在线刊发了中科院魏炜教授团队联合首都医科大学陶勇教授团队和昆士兰大学余迪教授团队共同署名文章,开发出外泌体偶联VEGF单抗,利用Treg来源的外泌体(rEXS)为载体,通过基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)敏感肽段(cL)连接VEGF抗体(aV),创建了rEXS-cL-aV体系。
后续通过外泌体化学偶联技术,在外泌体上进行可控、可调节的多功能化改造,如构建融合表达特定蛋白和外泌体膜蛋白的质粒,通过转染等方式,让该融合蛋白在外泌体来源细胞中大量表达,使得这些细胞分泌的外泌体能够会携目标融合蛋白。
图片来源:参考资料1
最终,将外源性小分子化学药物或生物大分子药物与外泌体偶联结合,形成外泌体偶联药物(EDC),实现高效、稳定、广谱、可控的外泌体模块化药物装载与递送,突破了抗体偶联药物(ADC)载药率低、安全性有限的瓶颈。
在该领域上,天津外泌体科技有限公司是国内掌握该技术商业化的领先公司,根据其以往公布的数据显示,其EDC药物装载率可达到92.3%、溶解性提高71.4倍、半衰期提高36.2倍、药峰浓度提高3倍、 口服相对生物利用度提升2.6倍;装载Herceptin抗体的外泌体呈现靶向效果相比对照组提升174.5倍,数据着实惊人。
至少就目前而言,EDC技术是外泌体领域最具商业化前景的技术,也是最为经典的非抗体蛋白偶联技术。
重组人转铁蛋白偶联药物
铁蛋白作为一种脱铁蛋白组成的具有大分子结构的糖蛋白,通常情况下是由蛋白质外壳和铁内核两部分组成,在维持机体铁代谢平衡和细胞抗氧化过程中起着关键作用,并且与炎症、血管增生和肿瘤有关。
而人工条件下的铁蛋白是具有空腔结构的笼形结构,外部的蛋白质外壳可通过基因和化学修饰增加靶向性,以达到提高递送效率的目的,而空腔机构则可以用于装载药物,实现药物的包载荷递送。
图片来源:参考资料2
2005年铁蛋白被成功用于包载递送阿霉素,开启药物递送领域新篇章,之后铁蛋白药物载体(FDC)的概念得以面世,相较ADC等常规偶联药物,其在安全性、渗透性、稳定性与靶向性等方面具有天然优势,尤其是靶向性方面。
安全性:铁蛋白是来自生物体内的天然存在蛋白质,毒性低,具有良好的生物降解性和生物相容性,不容易引起排异反应。
渗透和滞留性:由于铁蛋白粒径较小,使其易于逃脱网状内皮系统的吞噬,半衰期较长,可在病变部位形成蓄积,增强药效。
稳定性:铁蛋白的环境要求低,部分情况分解成亚基后仍能重组恢复笼状结构,在制备和储存工艺上要求简便很多。
靶向性:该领域铁蛋白主要优势主要有两者,一者是肿瘤靶向性的基本要求,即肿瘤细胞对铁离子的需求远大于正常细胞,使得肿瘤细胞表面的转铁蛋白受体过度表达;二者是其脑靶向性,由于铁蛋白可跨越血脑屏障,同时转铁蛋白受体在血脑屏障中的表达水平明显高于正常细胞组织,被寄希望于多种中枢神经疾病的药物载体。
很明显,就算同属于蛋白偶联药物,在较EDC药物高效、稳定与免疫副作用等相同的优势,不同技术路线的蛋白偶联药物也有着差异化的优势(如FDC的脑靶向性),而随着生物医药基础研究水平的上升,未来也有望诞生更多非抗体蛋白偶联药物,进一步丰富领域优势性的同时,也可以拉高整个市场的天花板。
国内空白
蛋白偶联药物的蓝海市场
就蛋白偶联药物市场而言,尽管近年来受ADC大火所带动,但目前国内外对于该类型药物的研究尚不完善,领域内多项技术仍处于临床早期阶段,相关性报道并不多。
数据显示,全球活跃蛋白偶联类临床药物仅有20款,且绝大多数均处于临床前阶段,FutureChe的镥[177Lu]Ludotadipep是目前临床进度最快的管线产品。
而就在研药物适应症来看,实体瘤、肺癌、乳腺癌等热门疾病类型的集中度明显更高,但同时部分蛋白偶联药物管线也选择了自免、脓毒症、代谢疾病与神经系统疾病为主要突破点。
其中,Aro Biotheraputics的「ABX1100」与Alpha Cancer Technologies的「ACT-903」是目前在研药物中信息披露较全面的品种,也是蛋白偶联药物中具有代表意义的品种。
「ABX1100」
ABX1100由ARO利用其Centyrins专利平台技术开发的核心产品,其特色的Centyrin蛋白FF0C具有优异的稳定性和溶解度、包括体积较小、可大肠杆菌生产,免疫原性较低,化学偶联方法与生产方式相对比较简单等优势,特别适合靶向递送寡核苷酸。
图片来源:ARO官网
与抗体相比,Centyrins在早期内体中含量更高递送速度更快,这可能Centyrins分子量小具有强渗透性优势, 这样更多的药物分子能够实现内涵体逃逸从而发挥其作用。
作为ARO针对庞贝病的一种全新潜在治疗方法,ABX1100由结合CD71受体的Centyrin与特异性干扰Gys1 mRNA表达的小干扰RNA(siRNA)结合而成,从而降低肌肉组织中Gys1酶的水平和整体活性。在GLP毒理学研究中显示出良好的安全性,肌肉中Gys1 mRNA的持久减少,支持每月或每季度给药的潜力,目前已获得美国食品药品监督管理局颁发的孤儿药资格认定和儿科罕见病资格认定。
「ACT-903」
Alpha Cancer Technologies Inc. (ACT)是一家生物制药公司,专注于其特有的重组人α胎蛋白(AFP)平台开发和商业化靶向免疫肿瘤学和免疫调节疗法。
图片来源:ACT官网
ACT-903作为ACT公司下一代ADC技术靶向α胎蛋白受体治疗癌症新方法的重要管线,其在2023 ASCO大会上首次亮相,是一种新型甲胎蛋白(AFP)-美坦氨酸偶联物,在一项卵巢异种移植模型试验中,ACT-903四种给药方案下的临床数据进行了对照,并观察其细胞毒性,目前所有治疗组体积缩小与生存期增加上均有明显统计学意义。
ACT-903结合物对肿瘤体积的影响
图片来源:ACT官网
总研究结果显示,ACT-903在卵巢异种移植模型中的安全性和有效性,以及在患者来源的癌症类器官中观察到的细胞毒性,支持ACT-903进入临床研究。目前ACT已计划在2024年提交ACT-903的研究新药(IND)申请。
小结
随着ADC药物的越来越火、越来越卷,就连PDC、FDC、SMDC、ISAC、RDC等领域的竞争格局也同样开始不容乐观,稀有标的属性正在逐渐消失,如何在偶联领域形成更差异化的竞争成为行业后续主要的思考方向。
但同时,药物研发虽不能盲目跟风,但也不能为了差异化而差异化,应着重考虑临床优势与产业优势,而对于蛋白偶联药物而言,尽管目前各项研究都尚处于早期阶段,但其高效、稳定与特殊靶向性等特点也足够吸引人。
或许,随着未来研究的深入,蛋白偶联药物还真有望成为下一代更具潜力的ADC技术。
路漫漫其修远兮,吾等仍将上下而求索。
参考资料:
外泌体的五大商业应用(三):外泌体偶联药物,精致颜容, 2024年01月14日
药物递送(八)——铁蛋白技术, 药物递送,2021年10月08日
双靶向Centyrin-siRNA偶联物ABX300及其siRNA平台分析, 洞见conjugates 2022年06月19日
ALPHA CANCER TECHNOLOGIES PRESENTS NEW DATA FROM ACT-903, AN AFP-MAYTANSINE CONJUGATE, IN ONLINE PUBLICATION AT THE 2023 AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY (ASCO) ANNUAL MEETING,ACT官网
来源 | 博药(药智网获取授权转载)
撰稿 | 头孢
责任编辑 | 八角
声明:本文系药智网转载内容,图片、文字版权归原作者所有,转载目的在于传递更多信息,并不代表本平台观点。如涉及作品内容、版权和其它问题,请在本平台留言,我们将在第一时间删除。
商务合作 | 王存星 19922864877(同微信)
阅读原文,是昨天最受欢迎的文章哦
抗体药物偶联物多肽偶联药物
2022-05-17
在 5 月 9 日至 12 日在波士顿举行的2022 TIDES USA 会议期间,Aro Biotherapeutics (简称“Aro”)展示了用于治疗庞贝病的候选药物 ABX1100的第一个概念验证数据。研究结果表明,Aro 的肌肉靶向 Centyrin-siRNA 偶联物可有效减少庞贝病小鼠模型中肌糖原的毒性积累。
庞贝病(PD)也被称为糖原贮积病II型 ,是一种罕见的常染色体隐性遗传病,属于溶酶体贮积症(LSD),随着时间的推移,由肌肉中负责分解糖原的酶——酸性α -葡萄糖苷酶(GAA)的突变引起。由于这种突变,PD患者的糖原水平升高,从而推动疾病进展。它的特征是肌肉衰弱,目前主要的治疗手段为患者接受酶替代治疗(ERT),静脉注射重组GAA。由于现有的治疗无法靶向且有效地将ERT传递到骨骼肌,限制了疗法的有效性和安全性,因此需要新机制的药物来进一步改善患者的预后。据报道,全球范围内PD的新生儿发病率约为1:30,000~1:10,000,台湾地区可达1:16,919,中国大陆目前还没有准确的流行病学数据,但有研究指出PD是中国人群中最常见的LSD之一。
Aro成立于2017年,是一家组织靶向的基因药物研发公司,基于专有的Centyrins蛋白技术平台,开发用于多种疾病的组织特异性靶向药物。另外,Aro也致力于通过外部合作,将Centyrins与各种不同的药物类别相结合,以实现不同疗法的有效靶向和递送。2021年1月,宣布完成A轮8800万美元的融资。
Centyrins是一种小的、超稳定的、工程化的蛋白质,具有几种独特的特性,使其非常适合靶向特定细胞上的受体,并将复杂的药物有效载荷递送到特定的疾病部位。与抗体相比,Centyrins在早期内体中含量更高、递送速度更快,可能是由于Centyrins分子量小且具有强渗透性,从而有更多的药物能够实现内涵体逃逸而发挥作用。
Aro正在开发独特的Centyrin-RNA偶联物疗法,将RNA药物高效、选择性地靶向作用于疾病的特定部位,使其能够递送至肿瘤细胞、免疫细胞和其它组织,作用于被认为是"不可成药"的疾病靶点。此外,Aro 不仅开发了 Centyrin 与RNA 偶联疗法,还开发了双特异性和多特异性 Centyrin 管线。
RNA 疗法领域在近十年来不断取得突破,也成为投融资的热点,主要的RNA 疗法包括mRNA(信使RNA)、siRNA(小干扰RNA)、ASO(反义寡核苷酸)、tRNA(转运RNA)、miRNA(微小RNA)等。其中siRNA 是人工合成的短片段双链RNA 分子,能够以同源互补序列的mRNA为靶目标降解特定的mRNA,引发基因沉默,抑制mRNA 编码蛋白质的产生,从而治疗了由相关蛋白质引起的疾病。
期待Aro 的Centyrin-siRNA 偶联物,能够推动罕见病及siRNA领域的进一步发展!
内容来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系删除,谢谢
siRNA合作抗体信使RNA寡核苷酸
100 项与 Centyrin-Targeted Oligonucleotide 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 免疫系统疾病 | 临床前 | 美国 | 2018-12-11 | |
| KRAS突变肿瘤 | 临床前 | 美国 | 2018-12-11 | |
| 肌肉疾患 | 临床前 | 美国 | 2018-12-11 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

