预约演示
更新于:2026-02-07
NS-050
更新于:2026-02-07
概要
基本信息
药物类型 ASO |
别名 NCNP-03、NS 050 |
作用方式 调节剂 |
作用机制 DMD exon 50调节剂(DMD 外显子50调节剂) |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
原研机构 |
非在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段临床1/2期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
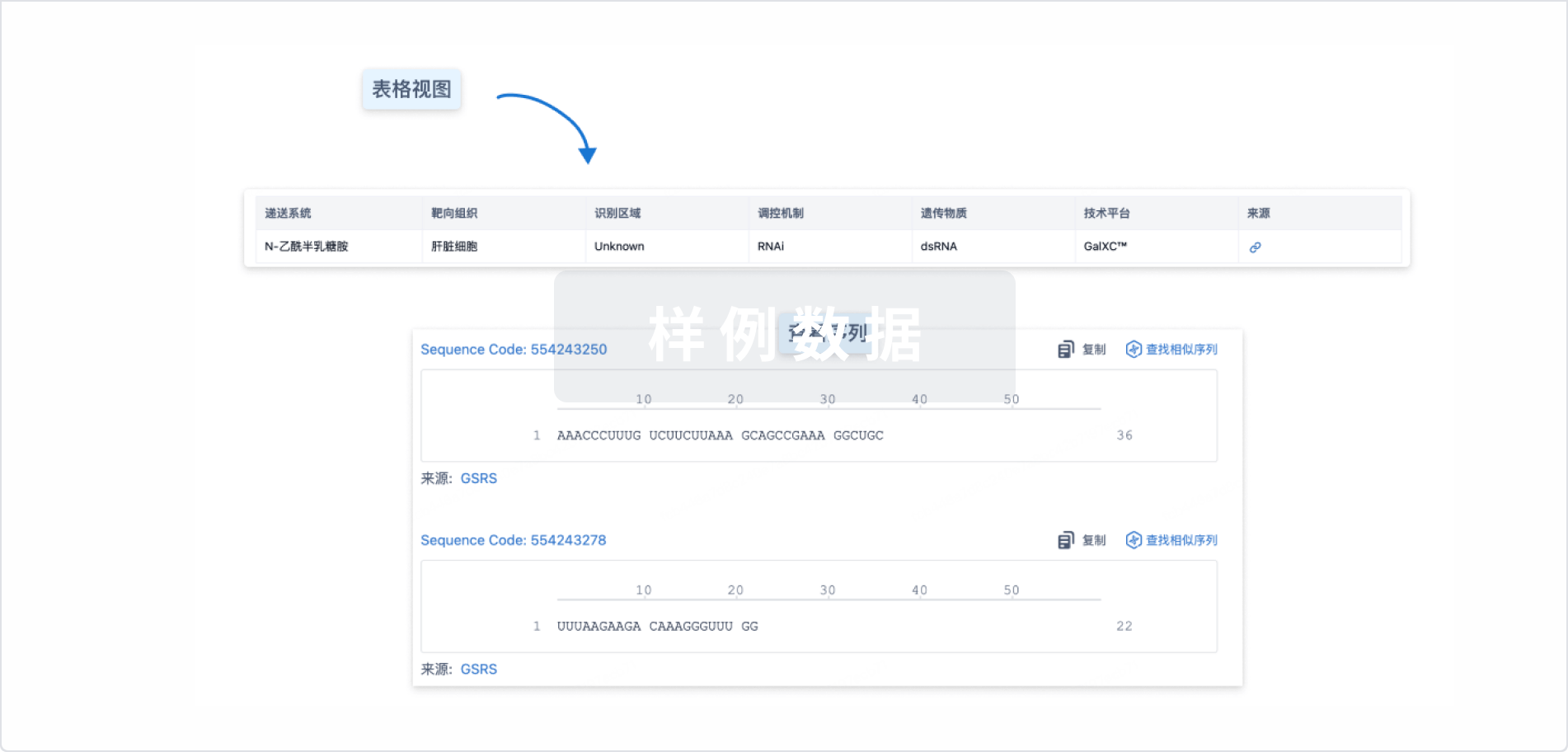
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
关联
1
项与 NS-050 相关的临床试验NCT06053814
A Phase 1/2, First in Human, Multiple-dose, 2-part Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of NS-050/NCNP-03 in Boys With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
This is a Phase 1/2 study of Multiple-Ascending Dose (MAD) levels for 12 weeks of treatment followed by 24 weeks of open-label treatment with a selected dose of NS-050/NCNP-03 administered once weekly to ambulant boys with DMD, who have a DMD exon deletion amenable to exon 50 skipping.
开始日期2024-09-18 |
申办/合作机构  NS Pharma, Inc. NS Pharma, Inc. [+1] |
100 项与 NS-050 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 NS-050 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 NS-050 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
2
项与 NS-050 相关的新闻(医药)2025-12-31
您好,我是大兵(尹相兵),是一名DMD孩子家长,也是专家型DMD家庭倡导者, 见字如面。
2025年已经过去,DMD药物在国内这一年有了一个很大的进步和发展,给7万多名DMD患者群体带来了新的希望。
在此,非常感谢这一年DMD领域的医生专家 ,研发DMD药物的药企和科学家,DMD患者组织和DMD患者家庭的一起努力,很多DMD药物在国内上市或陆续开展临床试验。
2026年,希望的曙光就在眼前,所有DMD的群体或个人,我们要继续一起努力,争取为DMD孩子早点用上好的药物,提升DMD患者生活质量,让DMD患者更好地享受美好的生活,体验有意义有价值的生命。 一、国内篇1.温和激素
温和激素,又叫安迦利(通用名:伐莫洛龙口服混悬液,vamorolone;规格:40mg/mL,100mL/瓶),在2025年12月11日,已获得中国国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)批准用于治疗四岁及以上的杜氏肌营养不良(DMD)患者。
在 Vision-DMD 研究中,安迦利(伐莫洛龙)6mg/kg/ 天与足量泼尼松 0.75mg/kg/ 天在所有运动功能上疗效相似,且该改善可持续 48 周;VBP15-LTE 研究 30 个月数据显示,安迦利组患者由卧位至站立速度均值始终高于基线。
安全性上,安迦利较传统激素,临床相关不良反应的频率和严重程度更低,行为异常、糖尿病等不良事件更少,无白内障发生,对骨代谢和生长无有害影响,支持 DMD 患者长期足量规范治疗。
【洞察】:温和激素,2025年申请医保国谈没有成功,主要原因可能:
1.价格2万多一瓶,相对比较高,纳入医保可能有一定的难度,在医保测算中,性价比还有一定的距离;
2.审评药物的评委,对DMD可能缺少足够的了解和认识,认为是一种不治之症,其实DMD通过DMD药物也能很好的维持生病,也会像慢性病一样管理起来,目前通过激素+康复,延缓病情,提升生活质量;
3.DMD罕见病药物——温和激素,由于是第一次申请,不见得立马就能申请成功,每年有很多药物都会去申请,不一定都会第一次就成功,积累好经验,为以后做好准备。虽然没有纳入医保,但是温和激素进入了商保目录,至少江苏、安徽、广东、北京等地区,部分DMD家庭借助商保(惠民保)能够先用得起来,再加上温和激素药店在全国各省市陆续开通,拿药的便利性大大加强。
【展望】:2026年,温和激素,由于每瓶价格降到1万左右,大大减轻部分DMD患者用药的负担,同时在医保国谈审核阶段通过机会更大,结合医保测算,大概率会纳入医保目录,到时候大部分DMD家庭都可以用得起,再加上惠民保和V保等商业保险加持,再报销剩余的自费部分,大大减轻DMD患者家庭沉重的经济负担。2.西达苯胺
西达苯胺,(Chidamide;商品名:爱谱沙/Epidaza)是全球首个亚型选择性组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDAC)抑制剂、中国首个原创抗肿瘤化学新药、国家1类新药。西达本胺对肿瘤抑制性免疫微环境具有重新激活作用,可单独或联合其他药物治疗恶性肿瘤,具有广阔的应用前景。
【洞察】:微芯生物的研发团队严肃而审慎的研究:西达本胺显示出延缓DMD疾病进展、改善肌肉功能和患者生存质量的潜力。
2025年12月3日,在广州,一项由研究者发起的西达本胺治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)临床研究正式启动。
西达苯胺,针对DMD患者来说,正所谓老药新用,探索西达本胺治疗DMD的安全性及初步疗效。
西达苯胺对比于2024年美国FDA批准了一款小分子药物(平均年治疗费用约为490万元人民币),若能应用于DMD治疗,年治疗费用可能仅是海外的零头。
【展望】:2026年,西达苯胺,如果一年的扩大药物适应症临床试验顺利,并且效果比较好,那么DMD患者群体就可以及时用上西达苯胺,很好地延缓DMD患者病情,提高生活质量。
希望在2026年,西达苯胺成为DMD孩子们的一条安全、有效且能够负担的治疗路径。3.BBM-D101注射液
BBM-D101 是信念医药自主研发的 AAV 基因治疗药物,用于治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)。
通过单次静脉输注,以高效肌肉靶向工程化载体递送优化基因,拟实现 “一次给药、长期有效”。其剂量低于同类产品,获美 FDA 孤儿药等认定,临床数据显示安全性与疗效良好。
【洞察】:2025 年信念医药 DMD 基因治疗药物 BBM-D101 注射液研发与临床推进成果显著:1 月获批美国 IND,2 月其临床试验申请获 NMPA 受理;3 月上海儿童医学中心完成该药 IIT 研究首例给药,给药的孩子激素激酶下降了不少,验证了IIT临床的安全性和有效性;8 月北京协和医院戴毅主任带领的团队,顺利开展注册临床研究首例受试者给药,该药 “一次给药、长期有效” 的设计已在前期临床中展现良好安全性与疗效。
【展望】:2026年,信念医药会继续携带DMD患者群体的希望,应该会继续扩大DMD患者群体给药范围,加快国内迷你蛋白上市的步伐,尽早地惠及DMD患者群体,让更多的DMD孩子得到更好的基因治疗的效果。4.RAG-18
RAG-18是一款首创作用机制的双链saRNA药物,通过RNA激活机制特异性靶向激活肌肉细胞中UTRN基因表达。
由UTRN基因编码的肌营养不良蛋白(Utrophin)在结构和功能上与抗肌萎缩蛋白(Dystrophin)相似,它的上调可以功能性替代DMD肌肉细胞中缺失的抗肌萎缩蛋白,从而治疗所有突变类型的DMD和BMD患者。
【洞察】:2025 年 12 月 12 日,李龙承博士带领的中美瑞康研发团队研发的 RAG-18 药物,与北京协和医院联合发起 IIT 临床研究。
该研究由北京协和医院神经科副主任、神经肌肉病领域知名专家戴毅教授牵头主持,核心目标为系统评估 RAG-18 在 DMD 患者中的安全性与药代动力学特征,并探索其改善患者肌肉功能的临床潜力。
【展望】:2026年,RAG-18药物可能进行扩展DMD患者范围临床试验,可能会开展第1期的临床试验,到时候会有更多的DMD孩子参加临床试验的机会,早点得到saRNA候选药物的治疗。
5.FL-dystrophin
深圳湾实验室、上海思珀诺因生物科技等为突破 mRNA 递送瓶颈,研究团队依托长期临床前与转化研究基础,采用具备生物相容性好、低免疫原性、易跨越生物屏障等优势的工程化细胞外囊泡(EV)作为递送载体,打造 EV mRNA 平台。
该平台通过四大创新突破技术局限:递送 FL-dystrophin mRNA 实现全长蛋白质补充以修复基因缺陷,采用非病毒系统规避 AAV 载体毒性风险,适用于所有 DMD 突变类型,且可重复给药调整剂量,为相关治疗提供新方向。
【洞察】:2025 年 7 月,多方科研与医疗团队合作获准开展全球首例非病毒载体全长抗肌萎缩蛋白基因疗法治疗 DMD 的临床试验,该试验同时也是国际首个采用细胞外囊泡递送平台的 DMD 相关 IIT 试验,为这一致命性遗传病治疗开辟了新路径。
【展望】:2026年,希望通过细胞外囊泡递送平台的全长抗肌萎缩蛋白基因疗法治疗 ,能够在有效性和安全性性上效果显著,及时开展第1/2期的临床试验,扩大DMD患者用药的机会,尽早在五年之内能够推上市,惠及所有的DMD患者。6.GEN6050X
GEN6050X 基于新芽全球独家权利的无 RNA 编辑活性、靶向AID介导突变酶 (TAM) 胞嘧啶碱基编辑技术开发而成,是一款靶向外显子50跳跃可治愈的DMD静脉注射胞嘧啶碱基编辑药物。
通过单次系统给药,GEN6050X通过介导外显子跳跃的方式永久恢复抗肌萎缩蛋白的表达。
【洞察】:2025年6月25日,新芽基因宣布其体内碱基编辑创新疗法 GEN6050X 获 FDA 授予的儿科罕见疾病资格认定,该疗法采用独家 TAM 胞嘧啶碱基编辑器,通过 AAV 系统递送,靶向可经外显子 50 跳跃治愈的杜氏肌营养不良患者。
此前,该疗法已于 2025 年 3 月 6 日获 FDA 临床试验新药申请批准,同年 6 月 10 日获 FDA 孤儿药资格认定。
【展望】:2026年,新芽基因希望能再接再厉,在国内获得国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)IND批准,尽快开展国内的第1期的临床试验,扩大DMD患者临床试验的范围,尽早能在几年之内,国内能够上市,早惠及DMD患者们。7.反义寡核苷酸药物
反义寡核苷酸(ASO),药物是一类人工合成的短链核酸分子,可通过与靶基因 mRNA 互补结合,以抑制翻译、诱导 mRNA 降解或调控剪接的方式发挥作用,其具有靶向性强、作用直接的特点,需经化学修饰提升稳定性与细胞穿透性,且多采用静脉或鞘内注射给药。
该类药物在罕见病、神经退行性疾病等领域应用广泛,尤其在杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)治疗中,可通过调控外显子跳跃,让患者基因生成具有部分功能的肌营养不良蛋白,实现精准治疗。
【洞察】:2025年,有DMD部分患者家长们正在推动51、53、55等跳跃药物的研发,对于大部分外显子缺失的热点区域的DMD孩子,有机会能够早日用上国内价格低廉,用得起的跳跃药物。
【展望】:2026年,预计会有51、53、55等跳跃药物可能进行开展临床试验,让反义寡核苷酸(ASO)尽快在国内上市,早日惠及外显子缺失的DMD患者。8.GC801注射液
GC801注射液是一款蛋白酶类药物,有望突破载体介导的基因治疗过程中因预存抗体而产生的治疗局限,有效拓宽AAV基因治疗范围。
让原本因体内预存高滴度AAV抗体而无法接受基因治疗的患者获得先进治疗的机会,同时也让AAV基因治疗重复给药成为可能。
【洞察】:2025 年 12 月 23 日,锦篮基因自主研发的 1 类治疗用生物制品 GC801 注射液获国家药监局临床试验申请受理,该药物为 IgG 降解酶类创新药,可解决 AAV 基因治疗中预存抗体带来的治疗局限,这也是锦篮基因申报的第五款新药注册临床试验。
【展望】:2026年,GC801 注射液希望有新的图片进展,帮助DMD患者们在迷你蛋白的基因药物上早日实现重复给药。 二、国外篇
尽管过去十年,杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)的临床治疗已取得长足进步,但患者群体仍存在显著的未满足医疗需求。
为此,Satellos、Regenxbio、Wave、Dyne、Avidity 等多家生物医药企业,正积极布局新一代实验性疗法的研发工作,旨在进一步提升治疗效果、扩大适用人群覆盖范围。
2026 年或将成为 DMD 治疗领域实现突破性进展的关键之年。尽管近年来已有多款疗法获批上市,但儿童 DMD 患者的临床需求仍未得到充分满足。
值得关注的是,随着各企业下一代治疗方案的研发持续推进,叠加行业监管体系的日趋完善,业内专家预测,全新的治疗选择有望加速落地。
当前,Satellos、Dyne、Avidity、Wave Life Sciences 等企业正全力攻克现有治疗瓶颈。
依托新一代外显子跳跃疗法,以及 Regenxbio、Solid Bio 等公司在基因治疗领域的研发突破,业界对未来涌现更多 DMD 治疗方案抱有充分信心。1.Duvyzat
Duvyzat 是 Italfarmaco 集团子公司 ITF Therapeutics 研发的口服混悬液,活性成分为 givinostat(吉维诺司他),属于组蛋白脱乙酰酶(HDAC)抑制剂,是首个获批用于所有基因型杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)的非甾体药物。
【洞察】:2025 年是 Italfarmaco 旗下 DMD 治疗药物 Duvyzat(活性成分为 givinostat)的关键突破之年,该药继 2024 年获美国 FDA 批准后,于 2025 年 6 月凭借 III 期 EPIDYS 试验数据获欧盟有条件上市许可,覆盖 27 个欧盟成员国及冰岛、列支敦士登、挪威,适用于 6 岁及以上可行走的 DMD 患者(需与皮质类固醇联用);
作为一款不限基因突变类型的 HDAC 抑制剂,其通过抑制异常 HDAC 活性延缓肌肉退化,临床数据证实可显著改善患者运动功能、降低疾病进展速度,且口服剂型提升了用药依从性,同时欧盟获批要求企业开展后续临床试验以进一步验证长期疗效与安全性,该药的广泛获批填补了 DMD 治疗的部分缺口,成为惠及更广泛患者群体的重要治疗选择。
【展望】:2026年,这块对DMD患者非常重要的延缓病情的药物,能够像温和激素一样大范围的降价,能够引进到国内,早日惠及国内的DMD患者们。2.Satellos: SAT-3247
SAT-3247是加拿大 Satellos Bioscience 研发的首款靶向 AAK1(衔接蛋白相关激酶 1)的口服小分子 DMD 治疗候选药,为首创(first - in - class)、不依赖抗肌萎缩蛋白(dystrophin)的肌肉再生修复疗法,获美国 FDA 孤儿药与罕见儿科疾病资格。
【洞察】:2025年12月8日,Satellos公司宣布启动一项针对7至10岁杜氏肌营养不良症门诊患者的SAT-3247(NCT07287189)的IIa期临床试验。该试验将采用随机、双盲、安慰剂对照、周内给药方案,在12周内研究两种剂量的SAT-3247,以确定最佳剂量、安全性、耐受性和初步疗效。
【展望】:2026年,希望有更好的临床数据出来,能够早日上市,惠及全球的DMD患者。3.Regenxbio: RGX-202
RGX - 202 是 Regenxbio 研发的在研一次性基因疗法,核心为含功能性C端(CT)结构域的新型微肌营养不良蛋白构建体,借助 NAV AAV8 载体与肌肉特异性启动子Spc5-12靶向骨骼肌和心肌,用于治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD),获美国 FDA 孤儿药、罕见儿科疾病及快速通道资格.
【洞察】:2025年,RGX-202 正处于关键研究阶段,Regenxbio 正在基因治疗市场上与 Sarepta 的 Elevidys 展开竞争。
实验招募了30名年龄在1岁或以上的患者,因此总人群年龄小于Elevidys的现有标签。
截至 2025 年 12 月已完成关键III期试验入组。据 Kelly 称,2024 年 11 月发表的一小部分患者的首批研究结果“极其令人鼓舞”,表明患者的力量和时间功能测试有所改善,并且安全性良好。
【展望】:Regenxbio 预计将于 2026 年提交生物制品许可申请 (BLA)。Kelly 表示,DMD 基因的大小对于 AAV 载体来说太大,这是该领域基因治疗的一大障碍。
因此,人们使用了缩短的形式,但其最终产物无法像全尺寸蛋白质那样发挥作用。与 Elevidys 相比,Regenxbio 的结构允许使用稍大一些的基因版本。
Kelly渴望看到之前一项试验的结果能够推广到更多患者身上。他认为,如果有效,这将为正在寻找杜氏肌营养不良症基因疗法的父母提供另一种选择和机会。4.Avidity Biosciences: Del-Zota
Del-Zota(delpacibart zotadirsen)是Avidity基于AOC平台开发的抗体寡核苷酸偶联物,靶向1型转铁蛋白受体,精准递送寡核苷酸至肌肉组织,通过外显子44跳跃机制治疗特定突变型杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD),可显著提升肌营养不良蛋白水平并降低肌肉损伤标志物肌酸激酶。
【洞察】:2025年是其关键突破年,获FDA突破性疗法认定,临床数据显示患者治疗一年后多项功能指标显著改善,肌酸激酶下降超80%,公司推进年底前提交BLA,并启动患者管理获取计划。
据CureDuchenne首席科学官Michael Kelly介绍,delpacibart zotadirsen (del-zota) 在I/II期试验中将 DMD 患者的肌营养不良蛋白生成量提高到惊人的 25% 正常水平。这是从任何药物中观察到的最佳外显子跳跃证据之一。
此外,Del-Zota 将肌酸激酶降至几乎正常水平。Del-Zota已获得快速通道资格认定,并因其与FDA的关联而获得孤儿药资格认定。
【展望】:2026年核心展望为推动上市审批,依托诺华收购后的资源协同加速商业化落地,同时拓展全球市场布局,有望填补DMD外显子44跳跃治疗的临床空白,为罕见肌病治疗领域带来新突破。通过关注外显子 44(目前尚无批准的药物),Avidity 可能能够为易受外显子 44 跳跃影响的 DMD 患者的 6% 提供治疗。5.Capricor Therapeutics: Deramiocel
Deramiocel(CAP-1002)是Capricor Therapeutics研发的同种异体心脏球源性细胞疗法,专注治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)相关心肌病,获FDA孤儿药、RMAT等多重资格认证。
其通过双重保护机制延缓病程,III期HOPE-3试验显示可使上肢功能衰退减缓54%、心脏功能衰退减缓91%,安全性良好。
【洞察】:2025年初提交BLA遭FDA驳回,要求补充数据;年末公布HOPE-3积极顶线结果,推动公司计划年内补充提交数据回应FDA,股价因此暴涨超5倍,获Piper Sandler等机构看好。
同时,与日本新药的合作持续推进,为欧洲商业化奠定基础。
【展望】:2026年聚焦审批与商业化,预计FDA将开展6个月II类审查,中期或实现获批,成为全球首个DMD心肌病细胞疗法;获批后将获8000万美元里程碑付款,推动欧美市场落地,分析师预测公司股价存73%以上上涨空间。
如果获得批准,Deramiocel 将成为首个专门用于治疗杜氏肌营养不良症 (DMD) 心肌病的药物。
几乎所有患者在成年后都会出现心脏问题,这使其成为该疾病的主要死因。根据监管机构的意见,Capricor 已申请获得 FDA 的全面批准,这在 DMD 市场中较为罕见,因为大多数药物都是通过 FDA 的加速审批程序获得批准的。6.Dyne Therapeutics: Dyne-251
Dyne-251是Dyne Therapeutics基于FORCE平台开发的抗体偶联寡核苷酸药物,靶向转铁蛋白受体1实现肌肉组织精准递送,通过外显子51跳跃恢复杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)患者功能性抗肌萎缩蛋白表达,获FDA快速通道、孤儿药等多项认定。
【洞察】:2025年为其关键临床大年,不仅获突破性疗法认定,DELIVER试验注册性扩展队列数据积极,抗肌萎缩蛋白表达量较同类药物提升近10倍,且18个月长期数据验证持续功能改善与良好安全性,年底完成核心数据读取。
【展望】:2026年展望聚焦监管与商业化推进,计划年初提交美国加速批准申请,同步启动全球3期确证性试验,若进展顺利,有望成为新一代DMD疗法标杆,同时支撑公司DMD全外显子管线布局落地。
为了尽快获得其基于FDA基因输入的下一代外显子51跳跃疗法Dyne-251的批准,Dyne公司目前正在招募受试者参与一项关键性试验。肌营养不良蛋白的表达将作为替代终点指标。7.Wave Life Sciences: WVE-N531
WVE-N531是Wave Life Sciences开发的反义寡核苷酸(ASO)疗法,靶向杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)相关基因,通过外显子跳跃机制促进功能性抗肌萎缩蛋白表达,其肌肉组织高靶向性与良好耐受性为核心优势。
【洞察】:2025年,该药物完成关键1b/2a期试验扩展队列研究,进一步验证了肌肉中高浓度分布特性及明确的外显子跳跃活性,安全性数据持续积极,为后期研发奠定坚实基础,同时获FDA孤儿药认定。
【展望】:2026年,聚焦临床推进与管线协同,计划启动2期关键性试验以积累更多疗效数据,同步探索与公司其他神经肌肉疾病管线的协同价值,若进展顺利,有望成为DMD精准治疗的重要候选药物,强化公司在ASO领域的差异化竞争力。
在评估患者的需求后,Wave Life Sciences 首席执行官保罗·博尔诺 (Paul Bolno) 表示,更成功的治疗方法是改善细胞分布,以实现更高的肌营养不良蛋白产量和一致的表达。
这项二期临床试验的六个月中期分析显示,Wave公司的WVE-N531(一种外显子53跳跃突变体)在所有患者体内均持续表达9%肌营养不良蛋白。据Bolno称,这使得患者的肌肉外观更健康,并降低了血液中肌酸激酶(一种肌肉损伤的生物标志物)的水平。8.Generium: GNR-097
GNR-097 是俄罗斯 Generium 公司研发的杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)基因治疗药物,以血清型 9 重组腺相关病毒为载体,编码截短的肌营养不良蛋白基因,通过单次静脉注射给药,为进行性 DMD 提供创新治疗方案。
【洞察】:2025年,GNR-097药物进入关键 1/2 期临床试验,采用多中心、单盲、随机、安慰剂对照设计,在俄白两国多家顶级儿科医疗中心开展,聚焦安全性、耐受性与有效性评估,填补了俄罗斯该领域基因治疗临床研究空白,成为全球 DMD 基因治疗赛道的重要新增力量。
【展望】:2026年,若临床试验数据积极,有望推进至后期研究,加速上市进程以满足未被满足的医疗需求;或进一步拓展试验覆盖范围与人群,优化给药方案;同时可能推动俄罗斯基因治疗产业链完善,为同类药物研发提供技术借鉴,助力该领域创新突破。9.NS Pharma: NS-050/NCNP-03
NS-050/NCNP-03是NS Pharma研发的反义寡核苷酸类药物,靶向杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)的外显子50跳跃治疗,通过修正 dystrophin 基因剪接产生功能性蛋白以缓解症状,适用于特定基因突变患者,获FDA罕见儿科疾病认定。
【洞察】:2025年,药物处于Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床阶段(Meteor50研究),试验聚焦安全性、 dystrophin 生成及运动功能评估,全球多中心推进顺利,为约4%的DMD潜在受益人群带来新希望。
【展望】:2026年,随着试验持续推进(预计2027年结束),有望获取关键临床数据,加速疗效验证;若数据积极,将推动向后期临床转化,进一步填补外显子50跳跃治疗的未满足医疗需求,助力拓展NS Pharma在DMD领域的靶向治疗布局。10.Sqy Therapeutics: SQY51
SQY51是Sqy Therapeutics研发的首款三环DNA类反义寡核苷酸药物,靶向肌营养不良蛋白前体mRNA的51号外显子,通过外显子跳读机制恢复功能性阅读框,用于治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)。该药物采用静脉输注给药,具备新一代寡核苷酸药物的靶向优势。
【洞察】:2025年,SQY51临床与政策突破的关键年,AVANCE 1 Phase 1/2a临床试验完成12名患者入组,Phase 1阶段已结束,Phase 2a稳步推进;同时获欧盟EMA孤儿药认定,此前2024年已获美国FDA孤儿药资格,双重认定凸显其临床价值。
【展望】:2026年,核心看点为AVANCE 1试验关键数据公布,将验证药物安全性与药效;同时计划启动临床试验延伸阶段,持续积累长期用药数据,为后续临床推进及全球市场布局奠定基础,有望填补DMD患者未被满足的治疗需求。11.BioMarin: BMN 351
BMN 351是BioMarin研发的针对杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)的创新疗法,聚焦51号外显子跳跃患者群体,核心目标是提升患者肌营养不良蛋白水平,目前处于Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床阶段。
【洞察】:2025年为该药物关键临床数据窗口期,年底前公布了6mg和9mg/kg队列活检数据,且模型预测其肌营养不良蛋白水平有望在稳态阶段实现2-3倍提升,能否达成10%的关键阈值成为推进注册的核心前提。
【展望】:2026年展望聚焦临床推进,基于2025年数据完成风险-获益评估以确定最优剂量,进一步推进临床研究;同时依托BioMarin在罕见病领域的战略布局,该药物有望加速研发进程,若数据达标,将为后续注册申报奠定基础,填补DMD治疗领域未被满足的需求12.NS Pharma: NS-089/NCNP-02
NS-089/NCNP-02(通用名brogidirsen)是NS Pharma旗下用于治疗杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)的 exon 44跳跃疗法,属新型吗啉代核酸制剂,通过修正 dystrophin 基因阅读框,诱导功能性 dystrophin 蛋白表达,适用于 exon 44跳跃适配型突变患者,已获美欧孤儿药等多项罕见病相关认定。
【洞察】:2025年,多项II期试验持续开展,数据显示其 dystrophin 表达水平优于现有获批疗法,且安全性良好,运动功能维持/改善趋势明确,为后续开发奠定核心依据。
【展望】:2026年,核心II期试验primary completion date预计落定,延伸试验将进一步验证长期疗效,有望启动关键注册申报,填补exon 44适配型DMD患者的治疗空白。13.Entrada Therapeutics: ENTR-601-44
ENTR-601-44是Entrada Therapeutics开发的外显子44跳跃疗法,基于专有EEV™载体平台增强药物递送,通过恢复肌营养不良蛋白生成治疗特定基因突变的杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD),目前处于1/2期临床阶段。
【洞察】:2025年为关键推进年,其全球1/2期ELEVATE-44-201研究获英国监管批准,在欧洲多国药启动,首组患者完成入组且经数据监察委员会审核支持继续推进,同时美国FDA解除临床暂停,为后续试验铺路。
【展望】:2026年展望聚焦数据突破与适应症拓展,预计Q2公布首组临床数据,上半年启动美国成人患者试验,有望凭借差异化递送技术在DMD精准治疗领域占据优势,填补外显子44突变患者的未满足医疗需求。 三、题外篇
2025年,对于大兵(尹相兵)个人来说,是最忙碌的一年,周一到周五白天工作外,还要晚上搜寻DMD最新药物信息,及时分享给广大DMD家友们,让每个DMD家庭成为专家型家庭,去推动药物的研发,积极支持医院和药企的临床试验。
同时,也会抽时间参加DMD相关的公益活动或大会,尽自己的微薄之力去推动DMD患者群体有药可用,有药可及。
除了这些事情外,大兵重新书本开始读研了,周六日满满的课程安排,学习投融资,会计财务学等等,还有晚上忙到很晚完成作业,虽然知道这条路非常辛苦,但还是希望进一步提升自己的认知,通过知识武装自己的头脑,让自己将来为DMD更有力量去做事。
除了学习外,还认识了更多优秀的同学和老师,从他们身上学到了除了书本之外的东西,学会包容、理解和帮助他人。
在闲暇之余,也开始对接一些资源,希望能够帮到DMD药物研发融到一些资金,虽然过程非常不容易,但是自己还是义无反顾的去努力。
2026年,更是一个忙碌的一年,除了工作和学习外,希望和DMD家友们,一起努力去推动DMD药物研发,让DMD药物在5年之内尽快国内上市,能够纳入医保,让DMD孩子们及早用上药。
蔡磊攻克渐冻症的精神和力量,在鼓舞着我们,只要相信相信的力量,一定可以创造奇迹,为DMD创造出一个有希望的未来!
2025年即将过去,2026年已经来到,在这里,CDMD家友会,这个DMD患者群体共有的信息平台祝福每个DMD孩子,每个DMD家庭,元旦快乐,在新的一年里,我们一起努力,我们相信一定会可以创造奇迹!为自己,为DMD加油呀!
恳切的希望,所有的CDMD(China DMD)家友们,一起努力好好学习专业知识,用知识武装头脑,成为 ⌈专家型DMD家庭⌋ ,为了DMD孩子们的明天,全力去推动 ⌈未来五年,药物可及所有DMD患者⌋。为了成为 ⌈专家型DMD家庭⌋ ,恳请CDMD家友们可以关注公众号后回复:DMD
打开链接登录网盘后,即可领取完整版资料
《DMD患者读本》和《DMD家庭与教育者手册》
【CDMD家友会】公众号分享最新的国内外DMD药物研发信息和临床招募信息,已经在【CDMD患者互助(一)群 或 (二)群或(三)群 或(四)群 或(五)群 或(六)群】就不要加入啦,请扫二维码加入【CDMD患者互助(七)群】啦!
申请上市引进/卖出
2024-09-10
PARAMUS, N.J., Sept. 10, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- NS Pharma, Inc. (NS Pharma), a subsidiary of Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. (Nippon Shinyaku), announced that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted rare pediatric disease designation to NS-050/NCNP-03 which is being developed for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (Duchenne). The FDA's rare pediatric disease designation is granted for treatments of serious or life-threatening diseases that affect children under the age of 18 and fewer than 200,000 patients in the United States.
Continue Reading
We are grateful for this designation which can help us accelerate the development of this therapy for Duchenne.
Post this
Yukiteru Sugiyama, PhD, NS Pharma President
"The journey from first symptom to diagnosis and finally treatment can be long and challenging for patients with rare diseases and their caregivers," said NS Pharma President Yukiteru Sugiyama, Ph.D. "We are grateful for this designation which can help us accelerate the development of this therapy for Duchenne."
Duchenne is a progressive muscle wasting disease caused by a deficiency of the dystrophin protein. It leads to weakness of skeletal, cardiac and pulmonary muscles. There are many types of genetic mutations that can cause Duchenne, and NS-050/NCNP-03 is being developed to treat patients with confirmed gene mutations amenable to exon 50 skipping therapy.
NS-050/NCNP-03 is an antisense oligonucleotide co-discovered by the National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry (NCNP) and Nippon Shinyaku. NS-050/NCNP-03 skips part of the genetic information of the dystrophin gene and produces a functional dystrophin protein with a slightly shorter chain length, which is expected to have the effect of suppressing muscle function deterioration.
NS Pharma is working to develop products for patients with rare diseases. We are preparing a Phase 1 / 2 study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of NS-050/NCNP-03 in patients with Duchenne in Japan and the United States.
About Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (Duchenne)
Duchenne is a progressive form of muscular dystrophy that occurs primarily in males. It causes progressive weakness and loss of skeletal, cardiac, and respiratory muscles. Early signs of Duchenne may include delayed ability to sit, stand or walk. There is a progressive loss of mobility, and by adolescence, patients with Duchenne may require the use of a wheelchair. Cardiac and respiratory muscle problems begin in the teenage years and lead to serious, life-threatening complications. For more information about Duchenne, please visit wespeakduchenne.com.
About NS Pharma, Inc.
NS Pharma, Inc., is a wholly owned subsidiary of Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. NS Pharma is a registered trademark of the Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. For more information, please visit nspharma.com.
U.S. Media Contact:
[email protected]
SOURCE NS Pharma, Inc.

寡核苷酸
100 项与 NS-050 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杜氏肌营养不良症 | 临床2期 | 美国 | 2024-09-18 | |
| 杜氏肌营养不良症 | 临床2期 | 日本 | 2024-09-18 | |
| 杜氏肌营养不良症 | 临床2期 | 加拿大 | 2024-09-18 | |
| 杜氏肌营养不良症 | 临床2期 | 韩国 | 2024-09-18 | |
| 杜氏肌营养不良症 | 临床2期 | 土耳其 | 2024-09-18 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
