预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
CYP8B1
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 7-alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one 12-alpha-hydroxylase、7-alpha-hydroxycholest-4-en-3-one 12-alpha-hydroxylase、CYP12 + [7] |
简介 A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in primary bile acid biosynthesis. Catalyzes the 12alpha-hydroxylation of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, an intermediate metabolite in cholic acid biosynthesis (PubMed:10051404). Controls biliary balance of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, ultimately regulating the intestinal absorption of dietary lipids (By similarity). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR; NADPH--hemoprotein reductase) (By similarity). |
关联
100 项与 CYP8B1 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 CYP8B1 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 CYP8B1 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
381
项与 CYP8B1 相关的文献(医药)2025-05-01·Molecular Metabolism
Glucagon-like peptide-2 pharmacotherapy activates hepatic Farnesoid X receptor-signaling to attenuate resection-associated bile acid loss in mice
Article
作者: Berlin, Peggy ; Witte, Maria ; Jaster, Robert ; Adamski, Jerzy ; Krause, Bernd J ; Reiner, Johannes ; Prehn, Cornelia ; Lamprecht, Georg ; Förster, Robert H ; Mohebali, Nooshin ; Elleisy, Nagi ; Vollmar, Brigitte ; Kurth, Jens ; Schwarzenböck, Sarah M ; Lindner, Tobias ; Cecil, Alexander
2025-04-01·Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety
Destruction of the intestinal microbiota and gut–liver axis homeostasis by microcystin-LR-induced inflammation in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Article
作者: Gao, Zhaolu ; Yang, Yanzhe ; Ding, Cuihong ; Li, Xiaoyu ; Ding, Weikai ; Ma, Junguo
2025-04-01·Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology
Hepatotoxicity from long-term administration of hepatoprotective low doses of oleanolic acid in mice
Article
作者: Liu, Jie ; Yang, Xi ; Xu, Yasha ; Lu, Yuanfu
2
项与 CYP8B1 相关的新闻(医药)2022-09-09
·生物谷
肠上皮屏障损伤在炎症性肠病(IBD)细胞和分子发病机制研究中备受关注。肠上皮屏障结构和功能的完整性依赖稳定更新的上皮细胞和具有正常功能的细胞旁通路。胆汁酸是肝脏中胆固醇分解的最终产物,主要通过法尼
肠上皮屏障损伤在炎症性肠病(IBD)细胞和分子发病机制研究中备受关注。肠上皮屏障结构和功能的完整性依赖稳定更新的上皮细胞和具有正常功能的细胞旁通路。胆汁酸是肝脏中胆固醇分解的最终产物,主要通过法尼醇X受体(FXR)和G蛋白偶联胆汁酸受体1(TGR5)调节机体能量代谢和免疫功能等。已有研究表明,胆汁酸是肠上皮屏障功能的重要调控物质,但内在机制尚不清晰。
中国科学院上海药物研究所、上海中医药大学龙华医院与美国国立卫生研究院合作,在肠道上皮屏障修复的跨器官调控机制研究中取得重要进展。相关研究成果以Hepatic cytochrome P450 8B1 and cholic acid potentiate intestinal epithelial injury in colitis by suppressing intestinal stem cell renewal为题,在线发表在Cell Stem Cell上。
研究发现,活动期IBD患者和结肠炎小鼠体内胆汁酸代谢紊乱,胆酸(CA)水平显著上调,且肝脏胆汁酸经典合成途径代谢酶CYP8B1出现过度活化。外源补充CA或过表达CYP8B1均能够加重小鼠IBD表型、损伤肠道屏障及其修复功能,而干扰CYP8B1的表达则可促进肠道炎症缓解,恢复肠上皮再生能力。
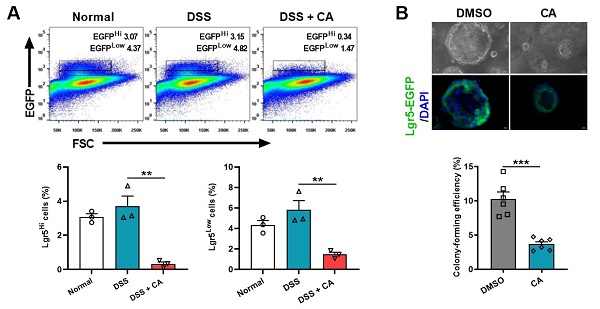
隐窝肠道干细胞(Lgr5+ ISC)的自我更新在维持肠稳态、抵御微生物入侵中发挥重要作用。为剖析CYP8B1-CA代谢轴影响肠干细胞(ISC)更新的机制,研究分离结肠炎小鼠的肠道隐窝和ISC进行体外培养,发现病理浓度的CA显著减弱结肠炎小鼠隐窝中类器官的出芽和传代能力,并直接抑制Lgr5+ ISC的增殖(图1)。
进一步的RNA-Seq和代谢组学分析中发现,CA可抑制结肠炎小鼠隐窝的脂肪酸氧化(FAO)过程及PPARα信号通路。研究通过肠特异性敲除Pparα的结肠炎小鼠证实了CYP8B1-CA代谢轴通过抑制PPARα介导的FAO,削弱Lgr5+ ISC的更新能力,加重肠道屏障损伤。研究应用FXR激动剂奥贝胆酸(OCA)间接抑制结肠炎小鼠体内CYP8B1的活性,可促进其Lgr5+ ISC的增殖和传代能力,验证了肝脏FXR-CYP8B1-CA代谢轴在IBD中的重要作用。
图1.CA直接抑制Lgr5+ ISC的增殖
该研究发现在炎症性肠病状态下,CYP8B1异常活化并导致其产物CA积累,远程抑制隐窝基底部ISC的自我更新,阻止肠上皮屏障修复。该研究提出了肝脏FXR和CYP8B1有望成为“肠病肝治”的新靶标,并发现了FXR激动剂能够兼顾调节炎症和修复受损的肠上皮屏障,因而FXR的激动剂有望成为更有前景的IBD治疗药物。。
研究工作得到国家重点研发计划、中科院战略性先导科技专项(B类)、上海市科技重大专项和国家自然科学基金等的资助,并获得中科院上海营养与健康研究所、上海交通大学精准医学研究院的科研人员的支持。
2022-09-05
肠上皮屏障损伤在炎症性肠病(IBD)细胞和分子发病机制研究中备受关注。肠上皮屏障结构和功能的完整性依赖于稳定更新的上皮细胞和具有正常功能的细胞旁通路。胆汁酸是肝脏中胆固醇分解的最终产物,主要通过法尼醇X受体(FXR)和G 蛋白偶联胆汁酸受体1(TGR5)调节机体能量代谢和免疫功能等。已有研究表明,胆汁酸是肠上皮屏障功能的重要调控物质,但其内在机制尚未阐明。2022年9月1日,发表在《Cell Stem Cell》上的一项最新研究中,来自中国科学院上海药物研究所、上海中医药大学龙华医院与美国国立卫生研究院联合团队在肠道上皮屏障修复的跨器官调控机制研究中获得重要发现。研究人员发现活动期IBD患者和结肠炎小鼠体内胆汁酸代谢紊乱,胆酸(CA)水平显著上调,且肝脏胆汁酸经典合成途径代谢酶CYP8B1出现过度活化。通过外源补充CA或过表达CYP8B1均能够加重小鼠IBD表型,损伤肠道屏障及其修复功能,而干扰CYP8B1的表达则可促进肠道炎症缓解,恢复肠上皮再生能力。隐窝肠道干细胞(Lgr5+ ISC)的自我更新在维持肠稳态、抵御微生物入侵中发挥重要作用。为深入了解CYP8B1-CA代谢轴影响肠干细胞(ISC)更新的机制,研究人员分离结肠炎小鼠的肠道隐窝和ISC进行体外培养,发现病理浓度的CA显著减弱结肠炎小鼠隐窝中类器官的出芽和传代能力,并直接抑制Lgr5+ ISC的增殖(图1)。图1. CA直接抑制Lgr5+ ISC的增殖在进一步的RNA-Seq和代谢组学分析中,研究人员发现CA可抑制结肠炎小鼠隐窝的脂肪酸氧化(FAO)过程及PPARα信号通路。他们通过肠特异性敲除Pparα的结肠炎小鼠证实了CYP8B1-CA代谢轴通过抑制PPARα介导的FAO,削弱Lgr5+ ISC的更新能力,加重肠道屏障损伤。最后,研究人员应用FXR激动剂奥贝胆酸(OCA)间接抑制结肠炎小鼠体内CYP8B1的活性,能够促进其Lgr5+ ISC的增殖和传代能力,验证了肝脏FXR-CYP8B1-CA代谢轴在IBD中的重要作用。综上,该研究发现在炎症性肠病状态下,CYP8B1异常活化并导致其产物CA积累,远程抑制隐窝基底部ISC的自我更新,阻止肠上皮屏障修复。研究人员不仅提出肝脏FXR和CYP8B1有望成为“肠病肝治”的新靶标,同时也发现FXR激动剂能够兼顾调节炎症和修复受损的肠上皮屏障,因此FXR激动剂有望成为更有前景的IBD治疗药物。(图2)。图2. 肝脏CYP8B1-CA代谢轴跨器官调控肠道上皮损伤修复的分子机制。论文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1934590922003447
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用