预约演示
更新于:2025-12-27
Lipoprotein(a) inhibitor(Shanghai Argo)
脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药)
更新于:2025-12-27
概要
基本信息
原研机构 |
在研机构 |
非在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
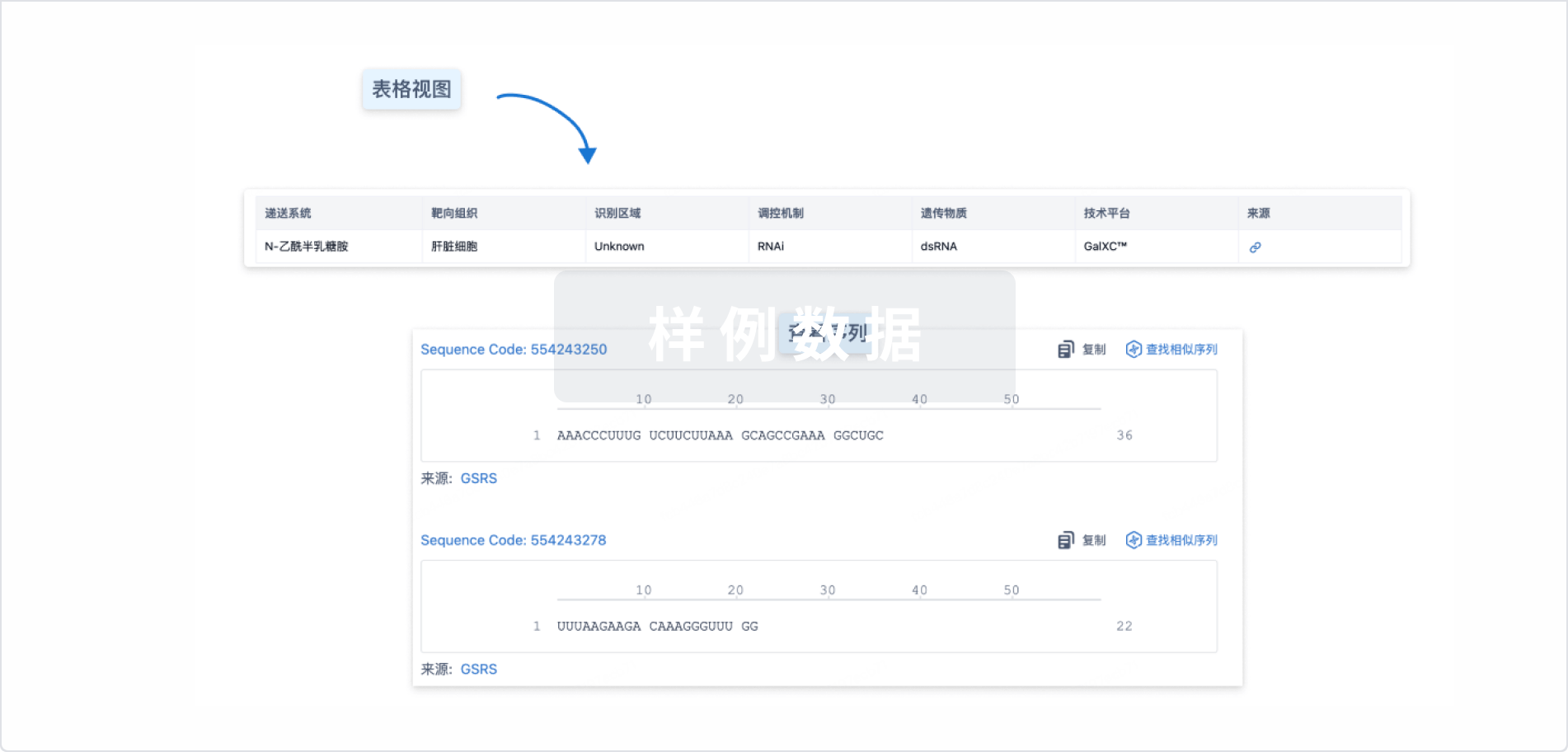
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
关联
100 项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
2
项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的文献(医药)2024-04-01·Current atherosclerosis reports
Novel Therapies for Lipoprotein(a): Update in Cardiovascular Risk Estimation and Treatment
Review
作者: Wulff, Anders Berg ; Langsted, Anne ; Nordestgaard, Børge G
PURPOSE OF REVIEW:
Lipoprotein(a) is an important causal risk factor for cardiovascular disease but currently no available medication effectively reduces lipoprotein(a). This review discusses recent findings regarding lipoprotein(a) as a causal risk factor and therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease, it reviews current clinical recommendations, and summarizes new lipoprotein(a) lowering drugs.
RECENT FINDINGS:
Epidemiological and genetic studies have established lipoprotein(a) as a causal risk factor for cardiovascular disease and mortality. Guidelines worldwide now recommend lipoprotein(a) to be measured once in a lifetime, to offer patients with high lipoprotein(a) lifestyle advise and initiate other cardiovascular medications. Clinical trials including antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNAs, and an oral lipoprotein(a) inhibitor have shown great effect on lowering lipoprotein(a) with reductions up to 106%, without any major adverse effects. Recent clinical phase 1 and 2 trials show encouraging results and ongoing phase 3 trials will hopefully result in the introduction of specific lipoprotein(a) lowering drugs to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
2024-01-02·EXPERT OPINION ON INVESTIGATIONAL DRUGS
Potential of muvalaplin as a lipoprotein(a) inhibitor
作者: Hooper, Amanda J. ; Fernando, P. Mihika S. ; Burnett, John R.
A review.Discovered 60 years ago, lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a unique lipo-protein class found only in hedgehogs and primates, and whose physiol. function is unknown [1].Muvalaplin exhibits promising potential as a lipoprotein(a) inhibitor, offering a novel therapeutic avenue for addressing cardiovascular diseases associated with elevated lipoprotein(a) levels.Through its mechanism of action, muvalaplin demonstrates efficacy in reducing lipoprotein(a) levels, thereby mitigating the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular events.This abstract highlights the therapeutic promise of muvalaplin in targeting lipoprotein(a) and underscores its significance in cardiovascular disease management.
14
项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的新闻(医药)2025-11-10
·搜狐新闻
最近几年,中国医药领域迅猛发展,在全球舞台上崭露头角。在此之前,中国也早已成为全球第二大医药消费市场。作为较早进入中国的跨国药企之一,默沙东深度参与也见证了中国医药生态的演变。三十余年来,这家全球制药巨头在中国持续投入、布局创新,将高质量的创新药物和疫苗源源不断地带给广大中国患者和消费者,在中国拯救生命、改善生活。而随着国内医药领域发展和本土研发实力渐强,默沙东在中国市场的参与方式也从商业化销售、本土化生产制造逐渐向药物开发的上游环节延伸。在对中国市场的坚定承诺、持续看好和充分信心下,默沙东还将携手中国合作伙伴,进一步深度布局中国市场,积极推动本土创新。2025第八届进博会默沙东展台持续投入布局,惠及中国患者实际上,作为长期位列全球制药行业第一梯队的跨国药企,默沙东业务范围覆盖创新药和疫苗为主的人用医药产品,以及动物保健产品,持续布局中国市场超30年,并且早已为国人所熟知。1992年,默沙东正式进入中国,成为较早来到中国的跨国药企之一。而在此三年前,默沙东向中国零利润转让了当时世界上最先进的基因工程重组乙肝疫苗技术。其不仅承诺不在国内销售自己的同种产品,还帮助中国科学家、技术人员赴美接受培训,确保国内能生产出与默沙东同等质量的乙肝疫苗。由此,中国开始逐渐摆脱“乙肝大国”的帽子。出于对中国市场的长期承诺与发展信心,2011年,默沙东在北京设立了研发中心,成为跨国药企在中国规模最大的研发机构之一,也是默沙东在美国之外,仅设的两个独立、全面、职能完备的研发中心之一。同样是基于重视、坚持中国市场,默沙东北京研发中心持续扩张,不断将其在全球的前沿创新药品引入国内,也由此参与到中国新药领域生态演变。伴随此后国内药审改革、鼓励新药研发的政策频出,截至2025年5月,默沙东已将超过80个创新药物、疫苗、新适应证和伴随诊断试剂带到中国,这其中,HPV 疫苗和肿瘤免疫疗法更屡屡创下国内新药获批速度纪录。与之相伴的是,默沙东还先后在杭州、宁波、天津设立人类健康和动物保健工厂。2013年, 其在杭州下沙建造的新厂正式投入运营。这成为默沙东在亚太地区规模最大的药品生产包装设施,业务覆盖中国及整个亚太地区。2023年,杭州工厂还启动了糖尿病DPP-4抑制剂全流程生产,为更好、更快地服务中国糖尿病患者迈出坚实一步。也由此,作为全球战略核心区域,默沙东在中国构建了上海商业总部、北京研发中心及杭州生产基地的“三擎合一”体系,为中国境内提供涵盖疫苗、肿瘤、糖尿病、罕见病和抗感染等领域的约 30 种人用药物和疫苗,从疾病预防到治疗,满足中国未尽的医疗需求,造福患者和大众,助力实现“健康中国”战略目标。截至2025年8月,在默沙东强势的抗肿瘤板块,公司共计6款产品在中国境内获批32个适应证。其中帕博利珠单抗有19个适应证获批,覆盖11个癌症种类以及MSI-H/dMMR实体肿瘤,包含消化道肿瘤、女性肿瘤等多个中国高发的恶性肿瘤。另外,公司还预计2025年至2030年5年内在中国将有超40个新产品、新适应证在中国获批,以持续投入和创新布局不断惠及中国患者。加速创新合作,助力新药上市除自己在中国市场持续深耕和布局外,默沙东实际上也早早意识到国内本土公司的优势和潜力,携手后者深度参与国内医药行业发展。2011年,默沙东与国内民营疫苗龙头智飞生物达成战略合作。在双方十余年的共同努力下,截至2025年8月,默沙东轮状病毒疫苗已保护近1600万中国婴儿,四价及九价HPV疫苗已帮助超过5300万中国适龄女性及男性预防HPV及相关癌症和疾病*,共同支持了中国公共卫生事业的进步和发展。而随着国内新药研发领域土壤日渐肥沃、玩家渐多、实力渐强,可以发现的是,包括默沙东在内的跨国药企对中国市场的参与方式都逐渐从商业化销售、本土化生产制造慢慢向药物开发上游环节延伸,即与国内公司展开新药早期研究、临床开发方面的商务拓展(BD)、收并购合作。实际上,新药研发不光是在解决当下及未来社会的沉重疾病负担、满足巨大健康需求,也更是在与时间赛跑。跨国药企与生物科技公司间的收并购不仅是将具备潜力的新药分子推进至临床、市场,尽快惠及患者的高效手段,也符合新药开发生态下不同体量、业务结构公司的分工定位。如2022年,默沙东牵手科伦博泰,合作开发多款用于治疗癌症的抗体偶联物(ADC)药物,为多种癌症寻找突破性治疗方案。默沙东中国始终以“拯救生命, 改善生活”为企业目标,坚持把高质量的创新药物和疫苗带给广大中国患者和消费者,同时不断顺应快速变化的市场形势、把握新的行业机遇。2024年一年时间内,默沙东接连与多家中国药企牵手,先后合作获得了同润生物医药的B细胞耗竭疗法在研药物CN201、翰森制药在研口服GLP-1受体激动剂HS-10535、礼新医药的PD-1/VEGF双特异性抗体LM-299。2025年3月,默沙东挖掘中国市场有潜力分子的热情不减,再度引进恒瑞医药的心血管疾病药物在研口服脂蛋白(a)抑制剂HRS-5346。这些在研创新分子中,B细胞耗竭疗法开始在自身免疫疾病这一肿瘤外第二大疾病领域崭露头角;PD-1/VEGF双抗被看作是PD-1单抗后的新一代肿瘤免疫疗法;GLP-1R激动剂和脂蛋白(a)抑制剂则指向了患者群体庞大的心血管代谢领域,小分子口服剂有力拓展并补充研发管线,未来有望为更多患者提供降低动脉粥样硬化风险的治疗新选。可以发现,这些市场潜力大、创新程度高、患者潜在获益更多的在研新药分子分布于默沙东的多个传统优势领域,不仅丰富了默沙东自身的创新研发管线,在各个治疗领域形成资产组合、发挥协同效应,还将使中国的早期创新能够加入全球临床开发,有望造福中国乃至全球的更多患者,并帮助国内创新药公司共同成长、壮大。正是在这样的生态分工、业务考量和对中国市场与创新的持续看好下,2024年11月,默沙东更进一步在北京设立默沙东研发中国创新合作中心(MCICC),关注中国市场上的全球首创新药(First-in-Class)、全球同类最优分子(Best-in-class)、创新平台技术与颠覆性突破项目。默沙东在抗肿瘤、心血管代谢等传统优势领域拥有深厚积淀和丰富洞见,后期国际多中心临床开发资源庞大,实力强劲。默沙东与中国创新项目的合作实际上可以以更高的效率来充分验证、开发新药的潜在创新价值、尽早惠及患者。长远来看,默沙东研发中国创新合作中心将通过专家咨询、临床开发服务、项目投资、公司投资等服务和支持方式,助力中国本土早期创新成果快速、高质量临床转化,最终将中国价值转化为全球峰值,为拯救并改善更多患者的生命与健康贡献默沙东与中国的力量。*Data on File返回搜狐,查看更多
疫苗诊断试剂
2025-10-03
·漫游药化
莱纳斯·卡尔·鲍林(Linus C Pauling,1901-1994 ) 是美国著名的化学家。他极富个性和创新精神,不断开拓边缘学科,在化学的许多领域卓有建树,是20世纪最伟大的化学家。
1901年,鲍林出生于美国俄勒冈的一个小镇,父亲是药剂师。他自幼聪慧超群,博览群书,被誉为科学奇才。由于年少失怙,家道中落,16岁时就近入俄勒冈农学院学习化学。大学毕业后赴加州理工学院深造,迅速掌握了具有革命性的X射线晶体衍射技术,进行创造性工作, 1925年获博士学位。次年赴欧洲研究将量子力学应用于化学,师从索末菲(A. Sommerfeld)、玻恩和海森伯。1927年回国,从事化学键本质的研究,创立了杂化键轨道理论和共振论,把经典的化学理论与量子力学相结合,从而改写了20世纪的化学。1931年成为加州理工学院最年轻的教授,1933年入选美国科学院,也是历史上最年轻的院士。
1934年开始,他把结构化学应用于生物学;在抗原和抗体蛋白质结构的研究上,把抗体生成的直接模板学说发展得更加完善。在40年代,鲍林在生物学上作出了二项重大的贡献:一是与科里(R. Corey)阐明了蛋白质的α螺旋结构;二是证明镰状细胞贫血是由于血红蛋白的变异,说明人的遗传性疾病是由于突变基因表达所产生的异常蛋白质,首先提出分子疾病的概念。1957年,英格拉姆(V. Ingram)证明,镰状细胞血红蛋白(HbS)是由于血红蛋白中的谷氨酸被缬氨酸所取代。1960年代初期,朱克坎德(E. Zuckerkandl)和鲍林提出,通过比较不同物种的同源蛋白质来确定不同物种的亲缘关系。(注1)这种方法已被普遍使用,成为确定不同物种的亲缘关系最重要的方法之一。
1954年鲍林因阐明了化学键的本质和分子结构的基本原理获诺贝尔化学奖。根据诺贝尔的遗嘱,他的奖只授予单项重大发现的科学家,而不适合于作出一批重要研究成果者。鲍林获奖首次突破了这条原则。
鲍林是“主张自由表达信仰的理想主义者”和激进的社会活动家。他直言不讳、话语尖刻,坚持己见,决不退让。二战结束后,他积极参与开展反战活动,坚决反对“以任何形式的战争作为解决国际冲突的手段”,奔走世界各地,唤起社会大众对核污染威胁的关注,不遗余力地反对核试验,致力于世界和平事业。1958年1月,他向联合国秘书长递交了由他起草并征得49个国家的11 000多位科学家签名的《科学家反对核武器试验宣言》,要求缔结一项停止核武器试验的国际协定。1963年10月10日美苏签署《部分禁止核试验条约》之日,诺贝尔委员会宣布把1962年和平奖授予这位坚持不渝的反核斗士。鲍林是迄今仅有的两度单独获得诺贝尔奖桂冠的人。由于他对化学与和平运动的贡献,他获得的荣誉博士学位和奖项不胜枚举。
然而,鲍林在思想观点和行为方式上又是颇有争议的人物,在获诺贝尔和平奖以后,他更加坚持己见,猛烈地抨击美国政府的政策,明显与公众舆论脱节。他既被视为具有敏感直觉、敢于冒险、不敬权贵、富有魅力的人物,同时又是自命不凡、一贯正确、桀骜不驯、我行我素的怪人,他的官司接连不断和失败,以至声名狼藉。美国主流媒体对他的政治观点颇有微词,甚至认为是“荒诞不经”;对他获诺贝尔和平奖也不以为然,他曾担任过主席的美国化学会的学报也冷眼相待,只在很不显眼的位置提及此事。
1950年代开始,加州理工学院院长和化学系教授们对鲍林感到不满,抱怨他“竭力发展个人所迷恋的化学生物学,远离了该系在物理化学方面的根基。”1964年他悻然离开加州理工学院,去圣巴巴拉的民主制度研究中心,不久发现这里也令他失望,不能实现他的宏大政治理想,又没有实验室,于是打算去加州大学圣巴巴拉分校,那里的化学系主任是他的学生,但被校长所否决。1967年,加州大学圣地亚哥分校接受他担任研究教授,二年后去了斯坦福大学,成为“学术界的流浪汉、漂泊谋生”,至1973年创立自己的研究所。
鲍林晚年致力于“营养保健”的研究,极力鼓吹正分子医学(orthomolecular medicine)、大剂量维生素疗法和其他旁道医疗(注2),支持庸医骗术,由于他的科学家声誉致使谬种流传,在社会上产生不良的影响,遭到美国医学界的一致批评。
其实,卓越的科学家在晚年误入歧途,鼓吹与科学格格不入的东西或者迷恋方术,科学史上并不罕见。当前我国的伪科学和骗术盛行,庸医假药泛滥成灾,其中就有不少科学家的参与。因此,对鲍林的晚年失误加以讨论,有重要的现实意义。
正分子疗法
1950年代初期,精神病缺乏有效的药物治疗,少数精神科医生采用大剂量维生素辅助治疗严重精神病,后来扩大到无机盐。1965年的一天,鲍林偶然在一位精神分析医生家里看到一本《精神病学中的尼克酸疗法》,作者是加拿大一个精神病研究所的所长。尽管鲍林缺乏精神病学的知识,但他对精神病的生化机制已经感兴趣多年,对文中所用的尼克酸(维生素B3)剂量之大而没有副作用,“对精神分裂症的大脑功能有相当积极的疗效”,感到惊奇,同时联想到应用其他维生素是否相同。对此他的兴趣更加浓厚。
1968年,鲍林与精神科医生霍金斯(D. Hawkins)的著作《正分子精神病学(orthomolecular psychiatry):一种治疗方法》问世。在斯坦福大学期间以及后来成立的研究所,他都一直醉心于“正分子医学”。其假说是:人的大脑是一种分子—电子能激发的场所,通过复杂的生化机制发送信号,这个机制由代谢物提供必要的营养。精神疾病是由于体内化学分子失衡引起的,所以,应用正常存在于人体的营养素的“最适分子和最适剂量”可以矫正分子平衡,为大脑提供最适的分子环境,达到治疗目的。因此他提倡应用大剂量维生素或无机盐治疗精神分裂症和各种精神病,以及躯体疾病,包括过敏性疾病、关节炎、高血压、癫痫、代谢异常和皮肤病,称为正分子疗法或正分子医学。
然而,他的假说不仅缺乏科学证据,而且不打算认真地用临床试验加以考核,因而不能得到医学家和营养学家的赞同和证明。1973年,美国精神病学会专题研究报告指出:大剂量维生素治疗不仅缺乏理论基础,诊断和治疗反应评价以及心理测试的方法既不可靠也缺乏特异性。报告结论是用词最严厉的批评:
“这项评审和批评仔细审查了大剂量维生素支持者以及试图重复他们的基础和临床工作的研究者的论文。结论是大剂量维生素支持者的论文可靠性低。由于他们在过去10年里一直拒绝进行对照试验和以科学上可接受的方式报告新的结果,致使他们的论文的可靠性更形降低。 在这种情况下,本专题研究组认为,他们运用象“大剂量维生素疗法”和“正分子治疗”等真正用词不当的流行语,通过广播、通俗出版物和大众书刊进行大规模广告宣传,应当受到谴责。”1979年,美国国立精神健康研究院研究咨询委员会审阅有关的科学资料后认为,大剂量维生素疗法不仅无效,而且可能有害。美国国防部小组委员会也调查了这一疗法,决定从军人家属的CHAMPUS保险项目覆盖中删除这种治疗。
美国儿科学会和加拿大儿科学会的营养委员会,先后在报告中揭露,大剂量水溶性维生素和无机盐治疗儿童的智能低下、神经症、孤独症、诵读困难和其他学习障碍有效的临床报告很不可靠,是虚假的,尽管在信仰者中已经形成一种“狂热宗教”。大剂量补充维生素或无机盐疗法提高智能低下儿童的智商也缺乏根据,对先天性愚型的行为和智商的改善与对照组没有不同。[11]这些报告警告说,不能证明这种治疗对上述疾病有任何益处,还可能招致严重毒性反应。
大剂量维生素C防治感冒
鲍林晚年的兴趣特别集中在大剂量维生素C上,与他的经历多少有些关系。1950年代末,鲍林在圣地亚哥医学会的一个聚会上演讲,医生们举杯饮酒、谈笑自若,令他恼火。随后他对医学界请他演讲的酬金与医生的不相称,也使他感到受怠慢,为此耿耿于怀,促使鲍林决定就维生素C问题挑起讨论。
1966年3月,鲍林获卡尔·纽伯格奖,这是对“医学与生物学新知识进行综合研究”的奖励。斯通(I. Stone) 博士特意去颁奖会结识鲍林,数天后他写信奉承鲍林,并大谈维生素C对健康和治疗疾病的作用,劝鲍林每天服大剂量维生素C预防感冒。他说他早就对维生素C有研究,并且获得了维生素C作为食品添加剂的专利。斯通认为,人自身不能合成维生素C,是由于进化过程中遗传变异导致一种酶的缺乏,因此坏血病不是简单的营养缺乏症,而是一种遗传性缺陷。根据世界各地的报道,他认为大剂量维生素C能治疗包括炎症、胶原病、心脏病和癌症在内的很多疾病。他和妻子每天服3克维生素C,增进了健康。可是,他的有关论文却屡遭医学刊物的拒绝。斯通自投鲍林旗下,显然是为开发“保健品”寻求支持。他自称是“生物化学家”,实际是酿造工程师,只有2年化学专业的学历,博士学位是一所未经认证的函授学院授予的。开始鲍林并不相信斯通所言,但他的“理论”打动了他,觉得此人的建议值得一试。于是便和妻子爱娃每天服维生素C,果然二人顿感精神日佳,也不感冒了,出现“神奇的”效果。
维生素C又称抗坏血酸,具有重要的生理功能,与动物不同的人体是必须从外界获得,缺乏可导致坏血病。成人的膳食标准日供给量(RDA)为60毫克,每日服250-300 毫克,几天内即达到饱和状态,过量吸收则排出体外。因此,美国医学会推荐(1987),维生素C每日的预防剂量为50-100毫克,治疗缺乏症为 250-500毫克。英国荐用的维生素C成人日摄取量为40毫克。由于维生素C具有抗氧化作用,人们一直推测它具有潜在的治疗作用,临床应用由来已久,但疗效未得到证明。1930年代开始就有维生素C防治感冒的报告,如Ruskin(1938)、Cowan等(1942)和Ritzel(1961)等的研究,但没有引起广泛注意。
1970年,鲍林的《维生素C与感冒》出版,声称维持健康所需要的维生素和其它营养素因人而异,差别悬殊,许多人的需要量远比日供给量大得多。一般人每日口服维生素C 1克,感冒的发病率可以下降近一半,有些人的需要量更大达4克。并且用很大篇幅阐述了关于矫正分子的假说和斯通的进化概念。由于当时社会正出现“自然健康”和“天然食品”热,加上他的科学家名声和亲身经验,该书立即畅销美国,维生素C的身价也因此陡增,销售量直线上升,以致“供不应求,超出了生产能力”。同时,鲍林还抨击医学界和药厂,为了感冒药的销售和医学刊物的广告利益,企图抹杀维生素C的有效证据。
由此,鲍林挑起了一场大辩论。美国食品药品管理局(FDA)迅速作出反应,指出全国范围的维生素C热是“荒唐可笑的”,“尚无科学证据,而且没有重要的研究可以表明维生素具有防治感冒的作用。”医学界同样对鲍林提出激烈的批评,认为这本书的观点 “只不过是理论推测而已”。《美国医学会杂志》(JAMA)书评说: “在此,我们看到的不是一位追求真理的哲学家或科学家作出的论述,而是一个为了推销某种货物的广告商声嘶力竭的叫卖,……甚至那些吹捧鲍林的人,也不希望他写这么一本书。”《药物与医疗通讯》(注3)批评说,鲍林的结论“是根据胡思乱想或很不严谨的临床研究得出的,因而是一家之言。”作为著名的科学家,鲍林曾试图在《科学》杂志上发表自己的观点,但未能如愿,论文被退回。
感冒是一种由病毒引起的上呼吸道感染,迄今尚无特效药物,病程为自限性,不治自愈。一个人每年可以多次患感冒,每次轻重不同。对这种疾病的药物治疗的效果评价,尤其须要采用随机对照双盲的临床试验。
在鲍林的《维生素C与感冒》问世之前,实际上已经有一些很好的研究否定了维生素C防治感冒的作用。如1967年英国蒂勒尔 (D.A.J. Tyrrell)领导的感冒研究组进行的志愿者实验:试验组每日口服维生素C 3克,对照组服安慰剂,再用病毒攻击,二组的感冒发生率、病程和病情轻重完全相同,结论是维生素C预防无效。但鲍林认为过去的研究无效,是因为所用剂量太小,和资料分析不当。由于他的影响,医学家重开维生素C防治感冒的临床试验,结果是至少16篇设计周密的双盲试验一致证明,除个别试验出现症状略微减轻外,大剂量维生素C对感冒无预防作用。加拿大流行病学家安德森领导的研究组先后进行三项临床试验:第一项结果是,大剂量维生素C组比对照组的感冒发病率低,症状较轻,统计学差别显著,但实际意义不大。第二项试验则完全无效,第三项试验是应用较小剂量的维生素C,每周服500毫克患感冒较对照组轻。施瓦茨等给志愿者每日口服3克维生素C,连续14天,然后用感冒病毒攻击,结果未发现有预防作用,患病天数没有缩短,仅症状略有减轻。这些说明,维生素C预防是无效的,“减轻症状的作用”也很不可靠。值得仔细一提的是,在美国国立卫生研究院的工作人员中进行的一项防治实验。受试志愿者随机分成二组,一组服维生素C药丸,对照组服安慰剂乳糖药丸,观察效果的医生和受试者都不知道谁或自己服的是什么药,即双盲试验。因为维生素C味酸,乳糖味甜,于是受试者中有102人试图咬破药丸尝味道猜出所服的药物,其中79人猜中了。结果如按服维生素C或乳糖二组进行分析,前组患感冒的症状较后一组轻。但细分发现,维生素C组猜中者,感冒的病情较对照轻,病程短;未猜中者,则二组没有差别。再进一步分析9个月观察期间的感冒≥2次的发病率为:猜维生素C实际是乳糖对照的为18%,猜乳糖但是维生素C的为67%,未猜的维生素C组36%,未猜的对照组47%。这说明,当一个人对一种药物或疗法信仰时,可以出现虚假的效果,即安慰作用,说明双盲试验的重要意义。
然而,要鲍林听取异见、改弦易辙是不可能的。1976年他的书再版,更名为《维生素C与感冒和流感》。推荐的维生素C剂量更大,还专门增加二章针对医学界的批评。
大剂量维生素C防治癌症与心脏病
1979年,鲍林与卡梅伦(E. Cameron)的著作《维生素C与癌症》出版,宣称大剂量维生素C对癌症有效。1986年,在《怎样才能长寿与健康》(How to Live Longer and Feel Better)一书中,鲍林把大剂量维生C说成是万应灵丹妙药,“可以增进健康,增加生活乐趣,有助于防治心脏病、癌症和其它疾病,并且延缓衰老。”他身体力行,自称每日至少口服12克,患感冒时增加到40克。1993年,鲍林患前列腺癌接受放射治疗,他断言,由于他长期服维生素C使癌症发病延迟了二十年。这种说法当然无法验证,不幸他最终仍死于癌症。
卡梅伦是苏格兰一所医院的外科医生,他在1966年出版的《透明质酸酶与癌症》中提出一个假说:癌症产生透明质酸酶使细胞间质溶解,是癌细胞扩散的原因,维生素C促进胶原生成,同时可抑制透明质酸酶,因此可以加强细胞间质,具有防止癌细胞扩散的作用。1971年他写信给鲍林,讲述自己应用维生素C 治疗晚期癌症病人的“意外发现”,每日10克或更大剂量的维生素C,可使癌症进展变慢、肿块缩小。鲍林对此非常重视,回信说“我感到你的思想的确很重要,而且很有根据。”
于是,鲍林帮助卡梅伦整理维生素C与透明质酸酶的理论,总结治疗经验,结论是每日服维生素C10克对100例晚期癌症病人有延长生存的作用。为了保证能够发表,鲍林将论文寄往《美国科学院学报》,但仍遭到一再退稿,使他大感意外和吃惊。最后只好把临床应用维生素C的建议作了低调处理,1976年才得以发表。尽管这篇文章中有1000例病人作为对照组,但这些病人是别的医生经治的,与卡梅伦治疗的100例不同。美国国立癌症研究所临床研究部主任德威斯(W. DeWys)博士指出,两组癌症病人的临床判断标准和治疗方法都是不可比的,而且未采用盲法评定效果。由于卡梅伦把自己的病人定为“不治之症”的状况提前,所以生存期比别的医生治疗的病人延长。
1979、1983和1985年,美国著名的梅奥医院(Mayo Clinic)先后三次在总共367例晚期癌症病人中进行随机对照双盲临床试验,试图加以验证,结果是每日给予维生素C 10克并不比安慰剂对照好。
1989年,德国青年医生拉思(M. Rath)前往美国向鲍林他讲述了自己的理论,维生素C与脂蛋白(a)(低密度脂蛋白颗粒外包粘附性apo蛋白)以及心血管病之间的关系,重新点燃了他研究心血管病的热情。对于鲍林来说,任何能说明维生素C有益的建议,他都会欢迎。
拉思认为:人类进化过程中由于膳食富含维生素C的植物,以致自身丧失合成能力。由于维生素C缺乏,替代的脂蛋白(a)便沉积在动脉壁,是动脉粥样硬化的原因。动物自身能产生维生素C,血液含量很高,脂蛋白(a) 浓度则很低。因此鲍林相信,维生素C是脂蛋白(a)抑制剂,可用于抑制动脉粥样斑块的形成、预防冠心病发作,甚至减少血液脂蛋白(a)含量。胶原蛋白是结缔组织的主要成分,维生素C可以促进胶原合成,因而加强皮肤和血管壁的力量。鲍林进而说,心血管病即是一种慢性坏血病或亚临床型坏血病。人的维生素C摄取量,应与动物体内生成的量相当,即每日10-12克。据说,他日常服用的剂量,从1960年代的每日3克,最后增加到18克。1994年,在逝世前不久接受《英国最适营养杂志》访谈时,鲍林断言“适当应用维生素C和赖氨酸完全能够控制、甚至治愈冠心病、心肌梗塞和中风。”
此外,鲍林还积极推荐螯合疗法治疗冠心病。EDTA(依地酸盐)是一种螯合剂,临床用于清除体内金属离子的积蓄和中毒。螯合疗法是一种旁道医疗,鼓吹者认为,EDTA螯合疗法可以清除动脉粥样硬化斑块的钙沉积,替代冠状动脉搭桥术;或者认为EDTA可以清除体内的有毒金属,从而减少自由基形成,能使动脉粥样硬化修复。然而,这些想象的机制和螯合疗法的作用尽管炒得很热,但完全没有科学根据和临床试验支持。
积极支持保健食品业和旁道医疗
鲍林始终坚持大剂量维生素C会给人类带来健康,提倡正分子疗法。1972年,斯坦福大学拒绝了鲍林扩大实验室的要求,同时提醒他已超过退休年龄。1973年5月,他用筹集的捐款成立了莱纳斯·鲍林正分子医学研究所。不久,美国精神病学会专题研究组发表了长篇报告,批评正分子精神病学的概念,认为“矫正分子”的想法纯粹是“胡说八道”。尽管鲍林作了激烈反驳,谴责他们的“偏见”,但他的声望和刚成立的研究所财政遭到沉重的打击,于是次年改名为莱纳斯·鲍林科学与医学研究所(简称鲍林研究所)。
鲍林并没有接受医学界的批评,反而与保健食品(或营养品)行业紧密联合,越陷越深。在第一本书《维生素C与感冒》中,鲍林还批评保健食品行业鼓吹所谓的“天然”产品是误导消费者;合成的与天然的维生素完全相同,追求价格昂贵的天然产品徒然浪费金钱,“有机的”食品也毫无意义,只不过是保健食品行业为了推销产品所用的一种行话。但是,由于此书出版后遭到医学界的强烈批评,因此他也一反常态,反而抱怨对保健食品的批评是“偏激的”,一部分的批评是针对他的,该书再版时也删去了他对保健食品行业的批评。这时鲍林对维生素C的态度,已经不是科学是非的问题,而是纯属恩怨之争了。
由于鲍林的影响力,1970年代美国大约有5000万人服用维生素C作为“保健品”,维生素C的需求量迅速上升,批发价格涨了三倍,连续多年的年销售额达数亿美元。为此药厂欢欣鼓舞,称之为“鲍林效应”。荷夫曼-罗氏(Hoffmann-La Roche)制药公司是世界上最大的维生素C生产商,获利最多,作为回报,每年向鲍林研究所捐赠10万美元。大剂量维生素C疗法在世界上也有很大影响,在我国也一度风行。上海一位著名的物理学教授晚年在记者访谈中,提到她坚持服用大剂量维生素C增进健康,或许是受到鲍林的影响。
维生素是人体正常代谢所必需的营养,但生理需要量不大。除孕妇和哺乳妇女外,健康成人摄取多样化的日常膳食,无须额外补充维生素。由于疾病导致维生素吸收和利用下降或需要增加,才须按医嘱额外补充。大剂量的维生素可能就变成药物,如大剂量烟酸治疗高脂血症。大剂量的维生素A、D、E、B3和B6都可以产生副作用和毒性。维生素C 口服或静脉注射500毫克或以上,尿中草酸和尿酸的浓度显著升高,可能促进形成尿路结石。此外,尚可引起腹泻和腹痛。1991年,鲍林医学研究所推荐每日补充的维生素量更大,比通常的日供给量高数十倍乃至200倍。如维生素A 25000 国际单位,维生素E 400-1600 国际单位,维生素C为6-18克。在长期服用的人口中难免不发生副作用。
“大剂量维生素或无机盐疗法”、“正分子疗法”、“正分子营养”和“最适营养”,现在都被归入旁道医疗,或被批评为“营养骗术”,而鲍林研究所研究推广的正是这类东西。研究所在筹集经费的宣传上,也充满不实之词,例如,为了强调维生素C治疗癌症的价值,就声称多少年来癌症治疗毫无进步,这正是推销癌症灵丹妙药的江湖庸医进行宣传,诋毁现代医学的惯用办法。1976年,鲍林协助领导美国“保健食品”业向国会施加压力,要求通过一项法案,旨在削弱FDA保护消费者免受营养品误导。1977、1979年,他接受了美国营养食品协会的颁奖,这个协会是专门制造和销售“保健食品”商家的组织。1981年,他向美国保健联盟(NHF)捐款,该联盟授予鲍林保健自由贡献奖,并接纳他的女儿为终身会员。保健联盟是一个促销各种保健骗术的组织,它的一些领导人曾经触犯法律,有的还因从事非法的“保健活动”下过监狱。1983年,“保健食品”推销商法尔可尼 (O. Falconi),因声称维生素C可以预防膀胱癌、控制尿路感染、戒烟戒酒以及清洗胃肠免受咖啡因不良作用的伤害等,遭到虚假产品宣传的指控,鲍林出庭为他辩护。由于英国《自然》杂志和当地报纸的报道,使这一事件广为流传。 鲍林与罗宾逊(A. Robinson) 博士的争端表明他有欠诚实,缺乏科学态度。罗宾逊是他的学生和助手,帮助他建立了鲍林研究所,成为首任副所长。1978年罗宾逊用裸小鼠研究给予不同组成的膳食,紫外线照射后皮肤癌的发生率。结果给予小鼠相当于鲍林荐用于人的1-5克维生素C的剂量时,能促进皮肤癌的发展,发生率为对照组的2倍;在相当于每日100克、接近致死量或营养不良组,小鼠的皮肤癌才受到抑制。鲍林对这项结果非常不满,因为与他提倡的维生素C可以防止75%的癌症说法相左。他还公开宣布罗宾逊的研究属“业余水平”,是不适当的。罗宾逊不久便被解雇,同时实验动物被处理,资料也被没收销毁。罗宾逊因此状告鲍林研究所毁约和伤害名誉,1983年此案在法庭外以57.5万美元的赔偿了结。鲍林接受《自然》杂志的采访时说,研究所接受这种结案办法,是因为厌倦旷日持久的官司和付出的代价较小,支付的费用只是对罗宾逊失去工作和诉讼费用的补偿。
可是,法庭协议书上却明白地写着,其中42.5万美元是对罗宾逊诽谤的赔偿。[28]1984年,在他处境艰难的时刻,美国化学会授予他普里斯特利勋章。(J. Priestley英国著名化学家,元素氧发现者。)1994年罗宾逊和他的同事发表了上述的小鼠实验。
整脊医疗是一种旁道医疗,为主流医学所不取。鲍林应邀在整脊医疗学院作荣誉性演讲,并和听众合影,供他们作宣传之用。1992年,庸医格伯(M. Gerber)和列文(W. M. Levin)因严重玩忽职守、欺骗性执业导致医疗事故受到指控,他先后为他们出庭作证辩护。
现在,与鲍林名字有关的网站非常庞杂,大量内容是在鲍林的大旗下,借他的名字和“理论”推销各种旁道医疗或医疗骗术和产品,包括提倡应用大剂量维生素C治疗阳痿,因为可以减少(阴茎)动脉壁的脂蛋白(a)粥样斑块。
(本文节选北京《自然辩证法研究》,祖述宪(安徽医科大学))
2025-07-31
·米内网
精彩内容随着系列政策的大力推动,叠加国内创新同质化严重的背景下,越来越多中国创新药企业纷纷踏上“创新转型、扬帆出海”的新赛道。据不完全统计,2024年至今达成的License-out交易150余项,交易总金额合计超1350亿美元;恒瑞医药、石药集团、三生制药等头部药企全速推进,合作交易金额屡创新高,国产1类新药频频登场......密集的出海交易,体现出中国创新药企业积极摆脱内卷、完成商业闭环并走向更高格局的决心。$1350亿总额惊呆了!创新药出海热度高涨自2015年开启药政改革以来,国内创新药研发能力快速提升,药物创新性和研发效率的优势逐渐得到国外制药巨头认可,海外授权(License-out)也逐渐成为国内创新药企业迈向国际化的敲门砖。据不完全统计,2024年至今我国创新药License-out交易至少发生150余项,合计交易总金额超1350亿美元。其中,2024年License-out交易共计94项,披露的交易总金额约542.9亿美元;2025年至今,国内已发生56项License-out交易,累计交易总金额超过817亿美元,可统计交易总额已突破去年全年水平,创新药出海热浪持续高涨。近年来License-out交易情况来源:公司公告、公开信息等,米内网整理近年来,随着系列政策的大力推动,叠加国内创新同质化严重的背景下,不论是国内传统大药企,还是Biotech新贵都纷纷踏上“创新转型、扬帆出海”的新赛道,License-out数量与授权合作金额均在逐年攀升。如此背景下,密集的创新药出海交易,NewCo交易新模式的登场,ADC、核药、CAR-T等高技术壁垒疗法的崛起......正体现出中国创新药企积极摆脱内卷、探索新品销售空间、完成商业闭环并走向更高格局的决心。$817亿创新高!三生、信达、石药......当仁不让据不完全统计,2025年至今已有至少56个项目达成出海交易,可统计累计首付款约37亿美元,总交易额超817亿美元,单笔交易达10亿美元及以上的项目有21个,包括三生制药的SSGJ-707、信达生物的IBI3009、石药集团的SYS6005、SYH2086、伊立替康脂质体注射液和免疫疾病小分子口服疗法、恒瑞医药的HRS-9821等。2025年至今创新药出海情况来源:公司公告等,米内网整理注:标红为总金额超10亿美元的交易,未披露交易金额用-表示今年5月,#三生制药 发布公告称,与辉瑞就旗下在研候选新药SSGJ-707达成合作协议。根据协议,三生制药将获得首付款,开发、监管批准和销售里程碑付款合计总额超60亿美元,一举刷新国产创新药单药出海交易总金额的纪录。SSGJ-707是一款靶向PD-1/VEGF双特异性抗体,为三生制药自主研发的1类创新药。据Ⅱ期临床阶段性数据显示,该药在治疗非小细胞肺癌上获得优异的客观缓解率和疾病控制率,具有best-in-class的潜力。今年4月,SSGJ-707获CDE批准纳入突破性治疗品种名单,目前其单药一线治疗非小细胞肺癌适应症已进入Ⅲ期临床,联合化疗一线治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌、一线治疗转移性结直肠癌、晚期妇科肿瘤等适应症均已进入Ⅱ期临床。SSGJ-707临床试验进度情况来源:米内网中国临床试验数据库2025年至今,#石药集团 已达成四项License-out交易,涉及SYS6005、SYH2086、伊立替康脂质体注射液和免疫疾病小分子口服疗法等产品,合计总交易金额超过97亿美元,成为今年以来BD出海交易最大的赢家之一。SYS6005属于靶向ROR1 ADC,为石药集团开发的1类创新药,拟用于治疗血液肿瘤、非小细胞肺癌等晚期肿瘤;SYH2086是石药旗下的一款在研口服小分子GLP-1受体激动剂,临床前数据显示,该药具有优异的体外激动活性和体内降糖、减重效果等;伊立替康脂质体注射液用于治疗转移性胰腺癌等,石药集团为该药首仿+首家过评企业,2024年中国三大终端六大市场(统计范围详见本文末)伊立替康销售额超8亿元;今年6月,石药集团再度牵手阿斯利康,聚焦AI技术驱动免疫疾病等小分子口服疗法的开发,根据协议,石药集团有望获得总潜在价值超53亿美元的合作款项。中国三大终端六大市场伊立替康销售趋势(单位:万元)来源:米内网格局数据库今年7月,恒瑞医药宣布将HRS-9821及至多11个项目的全球独家权益有偿许可给GSK;而GSK将向恒瑞支付5亿美元的首付款,以及未来相关里程碑付款约120亿美元,合计总交易金额超125亿美元。HRS-9821为恒瑞医药自主研发的1类创新药,用于治疗慢阻肺(COPD),作为辅助维持治疗,无需考虑既往治疗方案。据其早期临床和临床前研究显示,该新药展现出强效的PDE3/4抑制作用,可显著增强支气管舒张效应并产生抗炎作用。IBI3009为#信达生物 自主研发的靶向DLL3 ADC,拟用于小细胞肺癌及其他神经内分泌癌。作为潜在同类最佳和开发进度领先的靶向DLL3 ADC,该药在多个肿瘤负荷小鼠模型(尤其在化疗耐药肿瘤类型)中展现出强效的抗肿瘤活性,并具有良好的安全性特征。据此,今年1月,信达生物宣布称,将授予罗氏开发、生产及商业化IBI3009的全球独家权益,同时也有望获得超过10.8亿美元的合作交易款项。$540亿大爆发!恒瑞、石药、明济......成绩斐然回看2024年,国内至少有94个项目达成出海交易,可统计累计首付款超43亿美元,总交易额超540亿美元,单笔交易达10亿美元及以上的项目有22个,包括恒瑞医药的HRS-7535、HRS9531、HRS-4729和SHR-4849、石药集团的YS2302018、翰森制药的HS-10535、明济生物的FG-M701等国产创新药。2024年创新药出海情况来源:公司公告等,米内网整理注:标红为总金额超10亿美元的交易,未披露交易金额用-表示#恒瑞医药 以两项交易、合计总金额超70亿美元的成绩,成为2024年License-out总交易金额最高的国内药企之一。其一项交易涉及1款ADC创新药SHR-4849,授权总额约10.45亿美元。该药为恒瑞自主研发的靶向DLL3 ADC,其有效载荷是拓扑异构酶抑制剂(TOPOi),可通过杀伤DLL3高表达细胞释放毒素来杀伤DLL3低表达细胞。米内网数据显示,全球至今已有20多款ADC新药(不含生物类似药)获批上市,2024年全球合计销售额突破100亿美元。另一项GLP-1创新药“打包”出海的交易,合计授权总额超过60亿美元,包括3款1类新药——HRS-7535属于小分子GLP-1受体激动剂,目前全球暂无国产口服小分子GLP-1激动剂获批上市;HRS9531为靶向GLP-1/GIPR双受体激动剂,其同靶点药物礼来的替尔泊肽2024年全球销售额超164亿美元;HRS-4729属于GLP1R/GIPR/GCGR三靶点激动剂,能通过激活多靶点,有望实现更好的控糖、减重等效果。替尔泊肽全球销售销售趋势(单位:亿美元)来源:米内网跨国上市公司数据库YS2302018是一款口服脂蛋白(a)抑制剂,用于开发新型降脂疗法,以及多种心血管疾病的单一疗法或联合疗法。2024年10月,石药集团与阿斯利康就该新品订立独家授权协议。根据协议,石药集团将获得1亿美元的首付款,未来还将有资格获得最高19.2亿美元的开发和商业化里程碑付款,合计授权总额超过20亿美元。据悉,YS2302018能有效阻止脂蛋白(a)的形成,在体外实验及动物模型中均展现出优异的药效和药物代谢动力学表现,并保持较低的安全风险,有望为心血管疾病患者带来新的希望。米内网数据显示,2021-2024年中国三大终端六大市场心脑血管系统药物(化+生)销售额均在1300亿元以上。中国三大终端六大市场心脑血管系统药物(化+生)销售趋势(单位:万元)来源:米内网格局数据库FG-M701是明济生物自主研发的一款TL1A(TNFSF15)抗体药物,可用于治疗炎症性肠病,目前正处于临床前开发阶段。2024年6月,明济生物与艾伯维针对该药达成的合作授权总金额高达17.1亿美元。研究结果指出,根据TL1A靶点开发的药物还有望用于溃疡性结肠炎、克罗恩病等多种自身免疫性疾病,目前全球已有多款TL1A抗体新药处于临床研发阶段,其中默沙东/武田的PRA-023、罗氏/辉瑞的RG-6631已进入Ⅲ期临床,赛诺菲/梯瓦制药的TEV-48574、Xencor的XmAb-942已进入Ⅱ期临床。部分靶向TL1A(TNFSF15)的在研新药情况来源:米内网全球新药研发数据库结语国产创新药License-out已从“试水阶段”进入“深水区”,部分头部药企正通过技术输出和资本运作在全球价值链中占据一席之地。尽管终止合作、退货、里程碑无法兑现等情况偶有出现,但中国凭借系列新政支持、企业研发效率上的优势,不断推动创新药行业从“管线出口”向“全球策源”转型。未来,随着更多国产创新药步入商业化阶段,License-out将成为验证中国创新药全球价值的关键窗口。资料来源:米内网数据库、公司公告等注:米内网《中国三大终端六大市场药品竞争格局》,统计范围是:城市公立医院和县级公立医院、城市社区中心和乡镇卫生院、城市实体药店和网上药店,不含民营医院、私人诊所、村卫生室,不含县乡村药店;上述销售额以产品在终端的平均零售价计算。数据统计截至7月31日,如有疏漏,欢迎指正!免责声明:本文仅作医药信息传播分享,并不构成投资或决策建议。本文为原创稿件,转载文章或引用数据请注明来源和作者,否则将追究侵权责任。投稿及报料请发邮件到872470254@qq.com稿件要求详询米内微信首页菜单栏商务及内容合作可联系QQ:412539092【分享、点赞、在看】点一点不失联哦
引进/卖出免疫疗法细胞疗法抗体药物偶联物
100 项与 脂蛋白(a)抑制剂(上海舶望制药) 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 心血管疾病 | 临床前 | 中国台湾 | 2023-12-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用