预约演示
更新于:2025-01-23
更新于:2025-01-23
概览
关联
246
项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的临床试验ChiCTR2400094319
Effect of radiotherapy dose at implant site on implant survival: a prospective study of dual dose digital guided implant repair in head and neck radiotherapy patients based on radiotherapy dose and bone mass
开始日期2025-01-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT06498180
A Randomized Self-control Study of Periodontal Initial Treatment Under Local Anesthesia Combined With Glucocorticoid Therapy for Erosive Oral Lichen Planus
The purpose of this clinical trial is to understand whether the combination of periodontal initial treatment under local anesthesia and glucocorticoids can improve the effectiveness of treatment for erosive oral lichen planus. It will also understand the safety of this treatment regimen.
This study is a single-center, parallel-group, randomized self-controlled trial. The researchers will compare the treatment of periodontal initial therapy combined with glucocorticoid therapy under local anesthesia with traditional glucocorticoid therapy to see if the treatment of periodontal initial therapy combined with glucocorticoid therapy under local anesthesia promotes the healing of erosive oral lichen planus.
Participants will:
One side received periodontal initial treatment combined with glucocorticoid under local anesthesia, while the other side received traditional glucocorticoid therapy Clinical examination at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after treatment Note down the size of their erosion lesion area and periodontal clinical parameters
This study is a single-center, parallel-group, randomized self-controlled trial. The researchers will compare the treatment of periodontal initial therapy combined with glucocorticoid therapy under local anesthesia with traditional glucocorticoid therapy to see if the treatment of periodontal initial therapy combined with glucocorticoid therapy under local anesthesia promotes the healing of erosive oral lichen planus.
Participants will:
One side received periodontal initial treatment combined with glucocorticoid under local anesthesia, while the other side received traditional glucocorticoid therapy Clinical examination at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after treatment Note down the size of their erosion lesion area and periodontal clinical parameters
开始日期2024-12-31 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT06654141
Influence of Healing Time on the Outcomes of Alveolar Ridge Preservation in Periodontally Compromised Extraction Sockets: a Randomized Controlled Trial
The goal of this clinical trial is to histologically, clinically, and radiographically evaluate the healing sequelae of periodontally compromised extraction sockets grafted with Bio-Oss Collagen® at 3 and 6 months following tooth extraction in molar sites. The main question it aims to answer is:
Does healing time influence the histologic, clinical, and radiographic outcomes following socket grafting (alveolar ridge preservation) in periodontally compromised extraction sockets.
Researchers will compare a healing time of 3 months to a healing time of 6 months (conventional healing duration) to see if a shorter duration is viable for implant placement.
Participants will:
Take a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan to prepare for the surgical procedure.
Undergo tooth extraction and the extraction socket will be grafted with Bio-Oss Collagen® and a collagen membrane Bio-Gide® will be placed to stabilize the graft material.
Return at 2 weeks for suture removal and either 3- or 6-months post-extraction for implant placement.
Return at 2 weeks post-implant placement for suture removal, 3 months for prosthesis fabrication, 4 months for final prosthesis loading, and 1 year post-loading.
Does healing time influence the histologic, clinical, and radiographic outcomes following socket grafting (alveolar ridge preservation) in periodontally compromised extraction sockets.
Researchers will compare a healing time of 3 months to a healing time of 6 months (conventional healing duration) to see if a shorter duration is viable for implant placement.
Participants will:
Take a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan to prepare for the surgical procedure.
Undergo tooth extraction and the extraction socket will be grafted with Bio-Oss Collagen® and a collagen membrane Bio-Gide® will be placed to stabilize the graft material.
Return at 2 weeks for suture removal and either 3- or 6-months post-extraction for implant placement.
Return at 2 weeks post-implant placement for suture removal, 3 months for prosthesis fabrication, 4 months for final prosthesis loading, and 1 year post-loading.
开始日期2024-12-01 |
申办/合作机构 上海第九人民医院 [+1] |
100 项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
2,729
项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的文献(医药)2025-04-01·Journal of Colloid and Interface Science
Dynamic and sustainable supramolecular biolubrication coatings through nanoarchitectonics with dynamic B N bonding
Article
作者: Hou, Xiaozheng ; Zhao, Xin ; Wang, Chenchen ; Han, Sheng ; Wang, Rujiang ; Li, Yanan
2025-03-01·Journal of Hazardous Materials
Effects of mixed exposure to PFAS on adolescent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Integrating evidence from human cohorts, toxicogenomics, and animal models to uncover mechanisms and potential target sites
Article
作者: Qian, Kelei ; Gao, Liping ; Li, Dan-Lin ; Xu, Xueming ; Pan, Chen-Wei ; Zheng, Ya-Jie ; Du, Xiushuai ; Zheng, Weiwei ; Li, Yue-Zu ; Du, Zhiyuan ; Wu, Yitian ; Qin, Yu ; Tao, Gonghua ; Xu, Jing ; Liang, Gang
2025-03-01·Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis
Application of a dual channel MPTS-modified two-dimensional cell membrane chromatography system for rapid screening of effective ingredients in Saposhnikovia divaricata targeting inflammatory macrophages and fibroblast synovial cells in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Article
作者: Shi, Yuhuan ; Gu, Yanqiu ; Li, Yueyue ; Chen, Xiaofei ; Pan, Shu ; Zhang, Bin ; Yuan, Yongfang ; Chai, Yifeng
20
项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的新闻(医药)2025-01-04
·丁香园
上世纪五十年代,中国医疗界百废待兴。
彼时上海的广慈医院,曾发生过这样一场「豪赌」:炼钢工人全身烧伤 90%,继发绿脓杆菌感染败血症、抗生素耐药,面临截肢风险。
当下,医院党总支书记程家贤要求大家「大胆突破现行医学文献的束缚,破除迷信,敢想敢做,不惜代价,千方百计地挽救为国家创造财富的灼伤工人」。
于是,上海所有医学专家汇聚在一起,在几乎无解的棋局作出解法,突破一道又一道治疗的关卡,打破了当时世界医学史上称为烧伤面积超过 80% 的必死无疑的定论。
有人说,「瑞金烧伤」是中国烧伤医学发展的缩影。而这一切,都可以回溯到那个夏天。
噩梦
5 月的一个深夜,初夏令人慵倦的暖风吹过外滩早已黯淡的灯光。暗夜笼罩下的上海,只剩下黄浦江还在徐徐涌动。
现在是凌晨 1 点,广慈医院的陈藏华医生已经困得睁不开眼,一整天如战役般的急诊工作早已耗光他最后一丁点力气。下班前,他最后一次巡视着急诊病人的情况。
突然,一大群人急促地冲进急诊大门,每个人几乎都是咆哮着喊出要说的话。
「3 个人!10 吨钢水」
「1300 多度沸腾的钢水砸下来!」
「全身都被烧穿了!」
乌泱泱的一大片人互相推搡,让本就不大的急诊间显得格外拥挤、狭窄。
陈藏华看过去,那群人中间躺着 3 名伤员。三人全身都被白布一层层包裹起来,不断渗血的脸上覆满黑紫色,只剩下两只白色眼睛无神地盯着天花板,像极了阎王爷贴的催命符。
患者邱财康被 1300℃ 的钢水烫伤全身,烧伤总面积近 90%
图源:《广慈医院抢救邱财康病史档案选载》
「他们可是为了大炼钢铁受伤的,你们一定要救活他们啊!」
伴随着职业惯性,陈藏华像往常一样火速将患者送进了手术室。那时的他还没有意识到,世界烧伤整形史上一次最伟大的抢救即将拉开序幕。
规训
这是 1958 年的上海。
接诊当晚,陈藏华做了一个噩梦。他梦见自己回到几千年前,被处以炮烙极刑,他在业火中翻滚、哀嚎,却没人能拉他出来。当陈藏华从梦中惊醒,才发现这个噩梦如同现世报,只不过被炮烙的对象不是他,是三个悲惨的年轻钢铁工人。
次日一早,科室进行了一次外科大讨论——三名患者,一名烧伤 24%,并不严重;炉长邱财康,烧伤面积 89.3%,三度烧伤面积 23%,其余为深二度烧伤;另一工人刘四小,烧伤达面积 94%,情况十分危险。
「烧伤面积超过 60% 几无生机!」在烧伤界,曾有这么一条不成文的「规训」。
这条「规训」需要回溯到 1947 年,美国核爆炸医学家 Everest Evans 在弗吉尼亚设立了烧伤病房,标志着世界上第一个烧伤学科的成立。作为烧伤学科的创始人,Evans 1952 年在 Annals of Surgery 上发表文章,提出了如今医学生必须学习的烧伤补液公式和烧伤面积计算法(初代)。
在这个基础上,他同时指出,补液公式只适用于烧伤面积 <50%,而针对 50% 以上的病人,补液几乎都并发肺水肿而去世,而烧伤面积超过 80% 则几乎必死无疑。据悉,他自己治疗的 11 名烧伤面积超过 60% 的病人,全军覆没。
1952 年,Evans 在外科学年鉴上发表文章,指出大面积烧伤病人的生存率之低(图源:参考文献 1)
冰冷的文献数据压力下,这帮上海医生不得已签下了「预后不良」的告知书。
这时,广慈医院外科医生史济湘眉头紧锁,他是邱财康的主治医师。
他知道,上午的晨会,大家心情是绝望的,但钢铁厂的请求信又让他犹豫不决:邱财康工作的上钢三厂党委和工人送来了一封表扬信和请求信,称赞邱财康是上钢三厂最优秀的炉长,工人们一致联名要求医院务必将三人救活。
勇者
勇者,勇于挑战。
史济湘与外科主任傅培彬发动 40 多名医生,在一个上午时间读完了全世界几十年与烧伤相关的所有文献。
无数文献的冲击下,大家对疾病的畏惧逐渐褪去,取而代之的是面对疑难病症的兴奋,他们随即总结出 15 条可能的治疗方法。
这样的医学渴望下,上海外科的精锐部队被集结起来:上海第一医学院副院长沈克非、中山医院院长崔之义、上海市一医院外科主任任延桂,以及广慈医院外科的傅培彬、董方中、史济湘、张涤生等,围坐一起讨论治疗方法。
面对 Evans 无法解决的休克和肺水肿问题,医生们最终否决了前人「补液不能过多」的经验,大胆提出了增加补液(尤其是血浆)以维持正常血容量的方法,直接改写了烧伤补液公式。
几年后,针对大面积烧伤的补液公式被广慈医院的医生不断完善,在总结了 600 例大面积烧伤病人的治疗经验后提出了早期液体复苏的中国方案。(图源:参考文献 2)
因为邱财康身上几乎已经找不到完好的血管可以注射,除了大隐静脉插管补液外,护理组和儿科组的成员还提出了口服补液或是额静脉注射的方法治疗。
面对入院后 3 人的高热和意识模糊,史济湘更首先提出采用「人工冬眠」的方法以缓解剧痛。
从理论上来讲,应用「冬眠合剂」可以降低应激反应、保护脏器功能以辅助大面积烧伤的治疗。
但实际运用上,这其实是「人工冬眠」首次被应用在烧伤液体复苏的辅助治疗。也因为这一成就,史济湘于 1988 年被美国烧伤学会授予「Evans」奖。
5 天,120 个小时,医护人员寸步不离三人的病床。最终,烧伤面积 24% 的工人伤愈出院,邱财康也在慢慢恢复。
绝境
绝处已过,却并不逢生——休克问题刚解决,严重耐药菌感染接踵而至。
时值初夏,细菌繁殖迅猛。入院第八天,邱财康与刘四小均出现了绿脓杆菌的局部感染,2 天后,烧伤面积达 94% 的刘四小因败血症和烧伤并发症离世。
不久,邱财康的绿脓杆菌血培养为阳性,证明已发生绿脓杆菌败血症。
对感染颇有研究的华山医院副院长戴自英,旋即加入治疗团队。在结合文献试验了 58 种抗菌素后,戴自英决定选择当时还需进口的多粘菌素 B 作为药物。
然而在用药剂量和时间上,他却面临了两难的境地——西方文献报道,多粘菌素的使用不能超过 7 天,否则会导致肾功能衰竭,这对邱财康无疑是致命的;可随着刘四小的失败,对治愈邱财康的要求也从单纯的医学任务,上升为上海医疗界的政治任务。
这样巨大的压力下,戴自英用药的手止不住颤抖起来。
尽管在专家的讨论和党委的要求下,戴自英适当调大了多粘菌素的剂量和使用时间,击退了数次死灰复燃的败血症,但最终邱财康体内的绿脓杆菌产生了极强的耐药性,再大量的多粘菌素也无法抑制绿脓杆菌的繁殖。
整个治疗团队再次陷入低沉的阴影。
小鼠烧伤创面铜绿假单胞菌感染的变化趋势
图源:参考文献 3
邱财康的身体状况日渐恶化:绿脓杆菌墨绿色的脓液和令人闻所未闻的腥臭味,无不刺激着他那早已被烧伤剧痛折磨得如惊弓之鸟的神经,冬眠疗法再强力也难以抑制过度兴奋的交感神经。
他的求生欲和意志逐渐动摇了,有时候在昏迷中喃喃自语,有时候又会被剧痛震醒而大喊一些胡话。
一切仿佛正在走向一个早就注定的结局。
不久,第二次全市专家大会诊举行,华山副院长戴自英、仁济院长黄铭新、以及广慈内科的邝安堃、王振义、王耆令等一众上海市内外科专家悉数到场,会议的主题是「如何对抗感染」。
会中,张涤生提出采用同种异体皮肤移植的方法暂时控制感染;第二医学院微生物组的余㵑提出采用噬菌体疗法对抗耐药菌;还有专家建议输注带有细菌抗体的血液以治疗败血症。
众说纷纭的情况下,医院还是决定尝试一切有希望救治邱财康的方法。
突围
眼下,窗外的蝉叫嚣着每个黑夜,白天是烈日撑起整个夏天。这样的高温下,巨大的创面裸露,是细菌良好的培养基。
史济湘、张涤生等主张先植皮,暂时「封住伤口」。
可接下来的问题是,邱财康全身烧伤面积 90%,是真正意义上的「体无完肤」,皮肤要从哪里找?
瑞金医院党总支迅速向全院职工发出「为邱财康献皮」的号召,外科医生、医院医护人员和工人踊跃报名,报名人数达到 800 多人。
作为整复外科的专家,张涤生认为从活人身上取皮可能会极大程度影响正常生活,因此转而征得部分死亡病人家属的同意,通过捐献的遗体取皮片,并采用冷藏方法短期保存皮片。
于是,在 6 月 9 日,邱财康接受了遗体皮片的植皮术。
董方中等为邱财康进行手术
图源:《瑞金医院医院志》
在后期多次的植皮术后,邱财康的暴露皮肤感染得以控制。这之后要解决的,就轮到系统性的败血症了。
团队决定尝试一种新方法——为邱财康输入带有细菌抗体的血液。
而至于怎么输「有抗体的血液」,可以在校党委会的那段汇报中窥见一二:「6 月 21 日,瑞金医院儿科系四年级学生共青团员江悦琴、护校二年级学生共产党员朱根梅,为了要输给邱财康有抗体的血液,自愿注射带有绿脓杆菌、链球菌、葡萄球菌的三种细菌培养液,注射后,又热切渴望自己快发高烧, 因为高热证明细菌和抗体在搏斗,待血液里产生抗体后再输给邱财康,以增加他身体的免疫力,帮助杀死血液中的细菌。」
而后,邱财康的这一段败血症治疗,才终于告一段落。
破局
可一阵风刮不热一个夏天,棘手的问题也没有因为阶段性的成功而消失。
最大的困难终于出现了:邱财康下肢烧伤极为严重,创面无法愈合导致败血症反复发作,若不根除局部的感染,无论怎样增强抵抗力也无济于事。
万般无奈下,救治组提出了下肢截肢控制感染的方法,并召开了第三次全市医学界大讨论。
这一次的会议再次凝聚了上海滩所有顶级医生:外科学界元老裘法祖,二军大副校长屠开元,华山医院院长李鸿儒、副院长戴自英,中山医院院长崔之义、副院长吴钰,原北京阜外医院院长陶寿琪,仁济医院外科主任兰锡纯,和杨之骏教授带领的瑞金医院全院的治疗小组。
长达三天的激烈争论后,大家决定暂不截肢,继续由内科控制感染,重担最终落到了噬菌体的肩上。
其实,噬菌体治疗细菌感染一直以来都是微生物学家追求的目标。只是自 1923 年噬菌体治疗研究所在前苏联格鲁吉亚成立以来,大多数噬菌体治疗案例都因效率低、不可控性等因素未能取得有效进展,在 1942 年青霉素投入使用后,噬菌体治疗更是销声匿迹。
抗生素与噬菌体治疗发展史
图源:参考资料 4
但中国微生物学奠基人之一的余㵑认为,当下抗生素治疗遇到瓶颈,噬菌体可以提供另一种解题思路(即利用特异性噬菌体在局部浸润的方式,杀灭感染组织的绿脓杆菌),未尝不可。
说干就干。
上海第二医学院的学生被迅速发动起来,60 多名学生接连几天到市郊去掏粪坑、找污水,把这些粪水和污水带回来,经过分离培养,得到足够的噬菌体。最终,这些培养液被用于邱财康感染灶的清除。
功夫不负有心人,不到 24 小时,脓液明显减少——局部感染终被控制。
整复
至此,邱财康挺过了「休克关」、「感染关」和「植皮关」,他的人生路线也终于向原来的轨道靠拢。
唯一的缺憾是,早期为了控制感染的需要,邱财康的左手最终还是被截掉了,这给当初坚持保留正常功能的张涤生带来了很大的触动。
几十年后,张涤生不无惋惜地指出,「邱财康左手的截除手术,严重影响了他的正常生活,如果内科能够早些控制感染就好了。」
其实,张涤生也并不是没有努力过。
感染控制后,他先后采用提前切除烧伤坏死组织、大面积同种异体皮移植等方法,并在烧伤两个月后,与董方中、史济湘等医生彻夜为邱财康做了一次「邮票植皮」手术。
这是在大张异体植皮片移植成活后,去掉约 1cm² 的异体皮,而代替以新鲜采集的自体皮片的手术,其目的在于降低了用皮率,尤其是自体皮用皮率,大大提高了植皮效率。
术后,张涤生也借此机遇于 1961 年在广慈医院成立了整形外科,1966 年广慈医院整复外科和口腔科整体成建制地迁至上海第九人民医院,成立了现在上海九院的整复外科和口腔科。此后,张涤生致力于器官和外形的整复,追求着「正常功能」的终极目标。
回到邱财康的人生路线,时隔半年痊愈后,他由妻子搀扶着走出医院。几个月后,他再次进入上钢三厂,加入自己原本的工作中。
瑞金医院百年长跑,邱财康夫妇站在队伍的正中央,左右分别是王振义院士和陈赛娟院士(图源:《瑞金医院医院志》)
2014 年 3 月,86 岁的邱财康因慢性疾病,走完了他的一生。
曙光
改编自邱财康经历的电影中有这么一句话:「医学不像工农业生产,不能只靠热情做出成绩。」
但时代背景下,这样的「热情」和科学精神同时创造了一个奇迹,也确实为新中国医学发展划下浓墨重彩的一笔。
自 1958 年救治邱财康以来,广慈医院成立了新中国第一个烧伤科,其治愈率远超美国 Evans 烧伤中心,我国这一学科的水平稳坐世界第一宝座近 10 年之久。
1977 年 6 月,史济湘等成功抢救烧伤面积 100%,其中 III 度烧伤 94% 的患者杨光明,创造 7 项世界烧伤医疗史新纪录(图为杨光明在家中康复,源自《瑞金医院院志》)
随之而来的还有整复外科的成立,广慈医院的整复外科成为中国整形外科四大发源地之一,如今上海九院的整复外科已经是中国最强的整复外科临床科室。
烧伤抢救,则是提升了广慈医院从上至下对「无痛治疗」的默契:拔牙不痛、开刀不痛、生孩子也应该不痛,于是带动了医疗操作技术、医疗器械、服务态度、药物舒缓多方面的技术革新。
在周总理表彰治疗团队后,我国的烧伤学科更在全国各地遍地开花:重庆、北京、上海、西安、南昌……
包括烧伤科在内,新中国整个医疗界也如同钢铁一般被反复考验、打磨:面对各类常见病、罕见病,仍苦思冥想、计谋百出,借助最原始、最简陋的条件创造了最难以置信的疗效。
而一切的一切,都开始在那个漆黑的夜晚,那一场场彻夜不眠的手术,一个个视触叩听的灵魂。
本文首发于 2021 年 10 月 29 日,作者:颜可欣
策划:islay|监制:gyouza
题图来源:图虫创意
主要参考资料(上下滑动查看)
[1].Evans et al. 1958:FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE REQUIREMENTS IN SEVERE BURNS
[2].烧伤休克防治全国专家共识(2020版)[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(09):786-792.
[3].Brandenburg, K.S., Weaver, A.J., Karna, S.L.R. et al. Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Full-thickness Scald Burn Wounds in Rats. Sci Rep 9, 13627 (2019).
[4].Altamirano et al. 2019.clinical microbiology reviews
[5].巴金,1958:一场挽救生命的战争
[6].纪录片,《生命的凯歌——抢救邱财康的胜利》
[7].纪录片,《党救活了他》
[8].白杨等,1958:《春满人间》
[9].孙道临等,《共产主义凯歌》
[10].http://www.xinminweekly.com.cn/fengmian/2017/10/11/9308.html
[11].http://whb.cn/zhuzhan/jiaodian/20140320/4506.html
[12].秦翼,2020:一场公共事件的跨媒体创作——对献礼片《春满人间》的考察
[13].中共上海第二医学院委员会,1958:关于抢救烫伤钢铁工人邱财康同志的工作总结
[14].档案珍藏,1994:广慈医院抢救邱财康病史档案选载
[15].黑河专区人民医院外科,1958:抢救邱财康的共产主义精神在我院开花结果
丁香园是面向医疗从业者的专业平台,以「助力中国医生」为己任。在丁香园,可以和同行讨论病例 ,在线学习公开课,使用用药助手等临床决策工具,在丁香人才找可靠医疗岗位。
AHA会议
2024-10-30
·美通社
成都
2024年10月30日
/美通社/ --
全球医美生物制药
领域的领导企业艾尔建美学宣布旗下含利多卡因注射用交联透明质酸钠凝胶乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
(Juvéderm
®
VOLUX
®
)正式在中国上市。
今日,
乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
上市会以"解码轮廓,侧颜立现"为主题,诚邀国际及中国医疗美学专家及行业权威人士,共话下面部美学认知与治疗方案及面部年轻化领域的革新思路。
作为一款专为下面部轮廓精雕而设计的透明质酸产品,乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
用于面部骨膜上注射,以改善中度下颌后缩患者的下颌轮廓。临床研究表明,乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
能维持长达18-24个月
[1],[2]
清晰利落的下颌线条。同时,乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
含利多卡因,可以减少治疗过程中患者的疼痛,提升治疗舒适度。
艾尔建美学中国总经理丘汉华
表示:"乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
获批及上市再次印证了艾尔建美学在产品布局上的深度与前瞻性。自2015年登陆中国市场以来,乔雅登
®
家族不仅通过技术迭代不断激发新的求美需求,同时通过持续引入全球前沿创新产品,针对医美需求者最为关注的面部细分部位,打造高品质的医生培训体系和专业诊疗方案。作为医美行业始终的革新者,我们将继续以‘敬畏医疗本质,恪守循证原则'的态度矢志创新,为中国医美行业发展注入新的动力。"
研究表明,下颌骨是面部美学的重要组成部分,对整体面貌起到协调美观的重要作用。下面部的形态最富有变化,最能体现个性,同时是定义男性与女性面部特征的关键。随着衰老进程,下颌骨吸收变化导致下面部失去结构支撑,出现衰老迹象。
[3],[4],[5],[6]
因此,下面部对于抗衰以及面部美学风格的塑造具有重要意义。
此次,
全球顶级整形美容专家、面部注射领域开拓者
Dr.
Mauricio de Maio
特地莅临上市会现场,解读乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
轮廓密码——MD Codes™ 7&9-Point ∑hape™,及全球前沿的专属治疗方案。
全面理解面部结构对于提升面部形态至关重要。作为MD Codes™体系下的轮廓治疗方案, 7&9-Point ∑hape™旨在构建中面部基础,同时塑造下面部轮廓。
[7],[8]
为了使医美需求者获得更加满意的治疗效果,Dr.
Mauricio de Maio
提出了适合人们求美需要的情绪美学密码治疗方案,简称MD Codes™。MD Codes™不只是专注于个别治疗部位,更强调治疗的情绪动机,能够协助医生判断面部治疗部位与不同情绪特质的关联,确定合适的注射点位,满足医美需求者治疗后期望,呈现出自然外观的治疗效果。
与会专家纷纷表示,体系完整、具有可重现性并且不断更新迭代的注射技术体系和相关培训,对于医美需求者当下治疗的满意度以及长期、安全、可持续的治疗旅程都具有重要意义。
雕刻立体侧颜,创领行业新趋
一项纳入800例不同年龄、性别的中国人群研究显示,约有60%至80%中国人群具有下颏短小、下颌后缩等问题,严重程度随年龄增长而增加。
[9],[10]
中国整形美容协会面部年轻化分会会长、爱思特医疗美容集团总院长李勤教授
表示:" 亚洲地区的医美需求者对下颌和下颏区域的治疗需求高;同时,下颌、下颏的治疗需求复杂,医生需要谨慎选择具备理想特性的医美产品,包括强支撑能力、抗变形和抗位移能力,以及自然融合度高、安全可靠等。乔雅登
®
家族丰富的产品组合以及朔颜
®
强大的产品力,将成为医生能够实现三维全面部美学治疗的基础和保证。"
《中国人群面部年轻化透明质酸填充剂应用指南》指出,下颏和下颌的老化特征包括容量缺失和轮廓模糊,建议使用高弹性模量、中到高内聚力的透明质酸填充剂,在骨膜上或皮下注射,以重塑下颏轮廓和下颌缘线条。
上海上实医疗美容医院副院长方建蔺
表示:"当前中国市场缺乏能够塑造从下颏到下颌线整体轮廓的塑形产品,乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
的上市恰逢其时,其定制化的弹性模量和内聚力配比符合下颌区域治疗需求。我们期待乔雅登
®
品牌作为全球品类领导者能够更进一步,树立行业新的治疗标杆并助力实现患者多元化的治疗目标。"
目前,玻尿酸已经成为面部填充和塑形的主流产品之一。产自法国Pringy工厂的乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
使用特有的Vycross
®
交联技术,是乔雅登
®
Vycross
®
系列中透明质酸浓度、弹性模量和内聚力最高的产品。
中国注册研究*临床数据显示,使用乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
治疗6个月后,下颌部位整体美观改善的满意度高达95.0%以上;在治疗后12个月,医美需求者仍然维持较高的满意度。数据充分证明了乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
在改善和塑造下颌线条方面的治疗效果。
乔雅登
®
家族目前已有6款产品(乔雅登雅致
®
、乔雅登极致
®
、丰颜
®
、缇颜
®
、质颜
®
和乔雅登
®
朔颜
®
)进入中国市场,涵盖面颊部、鼻唇沟、唇部、鼻部、下颌轮廓等多个部位的治疗,配置不同的理化特性,实现分层分部位定制化解决方案。
1. Ogilvie Petal. Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40:NP499–510.
2. Allergan Aesthetics. Unpublished Data. INT-VOX-2150005. Juvéderm® VOLUX: Final Clinical Evaluation Report 2019. Apr 2021.
3. 吴敏娟,等.下颌骨的生长发育及下面部衰老后的变化[J].中国美容医学,2007,(09):1302-1304.
4. Ozturk C N, et al. Dentition, bone loss, and the aging of the mandible[J]. Aesthetic surgery journal, 2013, 33(7): 967-974.
5. 张陈平. 下颌骨重建术[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志,2005,15(3):215-218.
6. 恒敏,等. 上下颌骨位置改变对上气道的影响[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志,2007,17(1):94-97.
7. de Maio M. Facial Plast Surg 2022;38(2):102–10. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1741499; 2. de Maio M. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2021;45:690–709. doi: 10.1007/s00266-020-01762-7.
8. de Maio M. Facial Plast Surg 2022;38(2):102–10. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1741499; 2. de Maio M. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2021;45:690–709. doi: 10.1007/s00266-020-01762-7.
9. Hsieh D M Y, et al. Chin microgenia: an anthropometric analysis on the prevalence and severity in a Chinese population[J]. Dermatologic Surgery, 2022, 48(5): 516-522.
10. 2020 BONE CLONES, INC. Human Male and Female Skulls: African, Asian, and European:https://boneclones.com/product/human-male-and-female-skulls-african-asian-and-european-COMP-120-SET 2. Racial Determination using
*参与该产品中国临床试验的机构包括北京大学国际医院整形美容外科、北京医院整形外科、华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院整形外科、南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院/南京鼓楼医院烧伤整形外科、南方医科大学南方医院整形美容外科、上海第九人民医院/上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院整形外科、中国医学科学院整形外科医院整形外科(排名不分先后,按拼音首字母排序)
###
关于艾尔建美学
艾尔建美学是一家艾伯维旗下的公司,致力于研发、生产和销售一系列领先的美学品牌和产品,覆盖面部美学、身体塑形、整形、皮肤护理等领域。
艾尔建美学拥有独立的研发部门,专注于推进美学领域的突破创新,提供全面、科学的美学产品。
如需更多信息,请登录:
https://www.allerganaesthetics.cn/
。
上市批准申请上市
2024-05-25
·梅斯医学
5月24日22时50分,上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院发布讣告:中国共产党优秀党员,卓越的医学家、教育家、科学家,中国口腔颌面外科、头颈肿瘤外科以及口腔颌面修复重建外科的创建者和开拓者之一,中国工程院院士,中国医学科学院学部委员,国家口腔医学中心、国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心名誉主任,中华口腔医学会名誉会长,国际口腔颌面外科医师协会理事,全国先进教师,全国卫生系统先进工作者,上海市教育功臣,上海交通大学荣誉讲席教授,上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院原院长,上海交通大学口腔医学院原院长邱蔚六同志,因病医治无效,于2024年5月24日16时08分在上海逝世,享年92岁。现定于2024年5月28日9时在上海龙华殡仪馆(漕溪路210号)大厅举行邱蔚六同志告别仪式。邱蔚六院士生平据上海第九人民医院微信公众号消息,邱蔚六,男,汉族,四川奉节(今重庆奉节)人,1932年10月13日出生于四川省成都市。1955年10月毕业于四川医学院口腔系(现四川大学华西口腔医学院),同年11月参加工作。1955年至1966年任上海第二医学院附属广慈医院(现上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院)口腔科医生。1966年至1984年任上海第二医学院附属第九人民医院口腔颌面外科医生。1983年6月加入中国共产党。1984年至1996年历任上海第二医科大学附属第九人民医院院长、上海第二医科大学口腔医学系主任、上海第二医科大学口腔医学院院长。2000年获聘为上海第二医科大学附属第九人民医院终身教授。2001年当选中国工程院院士,成为口腔医学界首位院士。邱蔚六院士是卓越的医学家。他剑胆琴心、悬壶济世,在口腔颌面-头颈肿瘤外科、口腔颌面整复外科与颞下颌关节外科均有卓越建树。他是中华口腔医学会口腔颌面外科专业委员会和中国抗癌协会头颈肿瘤外科专业委员会的创建人之一。他引领“中国特色的口腔颌面外科”走向国际舞台,是第一位担任国际口腔颌面外科医师协会的中国理事。获国际口腔颌面外科医师协会颁发的最高奖项——杰出会士奖(Distinguished Fellow Award)(2009年)、国际牙医学院最高荣誉——大师(Master)称号(2010年)。几十年来,邱蔚六坚持只出普通专家门诊,不出特需门诊。慕名前来看他的病人太多,找他加号成了家常便饭,学生们一度担心他的身体,想劝退病人。但他总是说,来找他看病的多是些外地的疑难病人,来上海一趟不容易。面对形形色色病情不同、性格不同的病人,甚至是面对病人的唠叨,邱蔚六总是仔细听完病人的陈述,进行全面而有的放矢的检查,很快做出判断,制定诊治方案。邱蔚六院士是卓越的教育家。邱蔚六院士主编出版第2版至第6版《口腔颌面外科学》规划教材,耄耋之年仍笔耕不辍,主编出版国内首部医学人文规划教材——《口腔医学人文》。他两次获国家级教学成果二等奖(2018年、2022年),曾被评为全国先进教师(1989年)、上海市先进教师(1996年)、上海市科教系统伯乐奖(2007年)、上海市教育功臣(2018年)。他提携后学、诲人不倦,在人才培养上倾注了无数心血,以其深厚的教育情怀,赢得了广泛的尊敬与赞誉。邱蔚六常对学生说:要做一名学者型的外科医生,不要成为一名只会开刀的工匠。要善于寻根刨底,知其然,更知其所以然;要不断地学习、更新知识;要会做、会写、会沟通。谆谆善诱,因材施教,邱蔚六带教学生,会根据学生的个性特征,为每个人规划一条更适合他们走的事业道路。在邱蔚六的精心培养下,一大批优秀的口腔医学人才脱颖而出,包括中国工程院院士、教育部新世纪百千万人才、卫生部有突出贡献中青年专家以及多名口腔医学院校领军人才等,为我国口腔医学界培育出一片“人才森林”。邱蔚六院士是卓越的科学家。他开拓创新、潜精研思,先后获国家发明奖、国家科技进步奖等国家及省部级奖项36项,以及“何梁何利基金科学与技术进步奖”。主编、参编专著40余部,在国内外杂志上发表论文400余篇。他在口腔外科领域推出了诸多的“首创”技术,如在国内率先开展颅颌面联合切除术治疗晚期口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤;首次提出全额隧道皮瓣一次转移立即修复口腔癌术后缺损获得成功;上世纪70年代末,他率先将显微外科技术应用于口腔颌面外科整复畸形与缺损;他还倡导口腔癌的综合序列治疗,使生存率与生存质量都获得明显进步。邱蔚六院士的一生,是对医学事业执着追求和无私奉献的一生。他的逝世,是我国口腔医学界的重大损失,我们为失去了一位贡献卓越、享誉海内外的杰出医学家、教育家和科学家深感悲痛!他的医者仁心、人格魅力和学术风范将永远铭刻在我们心中。撰文 | 梅斯医学编辑 | Swagpp● 中山大学宋尔卫院士研究团队:高脂肪饮食促进癌症发展和导致不良预后,背后的机制找到了!● 一周饿2天,就能改善脂肪肝?Cell子刊:坚持这种轻断食法,能保护肝脏和改善代谢(不是16+8)● 燃气灶不仅致癌,还增加死亡率和哮喘发生率?Science:仅烹饪25min,燃气灶释放出的NO2远超阈值,3小时后依然高版权说明:梅斯医学(MedSci)是国内领先的医学科研与学术服务平台,致力于医疗质量的改进,为临床实践提供智慧、精准的决策支持,让医生与患者受益。欢迎个人转发至朋友圈,谢绝媒体或机构未经授权以任何形式转载至其他平台。点击下方「阅读原文」 立刻下载梅斯医学APP!
高管变更
100 项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 上海第九人民医院 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2025年07月05日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
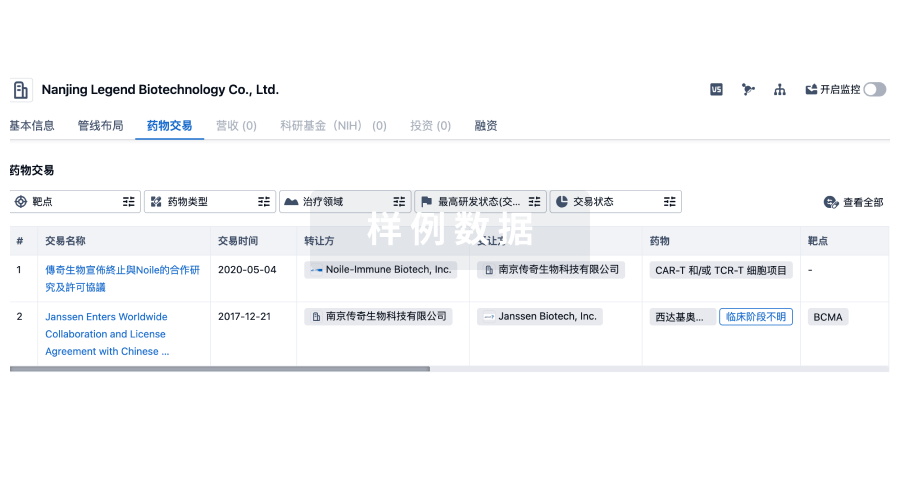
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
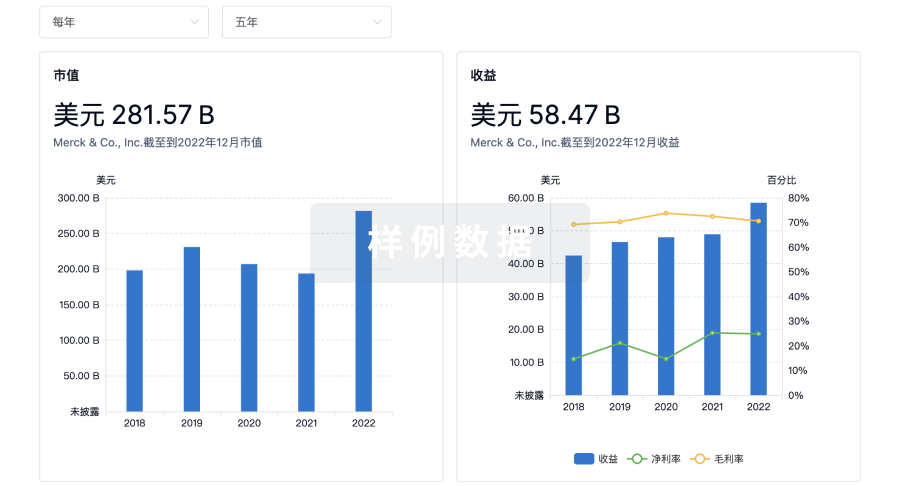
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
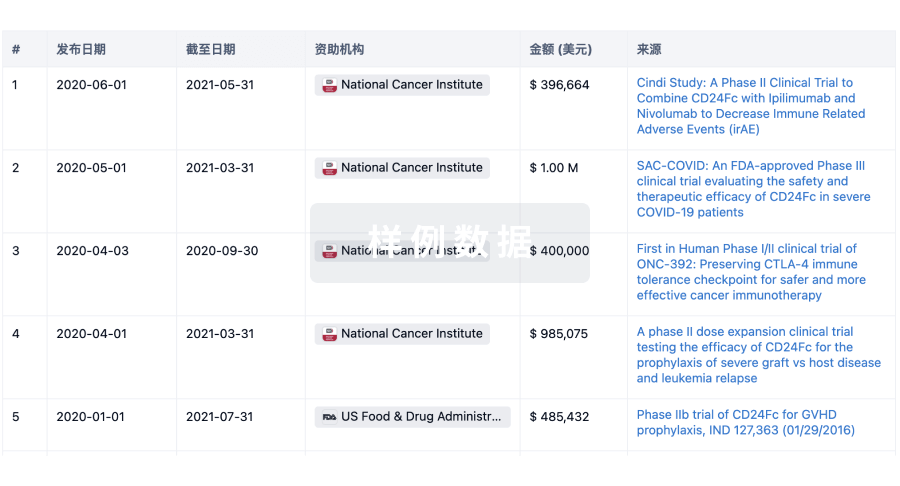
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或
投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或
融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用