预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
Shenzhen Longgang District People's Hospital
更新于:2025-05-07
概览
关联
9
项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的临床试验NCT06760065
A Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Study Comparing Keverprazan Hydrochloride-Amoxicillin Dual Therapy and Susceptibility-Guided Quadruple Therapy in Helicobacter Pylori Rescue Treatment
This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Keverprazan Hydrochloride combined with Amoxicillin in dual therapy compared to susceptibility-guided quadruple therapy in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections requiring rescue therapy. H. pylori is a common infectious disease associated with peptic ulcers, gastric cancer, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. However, the increasing resistance of H. pylori to antibiotics has reduced the eradication rates of standard therapies.
Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs), such as Keverprazan Hydrochloride, provide faster and more sustained gastric acid suppression compared to traditional proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), making them a promising option for H. pylori treatment. This multicenter, randomized controlled trial will provide critical evidence comparing the effectiveness of Keverprazan-based dual therapy to susceptibility-guided quadruple therapy, aiming to establish optimized rescue therapy guidelines for H. pylori eradication.
Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs), such as Keverprazan Hydrochloride, provide faster and more sustained gastric acid suppression compared to traditional proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), making them a promising option for H. pylori treatment. This multicenter, randomized controlled trial will provide critical evidence comparing the effectiveness of Keverprazan-based dual therapy to susceptibility-guided quadruple therapy, aiming to establish optimized rescue therapy guidelines for H. pylori eradication.
开始日期2025-01-15 |
申办/合作机构  中山大学附属第六医院 中山大学附属第六医院 [+3] |
NCT06772038
Dynamic Assessment of Fluid Responsiveness and Venous Congestion: Evolution of the VExUS Score During Volume Expansion
Fluid responsiveness is a critical determinant guiding fluid therapy in critically ill patients. However, excessive fluid administration can result in fluid overload, leading to venous congestion and worse clinical outcomes. Venous congestion, a marker of impaired fluid clearance, is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor to poor prognosis. Previous studies have demonstrated the coexistence of fluid responsiveness and venous congestion in critically ill patients. Notably, these studies were limited by the absence of fluid challenge-the gold standard for assessing fluid responsiveness-leaving the dynamic relationship between fluid responsiveness and venous congestion incompletely understood. This study aims to investigate the interplay and temporal evolution of fluid responsiveness and venous congestion following a standardized fluid challenge in critically ill patients.
开始日期2025-01-05 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT06713421
The Effects of Premedication With Pronase and Postural Exercise on Mucosal Cleanliness During Painless Esophagogastroduodenoscopy: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Study Based on Artificial Intelligence Assessment
Gastric cancer and esophageal cancer are common malignant tumors that threaten people's life and health. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is an important tool for screening upper gastrointestinal tumors, especially early tumors, and an effective method for detecting other upper gastrointestinal lesions, including ulcers and polyps. However, during EGD examination, mucus and foam can reduce the cleanliness of the mucosa and limit the operator's visual field, resulting in missed lesions and misdiagnosis. Previous studies have shown that preoperative medication with pronase and dimeticone is correlated with the improvement of upper gastrointestinal mucosal cleanliness. However, the number of samples in such studies is limited, and the artificial judgment is not objective enough to evaluate the cleanliness of upper digestive tract mucosa. And, whether a postural exercise is necessary for premedication with pronase or dimeticone remains unclear. Our team design this experiment to examine the efficacy of using premedication of dimeticone/pronase with a postural exercise on visualization of the mucosa before painless EGD. The investigators aim to provide new evidence to optimize the use of premedication with EGD.
开始日期2024-12-01 |
申办/合作机构 海军军医大学第一附属医院 [+25] |
100 项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
256
项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的文献(医药)2025-04-18·Science Advances
Earlier onset of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in females by ICAM-1–mediated accumulation of perivascular macrophages
Article
作者: Xin, Wen-Jun ; Chen, Li ; Zhang, Xiang-Zhong ; Liu, Cui-Cui ; Chen, Mu-Yang ; Yan, Pu ; Feng, Xia ; Zou, Xin ; Xie, Jing-Dun ; Shi, Jing-Ming ; Deng, Jie ; Xu, Ting ; Tang, Xiao-Qing ; Wang, Chen
2025-04-01·Science China Chemistry
Eliminating the solvent-induced distortions of the NIR-II fluorescent probe spectroscopy via deuterated solvents
作者: Zhang, Siwei ; Ma, Fulong ; Chen, Xinmeng ; Jiang, Jinhui ; Tang, Ben Zhong ; Alam, Parvej ; Zhao, Zheng ; Wang, Yifan ; Wang, Jinjin
2025-03-25·Zhonghua wei chang wai ke za zhi = Chinese journal of gastrointestinal surgery
[Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of multi-center fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of functional constipation: A retrospective real-world study].
Article
作者: Guo, G G ; Shi, J G ; Dong, X S ; Wang, L ; Liu, L ; Li, N ; Yuan, X G ; Li, L ; Chen, Q Y ; Fan, Y H
2
项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的新闻(医药)2023-12-25
·生物谷
由于经济水平的提高和人口老龄化趋势的改变,我国成人糖尿病患病率已攀升至12.8%,与之对应的是我国糖尿病知晓率、治疗率、控制率仍处于较低水平。
由于经济水平的提高和人口老龄化趋势的改变,我国成人糖尿病患病率已攀升至12.8%,与之对应的是我国糖尿病知晓率、治疗率、控制率仍处于较低水平。糖尿病作为一种以慢性高血糖为主要特征的代谢性疾病,其可怕之处不在于疾病本身,而在于它可能带来多种并发症,严重的甚至危及生命。这让我们清醒地认识到,优化血糖控制仍是我国糖尿病管理的巨大挑战[1]。
美国糖尿病协会(ADA)和《中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)》等指南均指出,2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者常合并高血压、血脂异常、肥胖等单个或多个代谢综合征表现,这些并发症同时也会加速T2DM的进展[1,2]。所以T2DM的治疗策略不应仅仅注重血糖的控制,还应包括血压、血脂和体重的综合管理[1]。
目前胰岛素是治疗糖尿病的重要手段之一,但胰岛素注射治疗存在一些不足,包括引起高胰岛素血症、夜间容易发生低血糖、体重增加以及增加心血管疾病风险等。新型降糖药物德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液(IDegLira)是德谷胰岛素与利拉鲁肽组成的联合制剂。在有效覆盖T2DM多重病理机制的同时弥补了胰岛素注射带来的不足,为T2DM患者保持正常的血糖水平开辟全新的治疗思路[3]。
下面将通过分享1例使用德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液治疗的案例来简单了解德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液的优势。
案例
患者,男性,53岁。
主诉:发现血糖升高11年,血糖控制欠佳1年
现病史:患者于11年前发现血糖升高,诊断T2DM,初服用“二甲双胍0.5 g bid、阿卡波糖50 mg tid”血糖控制良好;5年前至深圳市龙岗区人民医院内分泌门诊就诊,查空腹血糖(FPG)10.2 mmol/L,餐后2小时血糖(2hPPG)为16 mmol/L,调整治疗方案为“卡格列净0.1 g qd+西格列汀二甲双胍(50 mg/850 mg)1片bid”后血糖控制较好,但体重下降4kg;近1年血糖逐渐控制欠佳,测FPG 8~9 mmol/L,2hPPG 10~12 mmol/L。病程中,患者精神、饮食、睡眠可,大小便正常。
既往史:2012年有脑出血史 ,无遗留症状;2018年有脑梗死,遗留构音稍欠清,规律服用阿司匹林肠溶片及阿托伐他汀等药物治疗;否认高血压病、冠心病。
个人史:无特殊。
家族史: 家族中有脑中风病人,无糖尿病家族史。
体格检查
一般情况:身高160 cm,体重58 kg,体重指数(BMI)22.65 kg/m2,腰围84 cm,血压115/73 mmHg,体温36.5℃,呼吸18次/分,心率80次/分。
系统检查:无异常。
实验室检查
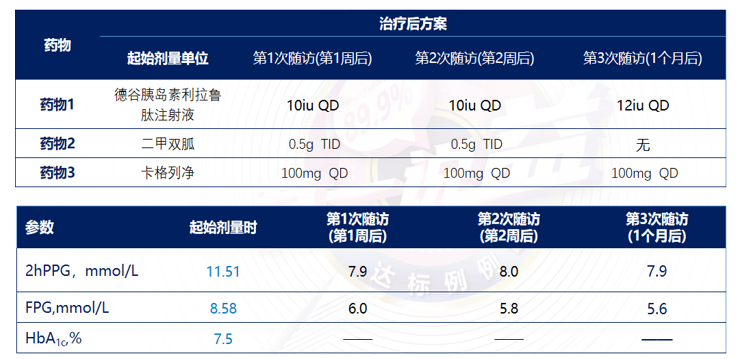
血糖:糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)7.5%↑;FPG 8.58 mmol/L↑;PPG 11.51 mmol/L↑
空腹C肽0.88nmol/L;餐后2小时C肽1.56nmol/L
血脂:总胆固醇(TC)4.19 mmol/L,低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)2.34 mmol/L,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)1.04 mmol/L,甘油三酯(TG)1.92 mmol/L↑。
肝功能:谷丙转氨酶(ALT)15.0 U/L;谷草转氨酶(AST)14.0 U/L ↓。
肾功能:血尿素氮6.98 mmol/L,血肌酐85 µmol/L,肾小球滤过率肾小球滤过率90ml·min-1·(1.73m2)-1,尿微量白蛋白/肌酐比值4.6mg/g,尿酸384μmol/L。
尿液分析:尿糖 3+;蛋白尿 -;酮体-。
影像学检查
心电图:1.窦性心律;2.偶发房性早搏;3.ST-T未见明显异常改变。
颈动脉超声:双侧颈动脉硬化并斑块形成,双侧椎动脉未见异常声像,双侧锁骨下动脉未见明显异常声像,双侧锁骨下静脉未见明显异常声像,基底动脉血流未见异常。
心脏彩超:心内结构、形态未见明显异常,主动脉瓣轻度反流,左室收缩功能正常,舒张功能减退。
眼底检查:眼底正常。
初步诊断
1.T2DM
2.T2DM性周围血管病变
3.脑梗死后遗症
4.高脂血症
预期目标
1.血糖控制目标:HbA1c≦6.5%,FPG4.4-6.1 mmol/L,PPG 4.4-8.0 mmol/L;
2.心脑血管获益;
3.治疗方案简单;
4.维持体重或不下降。
用药方案
德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液10剂量单位 qd+二甲双胍 0.5 g tid+卡格列净100 mg qd
案例讨论
本例患者病程长,合并脑血管病史,长期口服药物降糖,胰岛β细胞功能欠佳,期间调整过多种降糖药物,目前联合使用卡格列净+西格列汀二甲双胍降糖,但血糖控制仍不佳,近1年测FPG 8~9 mmol/L,2hPG10~12 mmol/L,HbA1c不达标,体重下降明显。
期望治疗方案能血糖达标、有心脑血管获益、简单、维持体重,故调整治疗方案给予德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液10iu QD+二甲双胍0.5TID+卡格列净0.1QD,随访1月,血糖达标(表1),未发现低血糖,体重保持稳定,无不良反应(表2),后续优化方案为德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液12iu QD+卡格列净0.1QD,血糖依然保持达标,患者满意度高。
表1. 患者后续治疗方案、剂量调整及随访
表2. 患者治疗期间低血糖、体重及不良反应发生情况
T2DM是一种慢性进行性疾病,需要根据血糖控制情况调整治疗方案以达到血糖目标。DUAL IX研究[4]旨在评估在既往接受钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂(SGLT-2i)治疗后血糖控制不佳的T2DM患者中添加德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液或甘精胰岛素U100的疗效和安全性。研究期为26周,主要观察指标是治疗后HbA1c的变化。研究结果表明,在既往接受SGLT-2i治疗血糖控制不佳的T2DM患者中,添加德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液治疗相比甘精胰岛素U100在降低HbA1c水平、减轻体重以及减少严重或确证性低血糖方面更具优势。而且德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液治疗组所需胰岛素日剂量更少。由此可见,DegLira可能是中国T2DM患者在口服多种降糖药物(包括SGLT-2i)治疗血糖控制不佳时的一种有效且耐受性良好的治疗方案。
本例患者曾有脑出血及脑梗死病史,可能与高血糖相关。高血糖会导致血管内皮细胞功能障碍,使血小板活化,加上多种诱导剂诱导聚集,产生大量超氧离子和血栓烷化合物,最终导致血栓形成。此外,由于氧与血红蛋白的解离速度减慢,血液中的氧气供应也会受到影响,从而也会导致脑部缺氧[5]。
Stefano Rizza等学者探究了德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液治疗对T2DM患者的血糖以及合并症的影响。研究共纳入57例患者(平均每天服用4或5种降糖药物),经过6个月的德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液治疗,患者的多个指标得到了明显的改善,即HbA1c水平下降了0.58%(或4 mmol/mol),FPG水平下降了52.07 mg/dL,BMI下降了0.81 kg/m2,TC水平下降了8.4 mg/dL,此外,患者的治疗满意度也显著提高。总之,德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液对血糖、心脑血管疾病的风险因素和炎症标志物均有临床意义的改善[6]。
综上所述,本例患者长期血糖控制不佳,德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液不仅可以保护胰岛β细胞、刺激胰岛素分泌、提高HbA1c安全达标率、体重影响小、耐受良好,长期使用还具有心血管获益,是临床糖尿病患者降糖治疗的新选择。
参考文献
[1]中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409.
[2]American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9.Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment:standards of medical care in diabetes-2022[J].Diabetes Care,2022,45(Suppl 1):S125-S143.
[3]Isabella R,Rosalia S .Use of IDegLira to Intensify, Simplify, and Increase Appropriateness of Type 2 Diabetes Therapy: A Real-Life Experience.[J].Diabetes therapy : research, treatment and education of diabetes and related disorders,2023.
[4]Janez A, Őrsy P,et al.Benefits of insulin degludec/liraglutide are maintained even in patients discontinuing sulphonylureas or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors upon initiation of degludec/liraglutide therapy: A post hoc analysis of the DUAL II and DUAL IX trials.Diabetes Obes Metab . 2020 Apr;22(4):658-668.
[5]H A B,M S P,Krzysztof P, et al.Predictors of neutrophil extracellular traps markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: associations with a prothrombotic state and hypofibrinolysis.[J].Cardiovascular diabetology,2019,18(1):49.
[6]Stefano R,Giacomo P,Maria M, et al.Effect of deprescribing in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: iDegLira might improve quality of life[J].Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy,2021,144112341-112341.
作者简介:
郭中秋
副主任医师、硕士研究生
广东省临床医学会--糖尿病教育与支持委员会委员
广东省医疗行业协会糖尿病学管理分会委员
深圳市医学会第四届糖尿病专业委员会委员
深圳市医师协会骨质疏松症和骨矿盐疾病委员会委员
毕业于广东医科大学内分泌代谢科专业,毕业后一直在龙岗区人民医院内分泌代谢科工作,曾到南方医科大学内分泌代谢科进修并获得优秀进修生,临床经验丰富,擅长糖尿病及慢性并发症、骨质疏松、甲状腺疾病、高尿酸血症诊治
临床研究
2023-12-16
12月15日,第二届深圳龙岗生物医药产业生态大会暨中国医药创新大会启动会在龙岗隆重举办。本届大会作为我市生物医药产业活动周重要系列活动之一,以“全链共建、生态共赢”为主题,由深圳市龙岗区人民政府主办,龙岗区科技创新局、卫生健康局承办,深圳湾宝龙生物创新投资发展有限公司协办,深圳市龙岗区人大常委会副主任郭雁通、深圳市科技创新委员会社会发展科技处处长黄葳、中国医药保健品进出口商会副会长王茂春致辞。龙岗区人民政府副区长平原、北京中医药大学副校长刘铜华、深圳市投资控股有限公司副总经理陈科、深圳市特区建工集团有限公司副总裁李锋等出席活动。郭雁通深圳市龙岗区人大常委会副主任黄葳深圳市科技创新委员会社会发展科技处处长王茂春中国医药保健品进出口商会副会长大会活动包含1场开幕式、1场产业生态展、2场专业卫星会、4场前沿技术论坛及30多个专业演讲,围绕CGT、小分子创新药、高端医疗器械、中药创新、产业资源精准对接等方向,汇聚国内各级政府部门、知名科研院所、联合国项目事务署、行业协会、医药研发企业、投资机构、生态服务链等关键创新主体代表共400余人,为生物医药行业呈现了一场深度融合的盛宴。“空间链”载体封顶为企业入驻发展打造坚实基础宝龙生物药创新发展先导区作为深圳市重点打造的五大生物医药园区之一,是深圳首个以生物药为特色的生物医药专业园区,也是龙岗在建的生物医药领域的重要空间载体。在本次大会上,宝龙生物药创新发展先导区核心启动区——深圳湾生物生态谷一期工程宣布封顶,这是一个重要里程碑,一座高标准、专业化的生物医药产业园区即将于2024年在龙岗区投入使用。深圳湾生物生态谷一期建筑面积约30万平方米,将为企业提供以生物医药高端厂房为主,集生产配套设施、共享实验室、公共服务平台于一体的高品质产业空间,可以满足企业全生命周期发展空间需求。在市发展和改革委员会、市科技创新委员会、龙岗区人民政府的大力支持下,宝龙生物药创新发展先导区积极引入项目合作,现场吸引了一批优秀项目落地龙岗。值得一提的是,得益于高标准的园区配套,直接吸引了市外20多家优质企业CEO走进园区现场对接合作。“创新链”资源集聚打造生物医药创新生态圈高地“创新之花,结出产业成果”。生物医药从研发到生产,都离不开产业生态的支持。近年来,龙岗区一直积极实施创新驱动发展战略,深耕牵动发展全局的核心技术研发,此次大会上发布亚辉龙公司的高性能免疫现场快速研发系统、精锋医疗的精锋®单孔腔镜手术机器人SP1000、艾克瑞的6米数字DR体检车和艾克瑞厢式体检车、库珀医疗的一次性使用输尿管支架(π管)及北京中医药大学深圳医院(龙岗)吴芬芳教授团队研发的类器官工厂及培养基系统等5个重大创新项目。左右滑动查看更多此外,龙岗区一步一脚印打通“产学研用”链条,形成了多项生态服务产品及公共技术服务平台,在AI赋能研发生产及医疗诊断、概念验证、动物及临床试验、注册审评、GMP等领域为企业提供强有力的服务支撑。活动现场发布了中国医学科学院“医学实验动物研究平台”、十一科技“GMP一站式服务平台”、深圳大数据研究院“医疗垂直领域大模型华佗GPT”、国信弘盛“园区产业基金产品服务”、华为云“盘古大模型”等9大创新生态服务产品,助力生物医药企业创新发展。左右滑动查看更多值得一提的是,深圳市龙岗中心医院、深圳市龙岗区人民医院、深圳市龙岗区第三人民医院在2022年首届生态大会上,与有关企业开展了优质临床资源签约合作,至今共开展20余项产学研合作,创新资源赋能结果显著。此次大会还安排了4场专业论坛,分别是中药创新发展论坛、细胞基因治疗发展论坛、小分子药物创新开发论坛、医疗器械创新发展等4个专业论坛,兼具广度与深度,为行业发展贡献智囊。··“产业链”政策发布多维度助力企业发展壮大根据区委区政府工作部署,结合龙岗区生物医药产业发展特点,《深圳市龙岗区关于促进生物医药产业高质量发展的若干措施》在大会上发布,从加快产业基础设施建设、提升产业研发创新能力、壮大产业发展规模、优化产业生态环境等4方面针对性地推出了13条扶持措施,其中创新平台最高可获支持3000万元、产业公共服务平台最高可获支持1000万元、临床研究最高可获支持1000万元、优质企业每年最高可获500万元产业用房租赁补贴。“人才链”多方合作中国医药创新大会永久会址落户龙岗人才是第一资源,龙岗区立足深圳辐射全球,积极与国家级协会资源、国内外顶尖医院、高校、创新机构链接,联动各方资源开展招才引智、技术对接、创新孵化等合作。活动现场,由中国医师协会指导、《中国医学人文》杂志社主办,以推动解决医药创新中重大难题,国家基础研究和科技创新能力建设为重要使命的“中国医药创新大会”永久地址选定龙岗,这项合作的推进为深圳再添专家智库、临床合作资源,新增活力。同时,龙岗区人民政府相关部门领导与深圳湾生物生态谷所属的欧洲、北京、深圳南山、成都创新中心代表共同上台为创新中心揭牌。回爱民惠正奇医药董事长中国生物医药产业创新与转化联盟副会长复星医药前执行总裁“资金链”助破寒冬政府找市场找资本给企业筑底生物医药行业的融资一直以来都是个难题,而由国信弘盛、龙岗金控联合举办的融资路演对接会给行业带来一股新的热潮,搭建起“双向奔赴”的桥梁,为企业发展找资本蓄力。···同时,宝龙生物药创新发展先导区通过在区外设立联动创新中心,与联合国项目事务署进行深入合作,帮助企业“敲开”了联合国的采购大门,邀请到了联合国项目事务署驻华高级项目官员陆瑞光先生,介绍75亿美金《联合国与国际组织卫生医疗健康产品采购项目》,现场反响热烈。陆瑞光联合国项目事务署高级项目官员目前,深圳龙岗生物医药产业生态大会已成为我市乃至湾区生物医药生态资源对接和集聚的靓丽名片,深圳湾生物生态谷全球范围征集时空合伙人,整合全球资源、汇聚全链条产业要素,全面建设打造国际一流的生物生态谷。·(现场活动照片)
100 项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 深圳市龙岗区人民医院 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2026年02月08日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或

科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用