预约演示
更新于:2026-02-28
Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.)
更新于:2026-02-28
概要
基本信息
在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段终止临床1期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
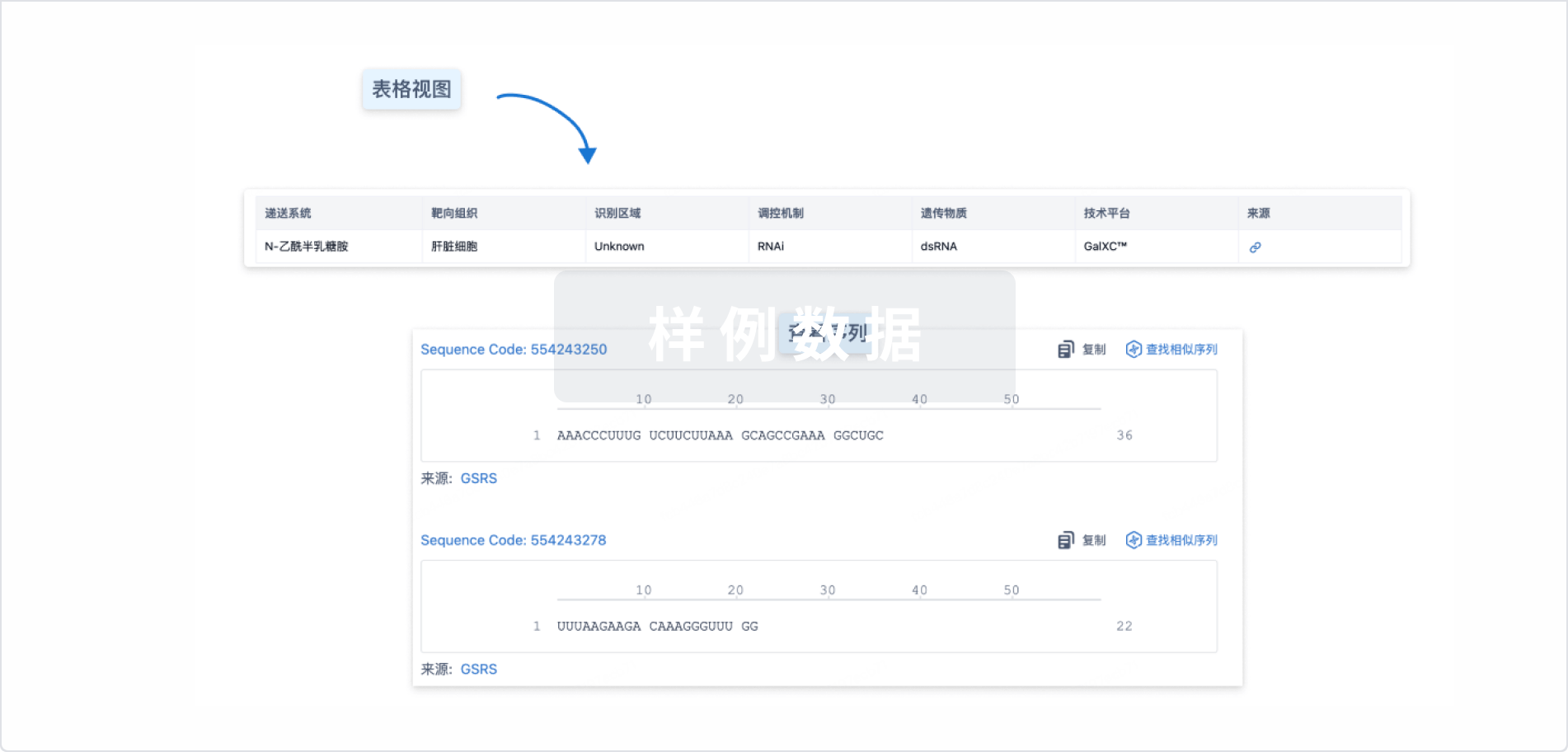
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
关联
100 项与 Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.) 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.) 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.) 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
4
项与 Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.) 相关的新闻(医药)2025-11-05
·儒百生物
上海儒百生物
体外数据优选批次展示
适合实验目录-优选批次
01
ADCC -PBMC Kill SKOV3-LDH
•E:T=20:1
•时间:4h
•对照阳参: Anti-HER2 (Trastuzumab)
•对照阴参: Anti-hel human IgG1
•优选批次最大杀伤率窗口均>50%
•库存>3000 million
ADCC -PBMC Kill Raji-LDH
•E:T=20:1
•时间:4h
•对照阳参: Anti-CD20 (Rituximab)
•对照阴参: Anti-hel human IgG1
•优选批次最大杀伤率窗口>50%
02
ADCP -(冷冻巨噬细胞)-FACS
03
CDC - Isatuximab Kill Daudi/RituximabKill Raji-FACS
•对照阳参:Anti-CD20 (Rituximab) /CD38(Isatuximab)
•对照阴参: Anti-hel human IgG1
•窗口Window> 40%为合适批次
04
TDCC-PBMC Kill H929-LDH
•E:T=10:1
•时间:24h
•对照阳参: Anti-CD3xBCMA (Teclistmab)
•对照阴参: Anti-hel human IgG4
•NCI-H929 (BCMA 阳性细胞系)
•优选批次最大杀伤率窗口均>60%
•库存>3000 million
TDCC-PBMC Kill SHP77-LDH
•E:T=10:1
•时间:24h
•对照阳参:Anti-CD3xDLL3(Tarlatamab/AMG757)
•对照阴参:Anti-hel human IgG4
•优选批次最大杀伤率窗口均>40%
•库存>3000 million
05
SEB
•对照阳参:
Anti-human PD-1 (Pembrolizumab)
Anti-human PD-L1 (Atezolizumab)
•对照阴参: Anti-hel human IgG4(S228P)
•阳参因子释放量为相对应阴参达到2倍以上选为合适批次。
06
T细胞活化及因子释放
• 分选T细胞后经CD3/CD28 activator(stemcell)W/ IL-2 活化3d检测marker变化及细胞因子(IFN-γ,TNFα,IL-6)释放;
• 刺激后有显著CD25/CD69表达变化及相应的细胞因子释放量显著变化选为合适批次;
T细胞增殖
• 分选T细胞后经CD3/CD28 activator +IL-2 活化4d检测CFSE变化;经刺激增殖后有显著CFSE代数变化选为合适批次
07
Other (PD-1expression)
• PBMC经CD3/CD28 Dynabeads 活化3天后检测CD4 CD8T中PD-1的表达变化以及CD25变化复证细胞活化情况
08
pDC高含量批次
Treg高含量批次
VV批次
感谢观看,若有批次测试或采购需求,请随时联系我司销售。
上海儒百生物科技有限公司
地址:上海市松江区云振路410号3号楼
网址:https://www.schbio.com/
电话:191-2182-6626
END
关于儒百
上海儒百生物科技有限公司,成立于 2016 年,作为上海市高新技术企业及专精特新中小企业,致力于为肿瘤及自免疾病领域创新疗法研发提供全方位服务。
公司专注于附加细胞功能学验证的体外药效服务和临床采集服务,历经多年发展,凭借在冷冻细胞活性控制、批间差稳定性控制、产品质检标准化流程以及不同批次功能验证准确性等方面的显著优势,与国内大型外资研发中心、医药公司、创新型生物制药公司和大型 CRO 广泛合作,服务涵盖抗体药体外药效验证、人源化小鼠模型构建、细胞治疗前期概念及工艺验证等前期研发领域。
公司产品丰富,包括 PBMC 及其亚型细胞、leukopak 单采血采集服务、进口 CB CD34+细胞、高效存储液氮罐、钙流检测试剂盒及CTG检测试剂盒等。
关于乐纯
上海乐纯生物技术股份有限公司成立于2011年,十余年来,始终坚持以技术创新为驱动,致力于为生物制药等行业提供优质、创新的上游耗材及工艺技术服务,是中国领先的生物工艺整体解决方案提供商。同时,以外延式增长路径并入格氏流体、康晟生物、斯坦利思等优秀品牌,持续拓展产品广度与服务深度。当前业务范围覆盖一次性使用系统、过滤纯化、细胞培养、洁净室污染控制、药物发现与研究工具品牌五大系列。使命愿景:以技术创新为驱动,提供高品质的生物工艺解决方案,致力于成为全球生物制药企业最信赖的合作伙伴。
临床结果抗体药物偶联物多肽偶联药物临床研究
2025-07-14
·抗体圈
摘要:本文深入解析了一项关于利用机器学习(ML)技术从 CHO 细胞培养的培养基标记预测抗体N - 糖基化质量的重要研究。研究通过对 12 种不同培养条件下的 Anti-HER2 抗体 fed-batch 生物反应器细胞培养进行分析,筛选出 18 种关键培养基标记,构建的机器学习模型在预测 N - 糖基化相关的岩藻糖基化、半乳糖基化、甘露糖基化和唾液酸化丰度方面表现优异(回归分析相关系数 0.80-0.92,分类分析 AUC 75.0-97.2)。该研究不仅为生物制造过程中抗体质量的监测与优化提供了新方法,还展示了机器学习在生物工艺开发中的巨大潜力,对提升治疗性单克隆抗体(mAb)的生产效率和质量控制具有重要意义。一、研究背景:N - 糖基化与抗体质量的密切关联在治疗性单克隆抗体(mAb)的研发与生产中,N - 糖基化是影响其质量的关键因素。N - 糖基化是指在蛋白质合成过程中,寡糖链(由多个单糖组成)通过酰胺键连接到天冬酰胺氨基酸的酰胺氮上的过程,这一过程发生在细胞的内质网 - 高尔基体复合体中,受糖基转移酶效率、核苷酸糖供体可用性以及糖基化生物合成途径的代谢前体或辅因子等多种因素影响。对于 mAb 而言,N - 糖基化主要发生在 CH2 结构域,是决定抗体治疗 efficacy(疗效)的关键质量属性(CQA)。根据结构差异,mAb 相关的 N - 糖基可分为岩藻糖基化、半乳糖基化、甘露糖基化和唾液酸化四大类,每一类都对抗体的免疫原性、半衰期和药代动力学等特性有重要影响。例如,半乳糖基化影响补体活性,岩藻糖基化影响抗体依赖的细胞毒性(ADCC),甘露糖基化影响抗体的清除速率,而唾液酸化则与糖蛋白药物的药代动力学和药效动力学特性相关。然而,糖基化生物合成途径极为复杂,在生物制造过程中难以控制。细胞培养的诸多参数,如培养基成分、pH、温度等,都可能通过改变宿主细胞代谢而影响 N - 糖基化的类型、复杂性、分支和拓扑结构。因此,如何通过调控培养条件实现对 N - 糖基化模式的精准控制,成为生物制造领域的重要课题。二、研究目标:利用机器学习预测 N - 糖基化质量传统的生物工艺优化多依赖于多变量数据分析(MVDA),如偏最小二乘回归分析和主成分分析等,但这些方法在处理复杂非线性关系时存在局限性。随着高通量实验技术的发展,大量可收集的数据为机器学习(ML)的应用提供了可能。本研究的核心目标是探索利用机器学习技术,基于 CHO 细胞培养的培养基相关变量(称为培养基标记)来预测 N - 糖基化类型的丰度。研究团队希望通过构建高效的机器学习模型,实现从细胞外培养基特性推断 N - 糖基化关键质量属性的目的,为生物制造过程中的工艺开发、上下游处理提供新的工具。三、实验设计:全面的数据采集与模型构建3.1 细胞培养与实验条件研究使用CHO-K1 细胞系生产 Anti-HER2 生物类似药(IgG1 亚型),采用 Ambr250 生物反应器进行 14 天的 fed-batch 培养。实验设置了 12 种不同的培养条件,通过改变pH(6.9-7.3)、溶解氧(dO₂)(30-50% 空气饱和度)、温度(是否在第 5 天从 37℃降至 33℃)以及两种商业培养基(Media platform 1 和 Media platform 2)来引入 N - 糖基化的变异性(表 1)。每个条件设置 3 个生物学重复,培养周期为 12 天(第 3-14 天),最终获得了包含 1296 个样本的大型数据集。3.2 糖基化分析与代谢物检测糖基化分析:通过 Protein A HP spin trap 柱纯化细胞上清中的抗体,使用重组 PNGase F 释放 N - 糖基,并用 8 - 氨基芘 - 1,3,6 - 三磺酸(APTS)标记,最后通过毛细管电泳(CE) 结合激光诱导荧光检测(激发 488nm,发射 520nm)对 N - 糖基进行鉴定和定量,计算每种糖基的相对丰度(占所有检测糖基的百分比)。代谢物分析:收集废弃培养基,经 10kDa 分子量截留膜过滤后,采用超高效液相色谱(UPLC)联用 QExactive Orbitrap 质谱仪进行分析,定量葡萄糖、乳酸、20 种氨基酸以及 145 个其他峰特征,并通过计算伪细胞消耗率(即培养基标记)作为模型输入。3.3 模型构建与评估研究选择随机森林(RF) 算法构建机器学习模型,因其训练效率高、适合小样本且具有非参数特性。同时,采用偏最小二乘回归(PLRS)作为 MVDA 方法进行对比。模型输入包括 8 类基础变量(如温度、pH、葡萄糖等)、20 种氨基酸、18 种筛选出的培养基标记等,通过 8 种不同的输入组合优化模型。评估指标包括:回归分析:皮尔逊相关系数(CC)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE);分类分析:受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)。采用留一法交叉验证(LOOCV) 评估模型性能,即每次用两个生物学重复训练,一个验证,最终取平均值。四、关键发现:18 种培养基标记的核心作用4.1 糖基化特征与培养基标记筛选通过毛细管电泳分析,研究共鉴定出 16 种主要 N - 糖基,并将其归为岩藻糖基化、半乳糖基化、甘露糖基化和唾液酸化四大类(图 1)。结果显示,不同培养条件和生物学重复间的糖基化丰度存在显著差异,这为模型训练提供了足够的变异性。通过相关性分析,研究从 167 个质谱峰中筛选出 18 种培养基标记(MMs),这些标记的变异系数(CV)<30%,且与至少一种糖基化类型的相关系数(CC)≥0.6。值得注意的是,这些标记主要包括 3 种核苷酸衍生物、3 种核苷酸和 4 种核苷酸糖(图 2),而传统认为重要的基础变量(如 pH、温度、葡萄糖、乳酸)和大多数氨基酸与糖基化的相关性较低(CC<0.6),仅 L - 谷氨酸的相关性达到 0.6。4.2 机器学习模型的优异性能回归分析:随机森林模型在使用 18 种培养基标记时表现最佳,岩藻糖基化、半乳糖基化、甘露糖基化和唾液酸化的相关系数(CC)分别为 0.94、0.84、0.94 和 0.80,显著高于 MVDA 方法(图 3)。其中,半乳糖基化的预测性能提升最为明显(RF 的 CC 为 0.84,MVDA 为 0.52),这得益于机器学习对非线性关系的捕捉能力。分类分析:对于预测糖基化异常值(如半乳糖基化 < 30%),随机森林模型的 AUC 显著高于 MVDA,部分阈值下 AUC 可达 93.79(图 4)。此外,研究发现加入 18 种培养基标记后,无论是 RF 还是 MVDA 模型的性能均显著提升,而使用所有 173 个特征时性能反而下降,可能因过拟合或维度灾难导致(图 5)。五、应用价值:推动生物制造的数字化与智能化5.1 工艺开发与质量控制该研究表明,通过监测 18 种培养基标记,可间接推断 N - 糖基化关键质量属性,无需直接检测糖基化,这将显著降低检测成本和时间,便于在上游生物工艺中实时调整培养条件,确保抗体质量稳定。例如,分类模型可快速识别半乳糖基化水平过低的批次,优先进行下游纯化,提高生产效率。5.2 优化 feeding 策略利用模型模拟不同培养基标记变化对糖基化的影响,可开发优化的 feeding 算法,通过调控核苷酸糖前体等关键成分,定向提高目标糖基化水平(如降低岩藻糖基化以增强 ADCC 活性),这与之前通过补充尿苷、锰离子等调控糖基化的研究思路一致,但更具精准性和系统性。5.3 实时监测与数字化制造若能开发出针对 18 种培养基标记的实时检测技术(如实时质谱联用微流控装置),可实现糖基化质量的在线监测,与拉曼光谱等方法形成互补,推动生物制造的数字化转型,符合质量源于设计(QbD) 理念,满足 FDA 等监管机构对工艺可追溯性和可控性的要求。六、研究展望与局限性6.1 拓展应用范围目前研究仅限于 CHO 细胞生产的 Anti-HER2 抗体,未来需验证该方法在其他细胞系(如 HEK293)和抗体类型中的适用性,以确认其普适性。此外,可尝试更复杂的机器学习算法(如深度学习),结合代谢网络模型,进一步提升预测精度。6.2 解析分子机制虽然 18 种培养基标记与糖基化密切相关,但其中部分标记的具体身份和作用机制尚未明确。深入研究这些标记参与的代谢途径(如核苷酸糖合成),将有助于从分子层面理解糖基化调控规律,为培养基优化提供理论依据。6.3 技术挑战实时检测 18 种培养基标记的技术尚未成熟,需要开发更高效的微型化检测装置和自动化数据分析流程,才能真正实现工业级别的实时质量监控。识别微信二维码,添加抗体圈小编,符合条件者即可加入抗体圈微信群!请注明:姓名+研究方向!本公众号所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系(cbplib@163.com),我们将立即进行删除处理。所有文章仅代表作者观点,不代表本站立场。
抗体药物偶联物
2024-07-01
Pertuzumab biosimilar developed by Zydus is a critical treatment for HER2 positive breast cancer and is being launched jointly by Zydus and Dr. Reddy’s in India
The product will be marketed by Zydus under the brand name
Sigrima
™
while Dr. Reddy’s will market it under the brand name
Womab
®
.
AHMEDABAD & HYDERABAD, India I June 28, 2024 I
Zydus Lifesciences Limited (including its subsidiaries/affiliates hereafter referred to as “Zydus”) a discovery-driven global lifesciences company and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., (BSE: 500124 | NSE: DRREDDY | NYSE: RDY | NSEIFSC: DRREDDY, along with its subsidiaries hereafter referred to as “Dr. Reddy’s”), a global pharmaceutical company, announced the execution of a licensing agreement to co-market Pertuzumab biosimilar in India. Pertuzumab is a critical treatment for HER2 positive breast cancer patients. The biosimilar has been developed in-house by the research team at the Zydus Research Centre (ZRC).
Under the terms of this agreement, Dr. Reddy’s will receive semi-exclusive rights from Zydus to co-market the product in India. The product will be marketed by Zydus under the brand name Sigrima™. Dr. Reddy’s will market it under the brand name Womab®. Zydus will receive upfront licensing income and is eligible to receive milestone income based on achievement of pre-defined milestones.
Speaking on the development, spokesperson from Zydus Lifesciences Ltd., said, “Our basket of cancer care therapies which includes cytotoxic, supportive and targeted drugs, has had a significant impact on patient survival and the quality of life. We are committed to providing comprehensive care for HER2-positive patients and with the launch of this critical drug, we will be offering all the three essential drugs, SigrimaTM, Pertuzumab biosimilar, VivitraTM the largest selling trastuzumab biosimilar and UjviraTM the world’s first antibody drug conjugate biosimilar of trastuzumab emtansine. Together, these treatments represent a significant advancement in HER2-targeted therapy. We are pleased to join hands with Dr. Reddy’s to expand the access to this novel medicine.”
Spokesperson from Dr. Reddy’s, said, “Oncology is a key therapy area for us, and we are working to offer a diverse portfolio of offerings from standard of care, innovations in formulations, access to novel medicines and beyond-the-pill initiatives. We are happy to collaborate with Zydus to make this breast cancer drug available to patients in India. HER2 positive breast cancer patients require access to a combination of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab, along with chemotherapy. We already offer biosimilar Trastuzumab (Hervycta®). With this product, we will be able to provide the complete standard of care to HER2 positive breast cancer patients in India.”
Human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) is a protein that makes cells grow and divide. Some cancers have large amounts of HER2 protein and are known as HER2-positive cancers. These cancers tend to spread fast if not treated optimally. There is an estimate of over 2,30,000 new cases of breast cancer in 2025 and around 25% of these can be HER2-positive. Pertuzumab is an anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody (mAB) and it works by locking onto HER2 on the cancer cells, supressing HER2-mediated cell proliferation. Pertuzumab is recommended for both early and late stage HER2-positive breast cancers in combination with other drugs such as trastuzumab and chemotherapy. Its addition helps in different ways like shrinking the cancerous tumour, making the surgery less extensive, conserving the breast tissue, delaying the cancer coming back, halting the cancer spread, increasing the lifespan etc. Every HER2 positive patient needs to have access to combination of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab, however, less than 5% patients have access to the same.1 With the launch of Pertuzumab in India, many more patients in need can benefit from the access to combination therapy.
Appendix:
1.
Breast cancer incidence:
https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.35188#:~:text=Breast%20cancer%20is%20the%20most%20common%20cancer%20in%20India%2C%20accounting,estimated%20216%2C108%20cases%20by%202022.&text=The%20age%2Dstandardized%20incidence%20rate,over%20the%20past%2026%20years
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in India, accounting for 28.2% of all female cancers, with an estimated 216,108 cases by 2022
HER2 positive: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-62618-3
Hormone receptor positive/HER2 negative, triple negative (TNBC) and hormone receptor any/HER2 positive cases were 55.2%, 24.2% and 20.6%, respectively. Access of Pertuzumab today: IPSOS Dec’23 Data
About Zydus:
Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. with an overarching purpose of empowering people with freedom to live healthier and more fulfilled lives, is an innovative, global lifesciences company that discovers, develops, manufactures, and markets a broad range of healthcare therapies. The group employs 26,000 people worldwide, including 1,400 scientists engaged in R & D, and is driven by its mission to unlock new possibilities in lifesciences through quality healthcare solutions that impact lives. Zydus has been actively discovering and developing New Chemical Entities (NCEs) novel biologicals, several biosimilars and vaccines as a part of its innovation pipeline. Over the last decade, Zydus has introduced several innovative, first-in-class products in the market for treating unmet healthcare needs with vaccines, therapeutics, biologicals and biosimilars. The group aspires to transform lives through path-breaking discoveries. For more details visit
www.zyduslife.com
About Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd:
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd. (BSE: 500124, NSE: DRREDDY, NYSE: RDY, NSEIFSC: DRREDDY) is a global pharmaceutical company headquartered in Hyderabad, India. Established in 1984, we are committed to providing access to affordable and innovative medicines. Driven by our purpose of ‘Good Health Can’t Wait’, we offer a portfolio of products and services including APIs, generics, branded generics, biosimilars and OTC. Our major therapeutic areas of focus are gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, diabetology, oncology, pain management and dermatology. Our major markets include – USA, India, Russia & CIS countries, China, Brazil, and Europe. As a company with a history of deep science that has led to several industry firsts, we continue to plan and invest in businesses of the future. As an early adopter of sustainability and ESG actions, we released our first Sustainability Report in 2004. Our current ESG goals aim to set the bar high in environmental stewardship; access and affordability for patients; diversity; and governance. For more information, log on to:
www.drreddys.com
.
SOURCE:
Dr. Reddy’s
引进/卖出上市批准
100 项与 Anti-HER2 ribozyme(Merck & Co., Inc.) 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳腺癌 | 临床1期 | 加拿大 | - | |
| 乳腺癌 | 临床1期 | - | - | |
| 乳腺癌 | 临床1期 | - | - | |
| 卵巢癌 | 临床1期 | 加拿大 | - | |
| 卵巢癌 | 临床1期 | - | - | |
| 卵巢癌 | 临床1期 | - | - |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

