预约演示
更新于:2026-01-24
MRG-229
更新于:2026-01-24
概要
基本信息
药物类型 miRNA |
别名 MRG 229、MRG-229 |
作用方式 抑制剂 |
作用机制 MicroRNA MIR29 family inhibitors |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
非在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
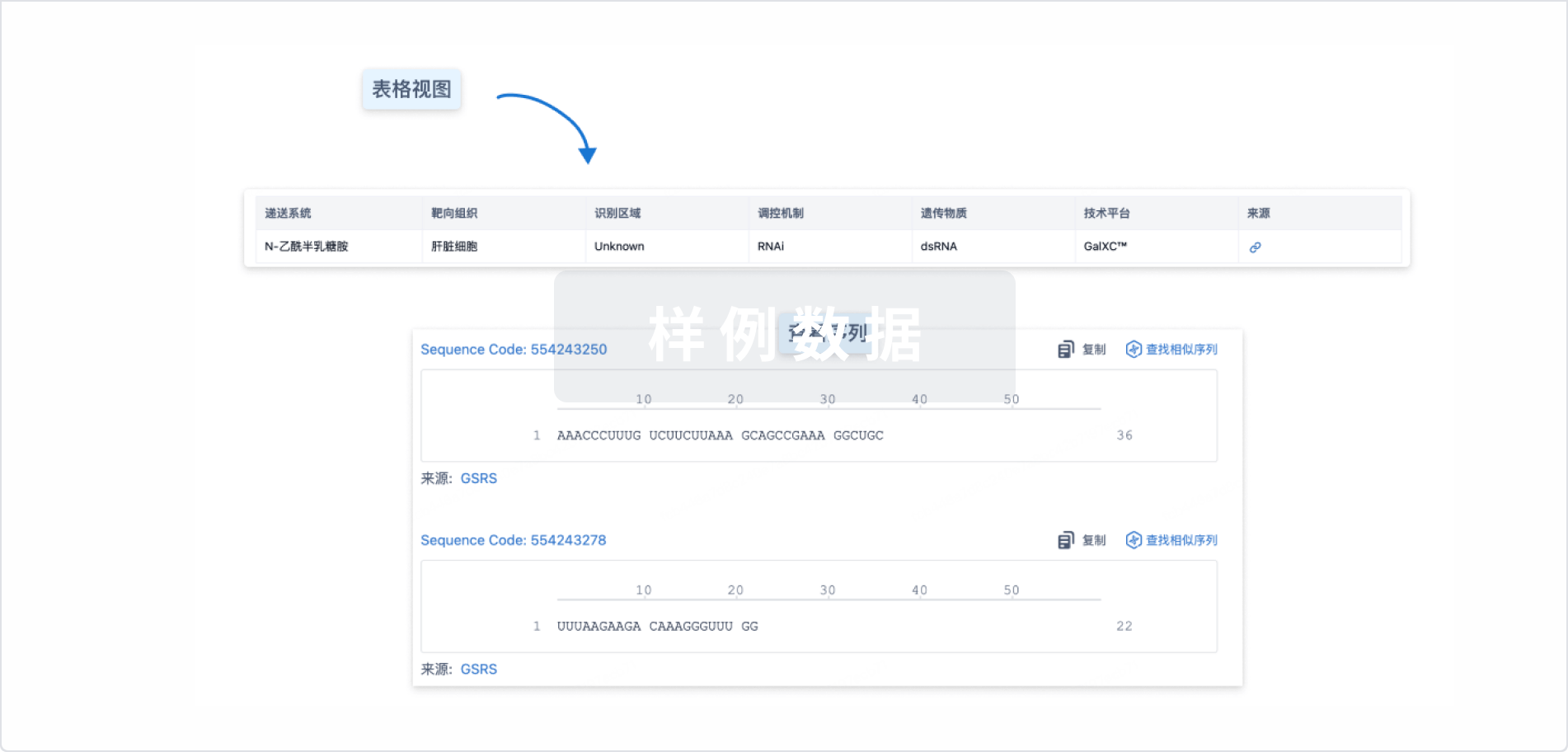
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
关联
100 项与 MRG-229 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 MRG-229 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 MRG-229 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1
项与 MRG-229 相关的文献(医药)2022-11-01·EBioMedicine
A lung targeted miR-29 mimic as a therapy for pulmonary fibrosis
Article
作者: Jenkins, Gisli ; Ian, Steward ; Braybrooke, Rebecca ; Dickinson, Brent ; Aurelien, Nachelle ; Chioccioli, Maurizio ; Kaminski, Naftali ; Ding, Shuizi ; Ahangari, Farida ; Pestano, Linda ; Johnson, Simon R ; Sauler, Maor ; DeIuliis, Joseph ; Herazo-Maya, Jose ; Saini, Gauri ; Roy, Subhadeep ; Montgomery, Rusty L ; Rigby, Kevin ; Yu, Guying ; Newell, Rachel
BACKGROUND:
MicroRNAs are non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate gene networks. Previously, we reported that systemically delivered miR-29 mimic MRG-201 reduced fibrosis in animal models, supporting the consideration of miR-29-based therapies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
METHODS:
We generated MRG-229, a next-generation miR-29 mimic based on MRG-201 with improved chemical stability due to additional sugar modifications and conjugation with the internalization moiety BiPPB (PDGFbetaR-specific bicyclic peptide)1. We investigated the anti-fibrotic efficacy of MRG-229 on TGF-β1 treated human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs), human precision cut lung slices (hPCLS), and in vivo bleomycin studies; toxicology was assessed in two animal models, rats, and non-human primates. Finally, we examined miR-29b levels in a cohort of 46 and 213 patients with IPF diagnosis recruited from Yale and Nottingham Universities (Profile Cohort), respectively.
FINDINGS:
The peptide-conjugated MRG-229 mimic decreased expression of pro-fibrotic genes and reduced collagen production in each model. In bleomycin-treated mice, the peptide-conjugated MRG-229 mimic downregulated profibrotic gene programs at doses more than ten-fold lower than the original compound. In rats and non-human primates, the peptide-conjugated MRG-229 mimic was well tolerated at clinically relevant doses with no adverse findings observed. In human peripheral blood from IPF patients decreased miR-29 concentrations were associated with increased mortality in two cohorts potentially identified as a target population for treatment.
INTERPRETATION:
Collectively, our results provide support for the development of the peptide-conjugated MRG-229 mimic as a potential therapy in humans with IPF.
FUNDING:
This work was supported by NIH NHLBI grants UH3HL123886, R01HL127349, R01HL141852, U01HL145567.
1
项与 MRG-229 相关的新闻(医药)2024-03-13
·药时代
前言在21世纪初,人类基因组计划完成后,人们发现许多疾病是由基因突变导致功能蛋白表达不足引起的。然而,在药物开发中,开发具有抑制或拮抗作用的药物更容易。随着大规模重组蛋白生产和纯化技术的创新,蛋白质替代疗法,即重组蛋白在临床上取得了成功,如治疗糖尿病的胰岛素。然而,这种方法主要适用于分泌的蛋白质或酶,并且受到这些分子复杂的药代动力学和成本相关问题的阻碍。此外,合成蛋白不太可能完全代表由选择性剪接、翻译后修饰和其他调节机制引起的蛋白质内源性功能的多样性。近年来,多种基于核酸的治疗(NBT)方式已成为内源性基因表达的有效和特异性激活剂。与基因治疗补充基因表达的方法不同,RNA靶向疗法通过选择性调节内源性RNA介导的细胞机制(如转录、剪接、翻译、mRNA稳定性和亚细胞定位)增强蛋白质生产的能力。目前,美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)和欧洲药品管理局已经批准了几种靶向剪接机制以调节突变外显子的疗法。这些方法可以特异性和可控地增加编码和非编码基因的表达,降低开发和制造成本,从而增加可治疗疾病的范围。基于已证明的治疗潜力和巨大的未满足的医疗需求,NBT在未来将迎来更加快速的发展。蛋白表达上调的生物学治疗性蛋白的上调可以通过调节细胞中蛋白质生产的任何阶段的生物过程来实现,包括转录、剪接、翻译或翻译后修饰。由于这些过程中的许多涉及DNA或mRNA,并由ncRNA网络调节,因此它们特别容易受到NBT的调节。转录激活是增加蛋白质表达丰度研究最多的方法。远端增强子元件通过染色体环与活性基因启动子的物理相互作用募集转录因子、染色质修饰物、中介复合体和RNA聚合酶II(Pol II),导致转录激活。启动子区和增强子的双向转录分别产生非编码启动子RNA(pRNA)和增强子RNA(eRNA)。从蛋白质编码基因座、反式作用的长非编码RNA(lncRNA)、pRNA和eRNA的反义链转录的天然反义转录物(NAT)可以对靶基因进行表观遗传修饰和转录调控。NAT的一个关键特征是,它们可以特异性地以顺式或反式的方式调节其正义基因的转录、RNA加工和翻译。此外,NAT还具有多种调节功能,包括吸附miRNA和与mRNA配对以提高其稳定性。但它们中的大部分是通过协调抑制因子来抑制其靶基因的表达。因此,用反义寡核苷酸(ASOs)靶向NAT可以导致正义基因的去抑制和蛋白表达的增加。此外,天然存在的修饰核苷酸,如N6-甲基腺苷、5-甲基胞嘧啶、N1甲基腺苷、假尿苷和2′-O-甲基化核糖,发生在mRNA和lncRNA的转录过程中。通过NBTs可以调节这些修饰从而影响转录和蛋白表达。翻译效率还可能受到mRNA结构特征的影响,使用NBTs阻断或增强这些结构的活性可能导致治疗性蛋白表达上调。临床阶段的NBT在过去的5-7年里,NBT经历了爆炸性的增长,其中一些已经获得批准,而其他多种NBT正在进行临床试验中进行探索,下表显示了已获批的NBT。调节拼接的NBT突变引起的RNA剪接异常经常导致非功能转录物被无义介导的降解(NMD)迅速破坏,导致受影响蛋白质的短缺,这是许多疾病的基础。此外,前mRNA的正常选择性剪接可以包含所谓的“有毒外显子”,导致转录物通过NMD快速降解,从而降低蛋白质水平。ASOs与调节剪接事件的前mRNA上的特定序列结合,可以防止突变或天然非生产性转录物的产生,并提高靶蛋白表达水平。Vesleteplirsen(SRP-5051),是针对外显子跳跃治疗的下一个寡核苷酸新药,其针对的是可以使用外显子51跳跃治疗的杜氏进行性肌营养不良(DMD)患者。在一项临床试验(NCT04004065)中,vesleteplirsen治疗导致外显子跳跃增加18倍,肌营养不良蛋白水平增加8倍。然而由于观察到严重的低镁血症,该试验暂时搁置,后来随着对尿液生物标志物和镁补充的扩大监测而恢复。WVE-N531,这是一种新型的全身给药反义寡核苷酸疗法,目前正在15名易发生外显子53跳跃的DMD患者中进行临床试验(NCT04906460)。中期结果表明,该药物的肌肉浓度很高,平均外显子跳跃率为53%。药代动力学数据显示半衰期为25天,这可能支持每月给药。WVE-N531的初步临床结果表明,与亨廷顿舞蹈症项目中的第一代DMD剪接转换NBT和敲低NBT相比,其可能具有药理学改善。在用于治疗其他疾病的剪接调节NBT中,sepofarsen(QR-110)在Leber先天性黑蒙的早期临床试验中显示出阳性结果(NCT03913143)。Sepofarsen靶向CEP290内含子26中的c.2991+1655A>G变体。STK-001是Stoke Therapeutics开发的用于Dravet综合征的SCN1A靶向剪接切换的寡核苷酸,目前正处于I/IIa期临床试验(NCT04442295和NCT04740476)。mRNA的递送与注射纯化蛋白相比,将外源性mRNA引入病变细胞具有几个优势,包括产生的蛋白产物的正确翻译后修饰和亚细胞定位、较低的免疫原性、更简单的制造过程和更低的成本。治疗性mRNA递送技术的代表性临床应用之一是由Translate Bio/Sanofi开发的用于囊性纤维化的CFTR mRNA疗法MRT5005,该疗法在II期临床试验(NCT03375047)中进行了测试。MRT5005由体外转录的、未修饰的CFTR mRNA组成,包裹在脂质纳米颗粒中,经雾化以允许吸入输送到肺部。MRT5005在囊性纤维化患者中的I/II期临床试验的中期结果显示出良好的耐受性。肺功能结果参差不齐,部分患者的ppFEV1没有明显改善,而16毫克剂量组的3名患者从基线到第8天,平均最大增幅为15.7%。由Moderna公司开发的mRNA-3927为丙酸血症患者提供丙酰辅酶A羧化酶亚基α和β的双重mRNAs。在进行的I/II期临床试验(NCT04159103)中,10名患者的耐受性良好,初步数据显示,在疾病的自然过程中发生的临床危机数量有所减少。促进核糖体翻译的小分子NBT与RNA的相互作用是基于它们的序列互补性,而RNA靶向小分子(rSM)靶向RNA的3D结构。使用rSMs调节RNA靶点的优点包括口服可用性,以及在某些情况下的血脑屏障通透性。RIBOTACs是一种类似于蛋白水解靶向嵌合体(PROTACs)进行蛋白酶体降解的小分子机制,其设计了与RNase募集部分相连的rSM,该募集部分可以靶向RNA进行降解,能够上调疾病相关蛋白。有设计团队通过在线计算平台INFORNA鉴定了一种获批的药物,受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂dovitinib是致癌前miR-21的选择性结合物。通过将dovitinib改造为RIBOTAC,这种dovitinib-RIBOTACs能够在小鼠模型中抑制乳腺癌症细胞向肺部的转移。此外,DT-216是治疗弗里德里希共济失调的一种rSM,在I/II期临床试验中(NCT05285540和NCT05573698),DT-216显示出良好的耐受性,单剂量给药后,可使frataxin(FXN)mRNA在24小时内增加1.2至2.6倍。miRNA靶向NBT近年来,miRNA已成为非常吸引力的治疗靶点。合成寡核苷酸已被用于干扰该途径,如miRNA模拟物(promirs)和miRNA阻断剂(antagomirs)。根据miRNA的作用机制,这两种干预类型都可能导致靶蛋白上调。Remlarsen (MRG-201)是一种 miR-29的promirs,研究发现肺部疤痕组织的积累与miR-29的减少有关。因此,创造一种类似miR-29的分子的可能会逆转这种疤痕。然而,由于高毒性,在人类的研究很快终止。随后,miRagen/Viridian开发了新的、改进后的MRG-229分子,他们对该分子进行了化学改进,使其更加稳定,并添加了一种肽,使其能够更有针对性地传递。MRG-229在动物模型中耐受性良好,没有产生任何不良反应。miRNA阻断剂的开发也已经进行了很长时间,但该领域一直受到多次失败的困扰。Regulus停止了RGLS4326的临床试验,RGLS4326抑制miR-17,用于治疗常染色体显性遗传性多囊肾病。然后又开发了下一代候选分子RGLS8429取代,RGLS8429没有观察到RGLS4326的脱靶中枢神经系统事件,目前,正在进行Ib期临床试验(NCT02855268)。另外,在罕见肾脏疾病Alport综合征(NCT05521191)的II期临床试验中,对一种抗miR-21的抗病毒药物lademirsen进行了测试。尽管该药物耐受性良好,但中期无效性分析结果导致研究终止。NBT的优势与挑战NBT的一些优点使其非常适合于治疗许多已知疾病导致的蛋白表达不足。NBT的特点是靶点特异性高,稳定性好,半衰期大大延长(如数周或数月),不用频繁给药。已批准NBT的多项临床试验证明了其良好的耐受性。NBT的开发时间周期短、成本低,可以对快速发展的癌症和罕见遗传疾病进行个性化治疗。然而,与传统的治疗模式相比,NBT也都面临着一些挑战。目前NBT的一个常见缺点是它们无法穿过肠壁或血脑屏障。目前,这个问题可以通过静脉、皮下、脑内、侧脑室或鞘内给药来解决。然而,这些方法是侵入性的,尤其是对中枢神经系统的递送,有一定的可能造成不良影响。因此,需要进行更广泛的研究,以开发化学修饰以及载体的给药技术,从而减少侵入性递送途径。此外,与大多数小分子相比,NBT具有复杂且目前知之甚少的药代动力学和药效学。尽管存在这些限制,但据报道,NBT开发的总体成功率与制药行业的平均水平持平或高于平均水平。对2006年至2015年间进行的7455项药物开发计划的分析表明,进入临床试验的新分子实体药物中只有约6%获得批准。在这项分析中,新型生物制剂的成功率为11.5%。小结最近,NBT的进展为蛋白质表达上调治疗疾病开辟了巨大的新机会。新冠肺炎mRNA疫苗的成功将RNA靶向蛋白上调技术推到聚光灯下,并可能加速该领域的重大突破。基因测序技术的改进,以及NBT在遗传疾病中的可行性所激发的新希望,将导致遗传研究的扩展。人类基因组学的重大进展使已知遗传病因的疾病数量不断增加。而这些都增加了NBT上调蛋白的适用性。随着对疾病基因组学和病理生理学理解的不断发展,以及NBT技术、制造和监管基础设施的改进,NBT的临床应用将不断扩大,为更好地治疗“罕见”疾病和个体化精准医学开辟道路。参考文献:1.Amplifying
gene expression with RNA-targeted therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov.2023
May 30.封面图来源:123rf版权声明/免责声明本文为授权转载文章。本文仅作信息交流之目的,不提供任何商用、医用、投资用建议。文中图片、视频、字体、音乐等素材或为药时代购买的授权正版作品,或来自微信公共图片库,或取自公司官网/网络,部分素材根据CC0协议使用,版权归拥有者,药时代尽力注明来源。如有任何问题,请与我们联系。衷心感谢!药时代官方网站:www.drugtimes.cn联系方式:电话:13651980212微信:27674131邮箱:contact@drugtimes.cn全球首款端粒酶抑制剂能否获批?为什么这场ODAC会议值得关注默克终止BTK抑制剂开发!啃不动“自免”的骨头,肝损伤风险谁来验证……Ferring首席科学家杨翼博士:肥胖症疫苗离我们还有多远?点击这里,欣赏更多精彩内容!
信使RNA寡核苷酸基因疗法核酸药物
100 项与 MRG-229 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特发性肺纤维化 | 临床前 | 美国 | 2022-11-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

