预约演示
更新于:2026-01-31
SPX-101(SparX)
更新于:2026-01-31
概要
基本信息
原研机构 |
非在研机构- |
最高研发阶段临床1期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
结构/序列
Sequence Code 565455567VL

Sequence Code 565455577VH

关联
1
项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的临床试验NCT05231733
A Phase 1, Open-label Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of an Anti-Claudin 18.2 Antibody SPX-101 in Patients With Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors
A Phase 1, Open-label Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of an anti-Claudin 18.2 Antibody SPX-101 in Patients with Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors
开始日期2022-05-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
5
项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的文献(医药)2022-02-01·Talanta2区 · 化学
Visualization of peroxynitrite in cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress by an activatable probe
2区 · 化学
Article
作者: Ye, Yong ; Cao, Wenbo ; Li, Zipeng ; Han, Xiaojing ; Zhao, Fangfang ; Li, Jinsa ; Liu, Jianfei ; Peng, Shuxin
Oxidative stress is considered to be one of the main contributors of cyclophosphamide (CP)-induced toxicity, and the generation of free radicals will cause the interruption of multiple signal transduction pathways. Peroxynitrite (ONOO-) has strong oxidation and nitrification ability and is considered as an indirect indicator of oxidative stress. Therefore, it is necessary to design a fluorescent probe that can detect ONOO- and monitor CP-induced oxidative stress during chemotherapy. Herein, we synthesized a lipid droplet targeting fluorescent probe SX-1 based on triphenylamine-benzoindocyanine. When ONOO- is added to the probe SX-1, the CC bond in the probe is broken, thereby releasing fluorescence. The good spectral response characteristics enable SX-1 to successfully track the fluctuations of ONOO- in living cells. Most importantly, we provided the first visual evidence that the level of ONOO- in HeLa cells was up-regulated under CP induction. All results indicated that SX-1 has great potential in detecting drug-induced ONOO-, and provided a new detection tool for a deeper understanding of drug-induced organism injury.
2017-09-15·American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine1区 · 医学
SPX-101 Is a Promising and Novel Nebulized ENaC Inhibitor
1区 · 医学
Article
作者: Lennox, Alison ; Myerburg, Mike M.
A discussion on SPX-101 as a therapeutic agent to reduce epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity in the cystic fibrosis airway.In this issue of the Journal, Scott and colleagues (pp. 734-744) report on the development of SPX-101, a potential peptide therapeutic that has been derived from S18 to stabilize and optimize the peptide for nebulization.
2011-11-01·Journal of applied microbiology3区 · 生物学
New exoelectrogen Citrobacter sp. SX-1 isolated from a microbial fuel cell
3区 · 生物学
Article
作者: Xu, S. ; Liu, H.
AIMS:
Isolation, identification and characterization of a new exoelectrogenic bacterium from a microbial fuel cell (MFC).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Exoelectrogenic bacterial strain SX-1 was isolated from a mediator-less MFC by conventional plating techniques with ferric citrate as electron acceptor under anaerobic condition. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rDNA sequence revealed that it was related to the members of Citrobacter genus with Citrobacter sp. sdy-48 being the most closely related species. The bacterial strain SX-1 produced electricity from citrate, acetate, glucose, sucrose, glycerol and lactose in MFCs with the highest current density of 205 mA m(-2) generated from citrate. Cyclic voltammetry analysis indicated that membrane-associated proteins may play an important role in facilitating the electrons transferring from bacteria to electrode.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first study that demonstrates that Citrobacter species can transfer electrons to extracellular electron acceptors. Citrobacter strain SX-1 is capable of generating electricity from a wide range of substrates in MFCs.
SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY:
This finding increases the known diversity of power generating exoelectrogens and provided a new strain to explore the mechanisms of extracellular electron transfer from bacteria to electrode. The wide range of substrate utilization by SX-1 increases the application potential of MFCs in renewable energy generation and waste treatment.
3
项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的新闻(医药)2025-06-11
·靶点圈
01CLDN18.2的靶点概述CLDN家族的结构与功能人类Claudin(CLDN)基因家族包含24个基因,编码26种蛋白,均为跨膜蛋白,调控细胞极性和屏障功能。CLDN蛋白通过胞外环(ECL)和胞内结构域与ZO-1等蛋白相互作用,动态调控细胞运输与降解。其表达水平有组织异质性的,不同的组织表达不同CLDN蛋白,同一组织中也可能表达多种。图1 CLDN蛋白的作用机制及靶向治疗表1 人类CLDN基因家族及在每个器官中的分布CLDN18的分子特性与亚型差异CLDN18基因位于3q22,由6个外显子和5个内含子组成。通过外显子1a和1b的可变剪接形成CLDN18.1和CLDN18.2两种亚型。二者在结构上存在一定差异,这也导致它们在组织表达和功能上有所不同。图2 CLDN18基因的结构示意图CLDN18.1(UniProt ID: P56856):表达组织:主要表达于肺组织。功能:参与肺上皮细胞的紧密连接功能,维持肺组织的屏障完整性,敲除会导致肺泡液体清除异常。在肺腺癌中表达下调,具有抑癌作用。CLDN18.2(UniProt ID: Q5XG92):表达组织:主要表达于胃黏膜上皮。功能:参与胃上皮细胞的紧密连接功能,调控离子通透性,维持胃黏膜屏障,缺失会引发炎症。在胃癌中表达下调,但在胰腺癌、食管癌等异位激活,促进肿瘤进展。CLDN18.2的结构CLDN18.2是一种四次跨膜蛋白,分子量在20-27kDa之间。由四个跨膜域(TMDs)、两个细胞外环(ECL1和ECL2)以及N端的短细胞质段和C端的细胞质尾部组成,通过与紧密连接蛋白(如ZO-1、Occludin)相互作用,维持细胞极性和细胞间屏障功能。图3 CLDN18.2的结构示意图CLDN18的氨基酸序列◆CLDN18.1:MSTTTCQVVAFLLSILGLAGCIAATGMDMWSTQDLYDNPVTSVFQYEGLWRSCVRQSSGFTECRPYFTILGLPAMLQAVRALMIVGIVLGAIGLLVSIFALKCIRIGSMEDSAKANMTLTSGIMFIVSGLCAIAGVSVFANMLVTNFWMSTANMYTGMGGMVQTVQTRYTFGAALFVGWVAGGLTLIGGVMMCIACRGLAPEETNYKAVSYHASGHSVAYKPGGFKASTGFGSNTKNKKIYDGGARTEDEVQSYPSKHDYV◆CLDN18.2:MAVTACQGLGFVVSLIGIAGIIAATCMDQWSTQDLYNNPVTAVFNYQGLWRSCVRESSGFTECRGYFTLLGLPAMLQAVRALMIVGIVLGAIGLLVSIFALKCIRIGSMEDSAKANMTLTSGIMFIVSGLCAIAGVSVFANMLVTNFWMSTANMYTGMGGMVQTVQTRYTFGAALFVGWVAGGLTLIGGVMMCIACRGLAPEETNYKAVSYHASGHSVAYKPGGFKASTGFGSNTKNKKIYDGGARTEDEVQSYPSKHDYVExtracellular28-80,144-174Helical7-27,81-101,123-143,175-195Cytoplasmic1-6,102-122,196-261CLDN18.2 的生理功能1) 维持胃黏膜屏障:CLDN18.2在正常胃黏膜上皮细胞中表达,它能够控制细胞间分子的流动,通过形成紧密连接,维持胃黏膜的完整性,防止胃酸和消化酶反渗,保护胃组织免受损伤。2) 调节细胞极性和细胞间的黏附作用:CLDN18.2通过调节细胞旁的离子通透性,参与细胞极性的形成和维持,确保上皮细胞的有序排列和功能,有助于维持细胞内环境的稳定。CLDN18.2 的病理功能1) 肿瘤细胞侵袭与转移:CLDN18.2通过改变细胞间的紧密连接,使肿瘤细胞更容易突破基底膜,促进肿瘤细胞的体外增殖和侵袭能力。2) 免疫逃逸:CLDN18.2通过调节肿瘤微环境,抑制T细胞浸润,促进肿瘤免疫逃逸。3) 化疗耐药:CLDN18.2可能通过调节紧密连接通透性,影响化疗药物的渗透,导致化疗耐药。4) 预后不良:CLDN18.2高表达与肿瘤分期晚、淋巴结转移及预后不良显著相关,可作为独立的预后不良指标。02CLDN18.2的表达调控CLDN18.2 的表达1)正常组织:除胃黏膜外,其他正常组织(如胆管、胰腺、肠道)几乎不表达CLDN18.2。2)肿瘤组织:在胃肠道肿瘤(包括胃癌、胃食管交界癌、胰腺癌、结直肠癌)中广泛表达,且在转移灶中持续表达。在胆管癌(CCA)中也有表达,肝内胆管癌(iCCA)中阳性率约43%,肝外胆管癌(eCCA)及胆管乳头状瘤(IPNB)中阳性率超80%。在其他肿瘤中(如非小细胞肺癌、乳腺癌、头颈癌、支气管癌等)亦有表达。3)检测方法:目前主要通过免疫组化(IHC)检测组织样本中CLDN18.2的表达,但存在异质性局限。CLND18.2的表观遗传调控1)甲基化:启动子CpG岛甲基化抑制CLDN18.1转录,CREB转录因子结合受阻导致CLDN18.2沉默。图4 CpG岛的甲基化状态和CLDN18基因表达2)miRNA调控:miR-1303和miR-767-3p通过结合3’-UTR抑制CLDN18表达,影响肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭。图5 miRNA调节CLDN18的表达CLDN18.2 的信号通路调控机制1)PKC/ERK/MAPK通路:PMA激活PKC和ERK/MAPK,通过AP-1转录因子增强CLDN18.2转录。图6 PKC通路和ERK/MAPK通路调节CLDN18.2表达2)HER2/HER3通路:IL-1β通过激活HER2/HER3信号下调CLDN18,参与肺屏障损伤。图7 HER2/HER3信号通路的激活及其激活后的影响CLDN18.2在肿瘤中的双重作用1)抑癌作用:在胃癌和肺腺癌中,CLDN18.2通过抑制IGF-1R/AKT、YAP/TAZ通路抑制肿瘤生长,其缺失与幽门螺杆菌感染及肿瘤进展相关。2)促癌作用:CLDN18.2在胰腺癌、胆管癌等异位表达时,通过EGFR/ERK正反馈loop促进细胞增殖和侵袭,与癌前病变形成相关。03CLDN18.2的靶向治疗CLDN18.2作为治疗靶点的优势1)肿瘤特异性:正常组织中表达受限,仅在肿瘤细胞表面异常暴露,可减少脱靶毒性,符合理想靶点的“肿瘤特异性”要求。2)可及性与药物设计:细胞外结构域(ECL)可被抗体识别,触发抗体依赖细胞毒性(ADCC)和补体依赖细胞毒性(CDC),便于开发靶向药物。图8 用于靶向和破坏肿瘤细胞的四种不同策略单克隆抗体(mAbs)◆ Zolbetuximab(佐妥昔单抗):首个获批的CLDN18.2靶向IgG1嵌合单抗,能特异性结合CLDN18.2,通过ADCC和CDC杀伤肿瘤细胞。III期试验(SPOTLIGHT、GLOW)表明,联合奥沙利铂或CAPOX化疗可显著延长CLDN18.2阳性晚期胃癌/胃食管交界癌患者的总生存期(OS)和无进展生存期(PFS),但客观缓解率(ORR)提升有限,常见不良反应为恶心、呕吐等胃肠道毒性。◆ AB011:人源化IgG1单抗,与化疗有协同效应。I期试验中,联合CAPOX方案展现出良好疗效,疾病控制率达100%,客观缓解率为65.2%,胃肠道毒性显著低于Zolbetuximab,适用于合并基础胃肠道疾病的CLDN18.2阳性实体瘤患者,目前处于早期剂量探索阶段。◆MIL93:基于ADCC机制设计的CLDN18.2单抗,临床前研究显示其抗肿瘤活性优于Zolbetuximab,尤其在对传统抗体耐药的肿瘤模型中效果显著。目前I期试验正在评估其在晚期实体瘤中的安全性和初步疗效。◆TST001(Osemitamab):高亲和力人源化IgG1单抗,增强了FcγRIIIa结合和ADCC活性,对CLDN18.2低至中度表达的肿瘤仍有效。在联合CAPOX一线治疗的I/II期试验中,客观缓解率高达100%,毒性谱较窄,还能上调肿瘤细胞PD-L1表达,正在探索与PD-1抑制剂联合应用。◆ASKB589:人源化IgG1单抗,优化了ADCC效应。I/II期试验显示,单药治疗部分患者肿瘤缩小,联合CAPOX时客观缓解率达75%,疾病控制率100%,常见不良反应有恶心、呕吐。◆NBL-015(FL-301):新一代全人源单抗,具有更强的ADCC和CDC活性,临床前研究显示其对胃癌和胰腺癌细胞株具有选择性杀伤作用。I期试验正在评估其在CLDN18.2阳性晚期实体瘤中的安全性与抗肿瘤活性。◆DR30303:基于人源化单域抗体(VHH)的CLDN18.2靶向抗体,分子量小,肿瘤穿透性强,可增强ADCC效应。临床前研究显示其对CLDN18.2阳性肿瘤具有高效杀伤作用,目前处于I期临床早期阶段。◆ZL-1211:通过激活自然杀伤(NK)细胞增强ADCC效应的单克隆抗体,对CLDN18.2高表达和低表达的胃癌模型均有效。I期试验正在评估其单药及联合治疗的安全性,初步数据显示其具有良好的抗肿瘤潜力。◆SPX-101:I期临床阶段的CLDN18.2单抗,适应症为晚期或耐药实体瘤(排除肺癌),主要用于经治患者的挽救治疗。目前试验聚焦于剂量扩展,旨在确定最大耐受剂量及初步疗效信号。双特异性抗体(BsAbs)与T细胞衔接器(BiTE)◆TJ-CD4B(ABL111):能同时结合肿瘤细胞表面的CLDN18.2与T细胞上的4-1BB,激活T细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤活性。临床前研究显示出强大的抑瘤效果,目前正在开展I期临床试验,旨在评估其在人体中的安全性和初步疗效。◆Q-1802:靶向CLDN18.2和免疫检查点PD-L1。兼具肿瘤靶向与免疫checkpoint抑制双重机制:一方面通过ADCC效应直接杀伤CLDN18.2阳性细胞,另一方面阻断PD-L1/PD-1通路解除免疫抑制。I期试验显示其在实体瘤中具有可控的安全性,初步抗肿瘤活性信号在胃癌和胰腺癌中显现。◆AMG910:属于CD3×CLDN18.2的BiTE,可将T细胞募集至肿瘤局部并激活其杀伤功能。其半衰期延长设计提升了临床应用便利性,目前正处于I期临床试验阶段,聚焦于晚期胃癌/胃食管交界癌患者,主要探索其在人体中的安全性、耐受性及初步抗肿瘤活性。◆ASP2138:是一种不对称的2+1BsAb,含二价CLDN18.2结合域和单价CD3结合域,可选择性识别高表达CLDN18.2的肿瘤细胞,减少脱靶毒性。I期试验正在胃癌和胰腺癌患者中评估其诱导T细胞介导的肿瘤杀伤能力及安全性。◆QLS31905:CLDN18.2×CD3的BsAb,通过结合T细胞CD3激活免疫应答,同时靶向CLDN18.2肿瘤抗原。其独特设计可降低细胞因子释放综合征(CRS)风险,I期试验在中国晚期实体瘤患者中评估安全性、药代动力学及初步疗效。◆ZWB67:CLDN18.2×CD3的BsAb,对CD3的亲和力较低,仅在CLDN18.2阳性细胞存在时激活T细胞,以减少免疫相关不良反应。临床前研究显示其在体外和体内均具有抗肿瘤活性,但目前尚未开展人体临床试验。◆PT886:CLDN18.2×CD47的BsAb,通过阻断CD47“别吃我”信号增强巨噬细胞对肿瘤的吞噬作用,同时靶向CLDN18.2提升特异性。临床前研究显示其在胰腺癌模型中可诱导完全肿瘤消退,且毒性较低,目前尚未进入人体临床试验。◆GB7004-09hu15:四价双特异性抗体(TetraBi),特异性结合CLDN18.2并避免与CLDN18.1交叉反应,采用定点聚乙二醇化技术增强稳定性。临床前数据显示其在CLDN18.2阳性肿瘤模型中有效,目前尚未进入人体研究阶段。抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)◆CMG901:抗CLDN18.2抗体与微管抑制剂MMAE结合的ADC,通过抗体靶向递送细胞毒性药物至肿瘤细胞,诱导微管聚合抑制和凋亡。I期剂量递增试验显示,其在经治实体瘤患者中安全性可控,展现出优异的抗肿瘤活性。◆EO-3021/SYSA-1801:全人源抗CLDN18.2抗体偶联MMAE,对CLDN18.2低表达和高表达肿瘤均显示临床前活性,克服了部分抗原异质性问题。在I期临床试验中,显示出一定的抗肿瘤效果,且与PD-1抑制剂联合可增强疗效,但需要关注患者的耐受性和毒性管理。◆TPX-4589(LM-302):重组人源化抗CLDN18.2抗体偶联MMAE。临床前研究显示,其在胃癌和胰腺癌模型中内化效率高于单纯抗体,目前I期试验正在招募晚期实体瘤患者,剂量扩展阶段聚焦胃癌和食管癌。◆RC118:人源化抗CLDN18.2抗体偶联MMAE,主要针对胃癌和胰腺癌。I期试验显示其具有可接受的安全性特征,目前在CLDN18.2阳性实体瘤中探索最佳剂量和联合治疗策略。◆SOT102:抗CLDN18.2抗体偶联化疗药物PNU-159862(尼莫柔比星衍生物),其作用不依赖CLDN18.2表达水平,适用于heterogeneous肿瘤。I/II期CLAUDIO-1试验正在评估其在胃癌和胰腺癌中的疗效及安全性,毒性谱以轻度血液学毒性为主。◆ATG-022:抗CLDN18.2抗体与MMAE结合的ADC,针对CLDN18.2低表达肿瘤设计,临床前研究显示对相关模型有效。目前正在晚期实体瘤患者中评估其安全性和初步抗肿瘤活性。CLDN18.2特异性的CAR-T 细胞疗法◆CT041:采用自体T细胞改造,通过单链可变片段(scFv)识别CLDN18.2抗原,激活T细胞介导的肿瘤杀伤。在I期临床试验中,超80%的患者出现肿瘤退缩,且未发生严重的CRS,展现出良好的有效性和安全性。◆LCAR-C18S:在相关研究中显示出一定的客观缓解效果,但目前仍处于早期研发阶段,还需更多临床试验数据进一步验证其有效性和安全性,探索最佳治疗方案。◆LY011:目前处于临床早期阶段,虽已观察到部分患者的肿瘤缓解情况,但还需扩大样本量、长期随访,以明确其在肿瘤治疗中的地位和潜力。其他新型疗法◆mRNA疗法(BNT141):以脂质纳米颗粒(LNP)为载体,递送编码抗CLDN18.2抗体的mRNA,进入人体后可在细胞内翻译生成抗体,激活免疫系统对肿瘤细胞的攻击。目前处于I/II期临床试验阶段,旨在探索其安全性、免疫原性及抗肿瘤活性,为肿瘤治疗提供新的给药模式。◆双功能分子(LB4330):能够同时靶向CLDN18.2和激活CD8+T细胞,通过双重作用机制,既精准识别肿瘤细胞,又增强T细胞对肿瘤的杀伤能力。目前已开展I期临床试验,重点评估其在人体中的安全性、耐受性以及初步的抗肿瘤疗效。表2 靶向CLDN18.2的治疗药物的临床开发04CLDN18.2的广泛应用CLDN18.2分子成像与诊断技术1)免疫正电子发射断层扫描(ImmunoPET):通过放射性核素标记抗体(如⁸⁹Zr、⁶⁴Cu),无创评估CLDN18.2表达水平,指导患者筛选和疗效监测。如⁶⁸Ga-NOTA-hu19V3、⁸⁹Zr-hu7v3-Fc,纳米抗体探针因分子量小(12-15kDa)、稳定性高,肾脏清除快,肿瘤穿透性优于传统抗体,可动态可视化CLDN18.2表达。2)近红外荧光成像:如FD1080-5C9探针,用于术中肿瘤边界识别,提高手术切除精准度。3)循环肿瘤细胞(CTCs)检测:分子信标(MB)技术检测CTCs中CLDN18.2RNA,与组织活检一致性达100%,为无创诊断提供新途径。技术瓶颈及优化策略◆技术瓶颈:缺乏天然稳定表达CLDN18.2的癌细胞系,依赖转染模型或患者来源异种移植(PDX)。 纳米抗体肾清除快,可能影响肾脏附近肿瘤的诊断,且治疗剂量存在肾毒性风险。◆优化策略:开发长效放射性核素标记抗体,减少成像周期和辐射暴露。 结合人工智能(AI)分析ImmunoPET图像,提升CLDN18.2表达评估的准确性。 统一IHC评分标准,开发高特异性区分CLDN18.1/18.2的试剂,推广液体活检(如CTCs RNA检测)。CLDN18.2在不同肿瘤中的作用◆胃癌:Lauren分型中弥漫型CLDN18.2表达率高于肠型,与神经侵犯、低分化相关,但与OS、预后无显著关联。◆胰腺癌:在癌前病变(如PanIN)中高表达,50%-90%的胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)高表达CLDN18.2,且在转移灶中持续表达,其阳性率与分化程度、淋巴结转移相关,但不影响OS,且联合化疗显示生存获益。◆胆管癌:肝内胆管癌中CLDN18.2高表达与淋巴结转移和预后不良相关,肝外胆管癌中表达与OS无关。◆食管癌:研究发现Barrett食管受损的鳞状上皮中CCLDN18.2表达显著增加,提示其异常激活可能是食管癌发生的早期事件。◆结肠炎相关结直肠癌:超20%病例表达CLDN18.2,与淋巴结转移相关,提示靶向治疗潜力。◆非小细胞肺癌:通过组织微阵列检测发现,在腺癌和大细胞癌的非重叠亚组中有3.7%的样本呈现CLDN18.2膜阳性,可能成为潜在治疗靶点。◆其他肿瘤:在乳腺癌、肝癌、头颈部癌等多种肿瘤中,CLDN18.2也常出现异常激活和过表达的情况。05CLDN18.2挑战与应对策略关键挑战1)靶点异质性:CLDN18.2在肿瘤组织中的表达存在不均,影响疗效,需开发更灵敏的检测技术,提高筛选精准度。2)毒性管理:靶向 CLDN18.2的疗法可能影响胃黏膜屏障,如Zolbetuximab相关呕吐发生率高达20%,需优化管理策略。3)耐药机制:长期治疗可能导致抗原丢失或胞内结构域突变,降低药物有效性,耐药机制尚需深入研究。应对策略1)精准患者筛选:利用液体活检监测CLDN18.2表达动态变化,优化患者分层,提高治疗获益率。2)联合治疗策略:Ø Zolbetuximab+PD-1抑制剂(KEYNOTE-859研究进行中),探索联合免疫疗 以增强抗肿瘤效应。Ø CLDN18.2 CAR-T+溶瘤病毒(临床前研究显示协同增效),突破实体瘤微环境的免疫抑制。Ø 新型靶向抗体设计:开发pH依赖性抗体,在肿瘤酸性微环境下精准激活,降低对正常组织的影响,提高安全性。未来,精准筛选、优化联合治疗、开发新型药物,将是提升 CLDN18.2 靶向疗法疗效、降低毒副作用的关键路径,加速其在临床实践中的广泛应用。抗体发现服务 & 产品01羊驼免疫&骆驼免疫—自建现代化养殖农场02万亿级天然抗体库产品—轻松DIY科研抗体03配套产品—助您轻松搭建基因工程抗体平台关于仁域生物成都仁域生物成立于2019年1月,是一家专注基因工程抗体技术和天然抗体库开发的公司,拥有优化的噬菌体展示抗体库技术和现代化的骆驼/羊驼养殖免疫基地。可为客户提供14天、100%成功率的先导抗体分子发现服务,彻底解决传统抗体定制的周期长、失败率高、成本高三大难题。目前已经成功完成300+靶点抗体筛选项目!protocol 获取 / 产品咨询邮箱|find@renyubio.com电话|19136178673地址|成都市经开区科技产业孵化园关注我们,小编将持续更新相关内容~参考文献Huang Y, Ye Y, Yi T, Yuan C, Li D. CLDN18.2: a potential nanotherapeutic target for cholangiocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1559558. Tojjari A, Idrissi YA, Saeed A. Emerging targets in gastric and pancreatic cancer: Focus on claudin 18.2. Cancer Lett. 2024 Dec 3;611:217362.Katoh M, Katoh M. Claudin 1, 4, 6 and 18 isoform 2 as targets for the treatment of cancer (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2024 Nov;54(5):100. Fassan M, Kuwata T, Matkowskyj KA, Röcken C, Rüschoff J. Claudin-18.2 Immunohistochemical Evaluation in Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinomas to Direct Targeted Therapy: A Practical Approach. Mod Pathol. 2024 Nov;37(11):100589. Mathias-Machado MC, de Jesus VHF, Jácome A, Donadio MD, Aruquipa MPS, Fogacci J, Cunha RG, da Silva LM, Peixoto RD. Claudin 18.2 as a New Biomarker in Gastric Cancer-What Should We Know? Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;16(3):679.Inamoto R, Takahashi N, Yamada Y. Claudin18.2 in Advanced Gastric Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 7;15(24):5742.Chen J, Xu Z, Hu C, Zhang S, Zi M, Yuan L, Cheng X. Targeting CLDN18.2 in cancers of the gastrointestinal tract: New drugs and new indications. Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 10;13:1132319. Zhang D, Huang G, Liu J, Wei W. Claudin18.2-targeted cancer theranostics. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Apr 25;13(2):64-69.Cao W, Xing H, Li Y, Tian W, Song Y, Jiang Z, Yu J. Claudin18.2 is a novel molecular biomarker for tumor-targeted immunotherapy. Biomark Res. 2022 May 31;10(1):38.Hashimoto I, Oshima T. Claudins and Gastric Cancer: An Overview. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;14(2):290.
临床结果临床研究基因疗法
2023-02-24
·生物谷
安斯泰来zolbetuximab III期研究成功的一声炮响,为CLDN18.2赛道的企业送来了信心和外界的更多关注。
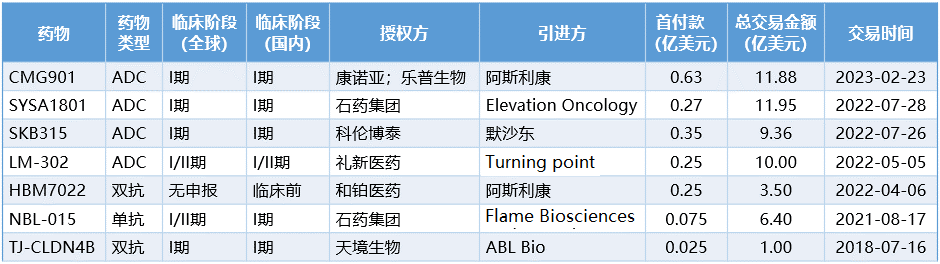
国内CLDN 18.2项目许可情况
从许可出去的CLDN18.2项目类型来看,ADC似乎更受青睐。这也不难理解,毕竟ADC是时下的热门概念药物,同时在单抗类CLDN18.2药物(zolbetuximab和osemitamab)开发进度遥遥领先的情况下,引入CLDN18.2 ADC更容易实现差异化领先优势。
另外一个有趣的地方是,出海名单上的7款CLDN18.2国产药物中,也只有昨天的CMG901揭开过临床数据的“面纱”。据康诺亚公告,在Ia期剂量递增研究(NCT04805307)中,8例接受CMG901治疗的CLDN18.2阳性胃癌或胃食管交界处腺癌患者的客观缓解率(ORR)为75%,疾病控制率达到100%。更为可喜的是,2.6、3.0、3.4mg剂量组患者的ORR达到了100%。
早期的优秀临床数据不一定能支持一个药品成功走到最后获批上市,但肯定能支持它找到一个好的“买家”。在拥挤的CLDN18.2赛道,CMG901打动阿斯利康的原因也必然是有上述惊人疗效数据的因素。
当然,对于许可方的康诺亚和乐普生物来说,这也是一笔很划算的买卖。首先,获得资金用于支持其他产品的开发,这一点自然不必多说。其次,CLDN18.2虽然成药前景变得更加明朗,但很可能马上就要上演PD1赛道最初拼开发速度的故事,这对进度不算领先的企业的开发能力和资金实力是一大挑战;另外,CLDN18.2药物国内竞争激烈,后来者的商业前景有一定的不确定性,能有巨头级别的大药企上门收购,不仅可以及早兑现商业价值,还可以赢得巨头的背书,提升公司的知名度,打开后续的BD合作的局面。
对阿斯利康来说,引进CMG901也是扩大胃癌业务版图的优选。如今阿斯利康管线中已有实力产品Enhertu覆盖HER2阳性胃癌,但尚未布局HER2阴性胃癌疗法,而CMG901针对HER2阴性胃癌疗效出色,是绝佳的产品补充(见:有望改写胃癌一线治疗格局!Zolbetuximab突破总生存期上限,OS超过18个月)。
国内创新药license out已成风潮,其它布局了CLDN 18.2的药企必定也心向往之。据医药魔方Nextpharma数据库统计,全球共49款处于临床开发阶段的CLDN18.2靶向药物,其中42款来自中国药企。虽然目前安斯泰来zolbetuximab的开发进度一骑绝尘,但部分国产CLDN18.2靶向药物的表现仍然值得期待。除了已“出海”的7款产品外,创胜集团osemitamab、科济药业CT041、荣昌生物RC118等产品也有可能凭借不错的临床数据得到海外药企青睐。
临床在研国产CLDN18.2靶向药物
从临床进度来看,已披露早期临床结果的CLDN18.2靶向药物共6款,来自科济药业、创胜集团、天广实和启愈生物。相比于仅有临床前数据的产品,临床疗效初显的产品投资风险更小,也就更容易被投资方看中。目前,创胜集团osemitamab已完成一项I期研究,一线胃癌ORR高达73.3%;科济药业CT041已完成3项I期研究和一项I/II期研究,二/三线胃癌ORR为33%,三线胃癌ORR为57.1%;AB011已完成一项I期研究,二线胃癌ORR为52.2%;天广实MIL93已完成一项I期研究,末线实体瘤ORR为8.0%;启愈生物Q-1802已完成一项I期研究,末线胃癌ORR为22.2%。
未来,已披露早期临床结果的osemitamab、AB011、MIL93和获得突破性疗法认定的RC118的出海前景均值得期待。
据WHO统计,2020年全球胃癌发病率和死亡率分别位列第5和第3。弗若斯特沙利文报告显示,2025年全球胃癌药物市场规模预计达303亿美元,2023年将达460亿美元,市场需求庞大。作为晚期胃癌治疗的潜力靶点,CLDN 18.2具有填补当前临床治疗空白的实力。随着CLDN 18.2靶向药物的开发进展越来越多以及相关BD交易的增多,该领域的竞争亦会愈演愈烈,胃癌患者也将有希望迎来更多的治疗选择。
并购临床3期抗体药物偶联物
2022-01-17
CHICAGO, Jan. 17, 2022 /PRNewswire/ -- With a mission of "Bolstering human immunity by utilizing empowered antibody therapies", the SparX Group is rapidly becoming a significant player in the field of discovering unique therapeutic target combinations and development of novel bispecific antibody constructs. Today, SparX announced that the FDA has approved their IND application for its organically developed anti-claudin18.2 antibody, SPX-101. The first patient is set to receive their initial dose in March of 2022.
Dr. Gui-Dong Zhu, the President, CEO and founder of the company stated, "This is a significant milestone for SparX. The FDAs approval validates the effectiveness of SparX's SAILINGTM antibody discovery platform. This platform is composed of seven proprietary modules, encompassing the entire process for antibody-based drug discovery and production. Few start-up biotech companies are able to identify unique targets, discover and optimize antibody therapeutics, produce the drug substance, and prepare the IND submission package, all in-house without the help of a CDMO or CRO. Our scientists felt we could accomplish this mission. It is gratifying that the FDA approval of our IND has substantiated SparX's capabilities to do so."
SPX-101 is a highly selective anti-claudin18.2 monoclonal antibody. The antibody was discovered, then biologically and biophysically improved, using a customized optimization funnel, taking advantage of the acidity in the tumor microenvironment and Fc-mediated immune effects. "Claudin18.2 is a highly specific tumor antigen, but optimizing therapeutic targeting could still benefit from a more sophisticated molecular design and selection algorithms in order to maximize the therapeutic window. We are aware of the fierce competition in the field, but we believe SPX-101 is a uniquely designed and carefully selected compound that has the potential to be a best-in-class molecule coupled with task specific formulation. Our sophisticated basket trial design, along with a first-in-class companion diagnostic, will help us to stand out during the development stage," said Dr. Zhu.
SparX Group has built a well-equipped pilot plant at its Mount Prospect, IL location. This facility encompasses process development through cGMP production, including QC laboratories, supplying the deliverables required for IND filing and early-stage clinical development. By the end of 2022, the company's Yangzhou facility will launch and be able to supply material needs for later stages of development, and ultimately commercial production. "We are committed to quality", added Dr. Zhu. "The "0" information request from the FDA over the CMC package demonstrates our dedication to the quality of manufacturing".
About SparX Group
Headquartered in the Cayman Islands, the SparX Group has a mission of "restoring and bolstering human immune system using empowered antibody therapeutics". The group of companies consists of four entities, each focusing on different phases of pharmaceutical development. Delaware-based SparX Biopharmaceutical serves as the engine and powerhouse for the discovery of novel biologic therapies. Their process utilizes a sophisticated AI-based target mining algorithm, which is combined with an integrated multi-component SAILING™ antibody optimization platform to yield novel target/therapeutic combinations. This subsidiary also possesses a cGMP-audited pilot plant facility for antibody drug manufacturing and characterization. Yangzhou-based SparX (Jiangsu) provides manufacturing capabilities sufficient for five commercial launches in parallel and the CMC needs for more than twelve programs in clinical trials at various stages of development. SparX Group will be evolving into a full-scale biopharmaceutical covering all phases of biologics drug development and commercialization.
CONTACT: [email protected]
SOURCE SparX Group
临床申请抗体药物偶联物临床1期
100 项与 SPX-101(SparX) 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 晚期恶性实体瘤 | 临床1期 | - | 2022-05-01 | |
| 肺癌 | 临床1期 | - | 2022-05-01 | |
| 实体瘤 | 临床1期 | 美国 | 2022-04-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

生物类似药
生物类似药在不同国家/地区的竞争态势。请注意临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

