预约演示
更新于:2024-09-22
Lp-PLA2
更新于:2024-09-22
基本信息
相关靶点 |
关联
7
项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 Lp-PLA2抑制剂 [+1] |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床1期 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期- |
靶点 |
作用机制 Lp-PLA2抑制剂 |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床1期 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期- |
靶点 |
作用机制 Lp-PLA2抑制剂 |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期- |
34
项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的临床试验NCT05792163
A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Study to Investigate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of SNP318 in Healthy Adult Participants
SNP318 is developed to treat neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease. In the current phase 1 study, the IP is tested in healthy volunteers, and the purpose is to investigate the safety, tolerability, and PK of single and multiple ascending oral doses of SNP318.
开始日期2023-03-20 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT02130661
A Phase I, Two-part, Open-label Study to Evaluate the Pharmacokinetics of Rilapladib (SB-659032) and Its Metabolites, and to Determine the Effect of Repeat Dose Itraconazole on the Pharmacokinetics of Rilapladib in Healthy Volunteers
Rilapladib is a potent and selective inhibitor of lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2), which was previously under development for the treatment of atherosclerosis and is currently being developed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
This study is a single-center, open-label, two-part study. The two study parts will run independently. Subjects dosed in one part of this study will not be permitted to participate in the other part.
Part A will investigate the pharmacokinetic profile of rilapladib and its metabolites, SB-664601 and GSK1174379, after single dose and steady state dosing of rilapladib 250 milligram (mg) along with the biliary and urinary elimination pathways of rilapladib 250 mg. Part B will determine the effect of repeat administration of itraconazole on the PK of a single oral dose of rilapladib 25 mg.
Healthy male and female subjects, aged 18-65 years, will be recruited for this study. Ten subjects will be recruited for Part A and 20 subjects will be recruited for Part B.
This study is a single-center, open-label, two-part study. The two study parts will run independently. Subjects dosed in one part of this study will not be permitted to participate in the other part.
Part A will investigate the pharmacokinetic profile of rilapladib and its metabolites, SB-664601 and GSK1174379, after single dose and steady state dosing of rilapladib 250 milligram (mg) along with the biliary and urinary elimination pathways of rilapladib 250 mg. Part B will determine the effect of repeat administration of itraconazole on the PK of a single oral dose of rilapladib 25 mg.
Healthy male and female subjects, aged 18-65 years, will be recruited for this study. Ten subjects will be recruited for Part A and 20 subjects will be recruited for Part B.
开始日期2017-10-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT02058641
An Open Label Study on the Effects of a Short Course of SB480848 (Darapladib) on Contents of Cantharidin-Induced Inflammatory Blisters in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
This will be an exploratory, open-label, single sequence, two part study (Part A and an optional Part B). The aim of this study will be to assess whether systemic inhibition of Lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) in humans, effected by 11 days of once daily dosing to steady state with 160 milligrams (mg) of enteric coated (EC) darapladib, will specifically reduce the number of macrophages and/or result in a higher proportion of M2 macrophages in skin blisters induced by cantharidin (a chemical agent that causes blisters). In Part A of the study, a cohort of 8 subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus will be recruited. In Part B of the study, a cohort of 8 additional healthy subjects with matching age (+/- 24 months) and gender to Part A may be recruited.
开始日期2014-02-26 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,546
项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的文献(医药)2024-09-01·JOURNAL OF TRACE ELEMENTS IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY
Essential trace element and phosphatidylcholine remodeling: Implications for body composition and insulin resistance
Article
作者: Chien, Mu-Ming ; Chang, Jung-Su ; Wang, Weu ; Tsai, Chien-Sung ; Tung, Te-Hsuan ; Patchara, Sangopas ; Skalny, Anatoly V ; Chang, Chun-Chao ; Huang, Shih-Yi ; Tinkov, Alexey A ; Lin, Wen-Ling ; Faradina, Amelia
BACKGROUND:
Recent studies indicated that bioactive lipids of phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs) predict unhealthy metabolic phenotypes, but results remain inconsistent. To fill this knowledge gap, we investigated whether essential trace elements affect PC-Lyso PC remodeling pathways and the risk of insulin resistance (IR).
METHODS:
Anthropometric and blood biochemical data (glucose, insulin, and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2)) were obtained from 99 adults. Blood essential/probably essential trace elements and lipid metabolites were respectively measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS).
RESULT AND CONCLUSION:
Except for LysoPC (O-18:0/0:0), an inverse V shape was observed between body weight and PC and LysoPC species. A Pearson correlation analysis showed that essential/probably-essential metals (Se, Cu, and Ni: r=-0.4∼-0.7) were negatively correlated with PC metabolites but positively correlated with LysoPC (O-18:0/0:0) (Se, Cu, and Ni: r=0.85-0.64). Quantile-g computation showed that one quantile increase in essential metals was associated with a 2.16-fold increase in serum Lp-PLA2 (β=2.16 (95 % confidence interval (CI): 0.34, 3.98), p=0.023), which are key enzymes involved in PC/Lyso PC metabolism. An interactive analysis showed that compared to those with the lowest levels (reference), individuals with the highest levels of serum PCs (pooled, M2) and the lowest essential/probably essential metals (M1) were associated with a healthier body composition and had a 76 % decreased risk of IR (odds ratio (OR)=0.24 (95 % CI: 0.06, 0.90), p<0.05). In contrast, increased exposure to LysoPC(O-18:0/0:0) (M2) and essential metals (M2) exhibited an 8.22-times highest risk of IR (OR= 8.22 (2.07, 32.57), p<0.05) as well as an altered body composition. In conclusion, overexposure to essential/probably essential trace elements may promote an unhealthy body weight and IR through modulating PC/LysoPC remodeling pathways.
2024-09-01·INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
Comprehensive analysis of miRNAs-lncRNAs-mRNAs modules and ceRNA network in acute liver failure: Hsa-miR3175 and C-reactive protein determination
Article
作者: Zhao, Xianyuan ; Chen, Chen ; Deng, Yuxiao ; Xu, Yuqing ; Gao, Yuan ; Feng, Junqi
Acute liver failure (ALF), also known as fulminant hepatitis, coagulation disorders, and worsening mental status. It has a poor prognosis and high mortality rate. Among these, the top 10 upregulated genes included GKA-DPA1, IGLL5, PLA2G7, CCL5, IGLJ, GUSBP11, RHOBT1, IGLL3P, CCL18, and ADRBK2. On the other hand, the top 10 downregulated genes were SLC6A1, PID1, AVPR1A, PP1R1A, ST3GAL6, TPST, ERO1LB, SLCO4C1, and KLF15. Furthermore, the DEGs were found to be enriched in processes related to LIAO metastasis and creighton endocrine therapy resistance. To explore the interactions among the DEGs, we constructed a PPI network. This network revealed 16 hub genes that play crucial roles in ALF pathogenesis. Within this network, hsa-mir-375 and hsa-mir-650 were identified as central nodes, indicating their potential importance in ALF. By identifying and analyzing the transcriptional-level ceRNA network, we have provided valuable insights into the etiology of ALF.
2024-09-01·Annales Pharmaceutiques Francaises
Review
作者: Bonnefont-Rousselot, Dominique
Over the last fifteen years, numerous studies have sought to decipher the role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) in vascular inflammation-related diseases, notably atherosclerosis. Despite the disappointing results of clinical trials using the Lp-PLA2 inhibitor darapladib, new pathophysiological, epidemiological and genetic data have enabled the development of new inhibitors. Recent studies also show that Lp-PLA2 is involved in vascular inflammation-related diseases other than atherosclerosis (ischemic stroke, Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia, diabetes, cancers…), and inhibition of Lp-PLA2 could have beneficial therapeutic in these diseases. This review aims to present new data on Lp-PLA2 and to evaluate its current interest as a biomarker but also as a therapeutic target.
16
项与 Lp-PLA2 相关的新闻(医药)2024-09-20
·生物谷
运动带来的益处,几乎是人人皆知的话题。它不仅能够帮助我们减重、增强免疫系统、降低慢性疾病的风险,还拥有提升记忆力和认知功能的神奇效果,让我们的大脑更加灵活和敏锐。此前,已有研究证明,体育活动对于认知能力的正面影响是可以遗传给下一代的[1]。
令人惊讶的是,我们的运动益处甚至能为跨后代的智力发展打下基础,即使他们从未亲身经历这些锻炼。
近日,J Neurosci期刊发表了研究成果[2],给予小鼠祖父(F0)运动或不运动干预,检测第二代(F2)雄性小鼠的行为特征、认知能力等来评估锻炼是否可以跨代延伸。研究表明:与运动相关的认知益处不仅能从父母遗传给后代,还能跨代延伸,即两代人之后也能持久地代代相传。
爷爷辈的锻炼竟可增强孙辈认知能力!
研究人员将久坐的F0动物的孙辈(F2SED)与运动的F0小鼠的孙辈(F2RUN)进行了比较。他们采用旷场实验来评价小鼠的活动能力,结果发现,第一天环境探索时,两组小鼠存在相似的探索活动,水平活动得分、垂直活动得分、活动总距离、活动时间、旷场中心地带及边缘地带探索时间均无统计学差异。当两组动物再次探索已经探索过的环境时,两组小鼠结果依然类似。
接下来,研究人员使用新目标识别测试、目标定位测试和情境恐惧条件反射来分析小鼠的认知能力。研究发现在新目标识别测试中,相比于久坐小鼠孙辈(F2SED),运动小鼠孙辈(F2RUN)的短期(1小时,STM)和长期(24小时,LTM)记忆能力显著增加,探索已知目标和新目标时间延长,且探索时间长短并不会影响记忆能力。而在困难版本的目标定位测试中,在相同的探索时间下只有F2RUN动物能够显著辨别出物体空间位置的微小变化。在情境恐惧条件反射测试中,两组小鼠没有差异。
图1:F2SED和F2RUN组小鼠行为学分析
综上所述,运动小鼠孙辈(F2RUN)表现出更强的认知能力,证实了爷爷辈的锻炼有助于孙子辈认知能力的增加,肯定了运动诱导的认知增强的跨代遗传性。
运动是通过什么方式代代相传?
研究人员采用了齿状回中的组织学标志物作为研究手段。研究结果显示,在神经干细胞的数量、颗粒细胞层的细胞数、祖细胞的数量、未成熟的新生神经元数量,以及齿状亚颗粒层的面积等方面,两组之间并未观察到显著的差异。这表明,在成年海马神经发生的过程中,两组动物之间并没有出现明显的变化。
图2:海马神经组织学变化
但值得注意的是,F0代锻炼会使得F1代成年海马神经发生出现变化。
随后,研究团队深入分析了海马区内的小RNA序列,揭示了35种与关键脑功能类别紧密关联的差异表达miRNA。在这35种miRNA中,15种的表达量有所下降,而另外20种则呈现上升趋势。更进一步的研究指出,其中两种miRNA——miRNA-144和miRNA-298,与认知能力表现出显著的负相关性。具体来说,当F0代小鼠经历了运动诱导后,这些miRNA的表达水平越低,其F2代的认知表现就越好。
为了更全面地理解这些变化,研究人员进行了描述性分析,将F2代的RNA测序结果与前两代(F0和F1)的数据进行了对比。结果发现,共有11种miRNA在三代间表现出一致性,这提示它们可能是重要的研究目标,同时也是跨三代表观遗传效应的关键驱动因子。
此外,研究团队还对比了F2代中显著差异表达的35种miRNA与F0和F1代RNA测序数据中的基因列表。这一分析揭示了6个具有显著差异的靶基因,这些基因同样值得进一步探索,以阐明它们在跨代遗传过程中的作用。
图3:F0、F1和F2小鼠miRNA比较
小结
这一研究首次报告了运动诱导的祖辈特征可以在孙子辈认知中跨代遗传,会对孙子辈认知产生持久的积极影响,且这些影响可能是由一组特定的 miRNAs 协调的,这些 miRNAs 可在多代人之间发挥影响。
没想到吧!运动的好处不止有短期内的,比如让你变得更健康,也有长长长期的好处,比如增强下一代、下下代的认知。看到这里,是不是已经跃跃欲试,准备出门运动了?所以说,不管工作、学习有多忙,都别忘了抽出时间运动。毕竟,我们个人和下一代、下下代都会因此受益匪浅!
参考文献:
[1] McGreevy KR, Tezanos P, Ferreiro-Villar I, et al. Intergenerational transmission of the positive effects of physical exercise on brain and cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(20):10103-10112. doi:10.1073/pnas.1816781116
[2] Cintado E, Tezanos P, De Las Casas M, et al. Grandfathers-to-Grandsons Transgenerational Transmission of Exercise Positive Effects on Cognitive Performance. J Neurosci. 2024;44(23):e2061232024. Published 2024 Jun 5. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2061-23.2024
撰文 | M
编辑 | lcc
部分文字来源于网络,本文仅用于分享,转载请注明出处。若有侵权,请联系微信:bioonSir 删除或修改!
精彩推荐:
1、别熬了!仅熬夜4天,死亡率就高达80%!Cell:清华大学研究团队揭示“睡眠不足免疫崩溃”的机制,深层原因在这儿....
2、吃饭要吃「八分饱」!研究表明:吃八分饱不仅能延缓衰老,还不会损害免疫功能!PLA2G7是关键因子
3、神药“二甲双胍”究竟几分真假?多项研究表明:二甲双胍能够降血糖、抗衰老,但也会诱发诸多副作用,例如肝中毒、乳酸中毒
4、“下半身”或许真的可以思考?研究表明:睾丸竟是最像大脑的器官,基因高度相似,共享13,442种蛋白质
5、你站起身来会容易眼前发黑吗?研究表明:直立性低血压患心血管疾病和痴呆的风险会升高,且症状出现得越早,认知衰退风险越高!
点击下方「阅读原文」,前往生物谷官网查询更多生物相关资讯~
临床1期
2024-09-19
·生物谷
人一生中,约有三分之一的时间在睡眠中度过。睡眠的重要性不言而喻,但随着社会飞速发展以及生活节奏加快,“拼命十三郎”们只能舍弃睡眠时间,转而投入996甚至007的“社畜”工作中。
除了繁忙的工作压缩了睡眠时间外,一个更常见的现象是“报复性熬夜”——白天被各种琐事儿缠身,只有当晚上躺在床上的那一刻,时间才开始属于自己,接着就是“无止境”的熬夜。当从手机中“缓过神”的时候,发现自己根本睡不了几个小时又要搬砖了!
据《中国睡眠研究报告2023》最新公布的数据,2022年中国人的入睡时间集中在23点至1点,比2021年向后推迟了1小时。此外,一项针对中国职场青年的报告显示,超五成职场青年每天在12点之后才睡觉,甚至有13%的要熬到凌晨2点后。
不过,正如大家调侃得那样“晚上不睡,白天崩溃”。崩溃的不仅是精神,还有身体的方方面面!早在2007年,国际癌症研究机构(IARC)就把熬夜(包括昼夜节律打乱的轮班工作)定义为2A类致癌物。除此之外,熬夜还会导致主要心血管不良事件的风险增加92%;增加海马体中抑制神经元活动,破坏记忆巩固;甚至于死亡!
去年,来自北京生命科学研究所/清华大学生物医学交叉研究院的团队进一步发现,睡眠不足免疫崩溃并非“耸人听闻”——睡眠不足可能会导致严重的病理生理后果,甚至诱发死亡!
在长达4天的熬夜之后,生物体表现出严重的炎症反应,约有80%死亡。具体原因在于,睡眠剥夺会增加大脑中前列腺素D2(PGD2)的水平,而穿过血脑屏障的脑源性PGD2外排的增加,会诱发循环中性粒细胞的聚集和细胞因子风暴综合症,给外周免疫系统带去严重的病理后果。
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.10.025
“长时间的睡眠剥夺会导致生物体的过早死亡”并非新闻,早已在果蝇、小鼠、大鼠和狗等动物模型中得到证实。同时,先前Cell上刊登过哈佛医学院团队的研究揭示,“熬夜至死”的关键原因不在于大脑,而在于肠道。
然而,睡眠与健康之间关联性非常复杂,睡眠调节免疫力的详细机制以及睡眠不足影响健康的具体原因仍没有完全阐明。与此同时,控制实验动物的睡眠模式并非易事,想要完全地剥夺小鼠的睡眠,还需要探索出更为规范的实验范式。
于是,研究者首先建立了一种改良版的小鼠睡眠剥夺系统,并将该方法命名为“Curling prevention by water(CPW)”。
简单来说,CPW范式是指:将小鼠关在一个装有水的笼子里,水位大概8毫米深,刚刚到达小鼠脚踝的位置。当小鼠表现出“身体蜷缩”的打瞌睡样,就会因为鼻子接触到水而迅速被“淹”醒。
为了确认CPW的有效性,研究者对小鼠开展了基于EEG/EMG的睡眠/觉醒分析,结果发现:暴露于CPW范式的小鼠确实处于“熬大夜”的状态——小鼠每天有长达1400分钟保持清醒,占全天时长的96%。与对照组相比,CPW小鼠有95%NREMS(约545分钟/天))和83%REMS(54分钟/天)被剥夺。
CPW的厉害之处在于,该范式能够同时极大地消耗小鼠的快速眼动睡眠(REMS)和非快速眼动睡眠(NREMS),且保持较长时间上(>4天)。同时,在排除了混杂因素影响以及与多种方法进行对比后证实,CPW能够有效地模拟“熬夜”,但不会诱发过度的应激或损害代谢平衡。
CPW范式的过程
在短短4天内,“熬夜”的成年小鼠中有80%死亡,死亡时间在睡眠剥夺开始后的72-96小时不等。在死亡之前,这些小鼠表现出平衡能力的丧失,以及对轻触刺激的反应极小或几乎没有。
对去世的小鼠进行全身病理分析显示,“熬夜”的打击是全身性、多系统的!多个器官组织受到了损伤,包括7/8的肝脏组织坏死伴随炎症细胞浸润、1/2的脾脏的髓质边界模糊、3/8的肺表现出急性损伤、1/4的肠道结构损伤以及1/8的肾脏出现了病变。
即使侥幸存活下来,“熬夜”的小鼠也出现了明显的生化改变。与对照组相比,暴露于CPW的小鼠表现出更高水平的血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)以及尿素。
睡眠剥夺情况下多器官受到损伤
为了明确长期睡眠剥夺诱导的多器官功能障碍(MODS)早期表型,研究者对“熬夜”48小时的小鼠进行了全面的病理检查。与先前开展的研究一致,研究者在睡眠剥夺小鼠中观察到ROS的积累;正如前文提到的那样,ROS是重要的信号分子和炎症标志物,可能会诱发睡眠不足引起的死亡。
但令人惊讶的是,当研究者使用抗氧化剂中和ROS之后,无法阻止睡眠剥夺诱导的MODS的发生,暴露于CPW的小鼠依然会走向死亡。
可见,长时间地熬夜,不仅是单一途径地“通过积累ROS而导致死亡”,一定还有其他途径/通路的存在,比如:通过诱发全身炎症反应,进而导致MODS的发生并最终死亡。
进一步的观察发现,长时间睡眠剥夺的小鼠表现出器官损伤和炎症细胞浸润;再鉴于人体中观察到的情况——随着促炎细胞因子的过度释放,这种细胞因子风暴往往会导致器官损伤、疾病和死亡,于是,研究者陷入思考:小鼠体内是否也经历了细胞因子风暴,从而导致了死亡的发生呢?
果不其然,随着熬夜的时间延长,小鼠体内的大多数促炎调节因子都随之上调,其中最主要的两种是IL-6和IL-17A。而这两种细胞因子均能介导人类细胞因子风暴的产生,尤其是IL-6被认为是这一过程的初始驱动因子。
此外,促炎因子趋化因子(C-X-C基序)配体(CXCL1)和CXCL2也显著上调,而这些分子在中性粒细胞招募和渗出的过程中发挥着重要作用。
总结来说,长时间的睡眠剥夺能够诱发促炎细胞因子的增加,且持续时间越长,释放出来的细胞因子数量也越大。随着细胞因子风暴在小鼠体内“席卷”,摧毁身体内多器官以及系统,最终导致疾病和死亡的发生。
睡眠剥夺导致血液中促炎细胞因子的积累
下一个要回答的问题便是:细胞因子风暴究竟是如何形成的?
进一步的分析发现,睡眠剥夺会诱导PGD2在大脑中不断的积累,在ATP结合盒转运蛋白C4(ABCC4)转运体的介导下,PGD2能够通过血脑屏障被外排至血液中,导致循环中促炎细胞因子的过度产生,最终形成细胞因子风暴样综合症和MODS。
这时候,如果能够阻断PGD2/PGD2受体1(DP1)轴,则能够显著减少睡眠剥夺诱发的全身炎症反应。
睡眠剥夺诱发细胞因子风暴炎症反应的机制
综上,不同于先前实验中提及的肠道ROS致死原理,来自清华大学的张二荃研究团队提出了一个“睡眠剥夺导致免疫崩溃甚至死亡”的全新机制——在搭建了有效的睡眠剥夺系统CPW之后,研究者发现长时间睡眠剥夺会诱导PGD2在脑内的不断积累,在穿透血脑屏障并进入血液循环之后,会导致促炎细胞因子的过量产生,最终诱发一系列的器官损伤以及死亡。
因此,“睡眠不足,免疫崩溃”是有科学依据的!睡眠的重要性不言而喻,不如就从今天开始拔起“早睡”的flag吧。
参考资料:
Sang D, Lin K, Yang Y, Ran G, Li B, Chen C, Li Q, Ma Y, Lu L, Cui XY, Liu Z, Lv SQ, Luo M, Liu Q, Li Y, Zhang EE. Prolonged sleep deprivation induces a cytokine-storm-like syndrome in mammals. Cell. 2023 Dec 7;186(25):5500-5516.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.10.025. Epub 2023 Nov 27. PMID: 38016470.
撰文 | Swagpp
编辑 | Swagpp
来源 | 梅斯医学
部分文字来源于网络,本文仅用于分享,转载请注明出处。若有侵权,请联系微信:bioonSir 删除或修改!
精彩推荐:
1、最延寿的运动是它!中山大学最新研究:久坐、步行、剧烈运动都“加速衰老”?但这种运动能抗衰老
2、吃饭要吃「八分饱」!研究表明:吃八分饱不仅能延缓衰老,还不会损害免疫功能!PLA2G7是关键因子
3、神药“二甲双胍”究竟几分真假?多项研究表明:二甲双胍能够降血糖、抗衰老,但也会诱发诸多副作用,例如肝中毒、乳酸中毒
4、“下半身”或许真的可以思考?研究表明:睾丸竟是最像大脑的器官,基因高度相似,共享13,442种蛋白质
5、你站起身来会容易眼前发黑吗?研究表明:直立性低血压患心血管疾病和痴呆的风险会升高,且症状出现得越早,认知衰退风险越高!
点击下方「阅读原文」,前往生物谷官网查询更多生物相关资讯~
临床研究临床结果
2024-07-08
BEIJING, July 8, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- DP Technology, an "AI for Science" paradigm-driven company, today announced the nomination of DPT0416, a novel CNS penetrable small molecule targeting Lp-PLA2, as a preclinical candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Continue Reading
AD is the most frequent cause of dementia (60%~70%), affecting approximately 57 million people worldwide. Neurovascular dysfunction is an early and predominant event in AD development, independent of classic amyloid pathology. Lp-PLA2 is a phospholipase secreted primarily by inflammatory cells, including peripheral macrophages and CNS microglia. It hydrolyzes oxidized phospholipids typically on low-density lipoprotein (LDL), producing lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC) and other potent proinflammatory factors. LysoPC is a key inflammatory mediator on vascular endothelial cells, causing vascular pathology including vessel leakage and BBB damage. The inhibition of Lp-PLA2 by Rilapladib significantly slowed down AD progression and repaired BBB damage
in a Phase IIa trial.
DPT0416 is a novel CNS-penetrable Lp-PLA2 inhibitor, exhibiting higher potency, better ADME and physicochemical properties than Rilapladib. In animal models, DPT0416 showed improvement in BBB integrity and a reduction in brain inflammation. The IND-enabling studies are ongoing.
"Alzheimer's disease imposes increasing burdens on the world. Approvals of three anti-amyloid β (Aβ) antibodies mark a pivotal moment in the fight against AD, but the modest clinical efficacy and side effects highlight the complexity of AD and call for more novel interventions with better efficacy. The future treatment of AD should address multiple aspects of the disease, including anti-oxidants, anti-inflammation, and enhancing brain resilience, among others," said
Xiaomin Zhang, Head of Drug Discovery at DP Technology. "Targeting Lp-PLA2 is a novel therapy that addresses multiple factors beyond amyloid. Given rilapladib's positive clinical results, the better molecule DPT0416 is expected to bring more benefits to AD and dementia patients."
"DP Technology is revolutionizing the AI for Science landscape by integrating 'AI + Simulation + Experiments' into our processes to address significant medical needs,"
said Weijie Sun, Founder and CEO of DP Technology. "The successful identification of DPT0416 highlights the power of our RiDYMO® platform, particularly the contributions of the Uni-FEP and Uni-QSAR modules in enhancing molecular interactions, drug-like characteristics, and BBB penetration. These real-world applications of our cutting-edge algorithms signify an important progression towards our envisioned future. We look forward to forging partnerships with trusted collaborators to advance this initiative to the next pivotal stage."
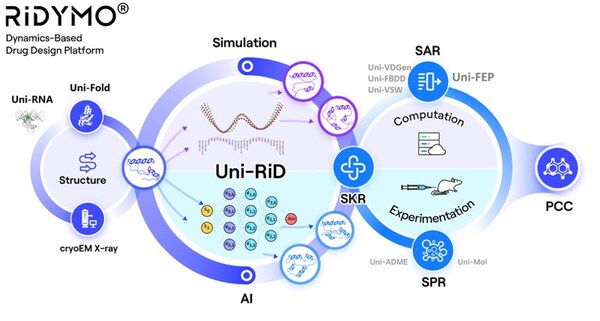
The RiDYMO® drug design platform integrates various AI and physical algorithms, dedicated to the development of drugs for "undruggable" targets and "best-in-class" molecules. As one of its core algorithms, Reinforced Dynamics (RiD) has a significant advantage in the sampling efficiency of molecular dynamics simulation. By fully leveraging the high-dimensional representation capabilities of neural networks, RiD can efficiently capture dynamic conformational changes in complicated biomolecular systems.
The RiDYMO® platform is dedicated to studying the dynamics of biological systems and revealing cryptic binding sites, encompassing a range of challenging systems including protein-protein interactions (PPIs), intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs), membrane proteins, RNA, and others. Its effectiveness has been confirmed through validation on challenging targets, including the c-Myc protein, c-Myc RNA, GPX4 protein, Kv1.3 protein, and others.
About DP Technology
DP Technology, an "AI for Science" new paradigm-driven company, dedicated to applying Artificial Intelligence and Molecular Simulation algorithms to solve important scientific problems by combining advanced computational methods.
Relying on DP Technology's Dynamics-based drug design platform, RiDYMO®, we have set up a world-leading hit discovery platform. The team has established external collaborations and built up strong internal pipeline, focusing on three areas of CNS, oncology and autoimmune diseases.
For collaboration and further information,please contact Dr. Xiaomin Zhang ([email protected]).
References:
[1] Alzheimers. Dement. 17(Suppl 10), e051496 (2021).
[2] Nat. Med. 25, 270-276 (2019).
[3] Med. Res. Rev. 40, 79-134 (2020).
[4] Alzheimers. Dement. 1, 131-140 (2015).
[5] Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 14, 200-213 (2017).
SOURCE DP Technology
临床2期临床结果临床1期
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用



