预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
SCN4A
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 HYKPP、HYPP、Nav1.4 + [10] |
简介 Pore-forming subunit of Nav1.4, a voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel that directly mediates the depolarizing phase of action potentials in excitable membranes. Navs, also called VGSCs (voltage-gated sodium channels) or VDSCs (voltage-dependent sodium channels), operate by switching between closed and open conformations depending on the voltage difference across the membrane. In the open conformation they allow Na(+) ions to selectively pass through the pore, along their electrochemical gradient. The influx of Na+ ions provokes membrane depolarization, initiating the propagation of electrical signals throughout cells and tissues (PubMed:12766226, PubMed:15318338, PubMed:16890191, PubMed:17898326, PubMed:18690054, PubMed:19347921, PubMed:25707578, PubMed:26659129, PubMed:26700687, PubMed:29992740, PubMed:30190309). Highly expressed in skeletal muscles, Nav1.4 generates the action potential crucial for muscle contraction (PubMed:16890191, PubMed:19347921, PubMed:25707578, PubMed:26659129, PubMed:26700687). |
关联
3
项与 SCN4A 相关的药物WO2022120215
专利挖掘靶点 |
作用机制- |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段药物发现 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
靶点 |
作用机制 SCN4A阻滞剂 |
在研机构- |
原研机构 |
在研适应症- |
非在研适应症 |
最高研发阶段终止 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
靶点 |
作用机制 SCN4A阻滞剂 |
在研机构- |
在研适应症- |
非在研适应症 |
最高研发阶段无进展 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
3
项与 SCN4A 相关的临床试验NCT03399435
An Exploratory Phase I Randomized, Single-site, Double-blind, Active-controlled, Parallel-group, Single-administration, Dose-escalation Trial to Investigate the Safety and Tolerability of Neosaxitoxin Alone and in Combination With Bupivacaine (With and Without Epinephrine), in Perineural Administrations for Brachial Plexus Blockade in Healthy Subjects
Neosaxitoxin is a new compound that is in clinical development as local anesthetic for surgical anesthesia and postoperative analgesia.
The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the systemic and local safety and tolerability of ascending doses of neosaxitoxin alone and in combination with fixed doses of bupivacaine (with and without epinephrine), following brachial plexus blockade in healthy male subjects.
Secondary objectives:
Evaluate the pharmacodynamics (PD) of ascending doses of neosaxitoxin, alone and in combination with fixed doses of bupivacaine (with and without epinephrine), following brachial plexus blockade.
Characterize the pharmacokinetics (PK) of neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine after brachial plexus blockade with neosaxitoxin alone or different drug combinations: neosaxitoxin and epinephrine, neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine, or neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine and epinephrine.
The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the systemic and local safety and tolerability of ascending doses of neosaxitoxin alone and in combination with fixed doses of bupivacaine (with and without epinephrine), following brachial plexus blockade in healthy male subjects.
Secondary objectives:
Evaluate the pharmacodynamics (PD) of ascending doses of neosaxitoxin, alone and in combination with fixed doses of bupivacaine (with and without epinephrine), following brachial plexus blockade.
Characterize the pharmacokinetics (PK) of neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine after brachial plexus blockade with neosaxitoxin alone or different drug combinations: neosaxitoxin and epinephrine, neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine, or neosaxitoxin and bupivacaine and epinephrine.
开始日期2018-01-30 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT01786655
Neosaxitoxin (NeoSTX) Alone and in Combination With Bupivacaine as Prolonged Duration Local Anesthetics: A Phase I Investigator-initiated Dose Escalation Study
The primary aim of this Phase 1 study is to evaluate the systemic safety of a novel prolonged-duration local anesthetic, Neosaxitoxin (NeoSTX), given by subcutaneous injection in combination with the commonly used local anesthetic, bupivacaine, and epinephrine.
The investigators hypothesize that a "minimal adverse effect threshold" NeoSTX dose for subcutaneous administration in combination with bupivacaine 0.2% and epinephrine 5mcg/ml respectively, can be defined for awake, young adult healthy volunteer subjects. At the same time, the pharmacokinetics of NeoSTX when delivered subcutaneously will be determined.
The investigators hypothesize that a "minimal adverse effect threshold" NeoSTX dose for subcutaneous administration in combination with bupivacaine 0.2% and epinephrine 5mcg/ml respectively, can be defined for awake, young adult healthy volunteer subjects. At the same time, the pharmacokinetics of NeoSTX when delivered subcutaneously will be determined.
开始日期2013-05-01 |
NCT00273065
Phase 1 Study of Local Infiltration of Neosaxitoxin as a Local Anesthetic
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the local anesthetic properties of neosaxitoxin in humans
开始日期2005-05-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 SCN4A 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 SCN4A 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 SCN4A 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
709
项与 SCN4A 相关的文献(医药)2025-06-01·European Journal of Pharmacology
SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin mitigates skeletal muscle pathology by modulating key proteins involved in glucose and ion homeostasis in an animal model of heart failure
Article
作者: De Luca, Annamaria ; Conte, Elena ; Berrino, Liberato ; Mele, Elena ; Lanza, Martina ; De Angelis, Antonella ; Cappetta, Donato ; Boccanegra, Brigida ; Urbanek, Konrad ; Dinoi, Giorgia ; Riemma, Maria Antonietta ; Liantonio, Antonella ; Imbrici, Paola
2025-04-22·Neurology
Pearls & Oy-sters: Severe Myotonic Crisis Resembling Malignant Hyperthermia
Article
作者: McSherry, Megan L. ; Wadhwani, Anil R. ; McGuire, Jennifer ; Brandsema, John Frederick ; Aggarwal, Ashna ; Loscalzao, Steven ; Matesanz, Susan ; Lockman, Justin L.
2025-04-09·The Journal of Neuroscience
MuSK Regulates Neuromuscular Junction Nav1.4 Localization and Excitability
Article
作者: Christian, Jan L ; Xi, Chengjie ; Arnold, William D ; Wang, Xueyong ; Wharton, Kristi A ; Jaime, Diego ; Shahtout, Justin L ; Fallon, Justin R ; Madigan, Laura A ; Rich, Mark M ; Feder, Rita E ; Ewing, Madison D ; Fish, Lauren A ; Funai, Katsuhiko ; Rich, Kelly A ; Chen, Isabella
2
项与 SCN4A 相关的新闻(医药)2024-11-15
·美通社
上海
2024年11月15日
/美通社/ -- 由
吉林省肿瘤医院程颖教授
牵头开展的特瑞普利单抗联合化疗一线治疗广泛期小细胞肺癌 (ES-SCLC) 的
III期EXTENTORCH研究
结果发表在国际肿瘤学顶级期刊《美国医学会杂志·
肿瘤学》
(
JAMA Oncology
,IF
2023
=22.5),为ES-SCLC一线免疫治疗再添重磅循证医学证据。
程颖教授为本文的第一作者和通讯作者。
来源:JAMA期刊官网
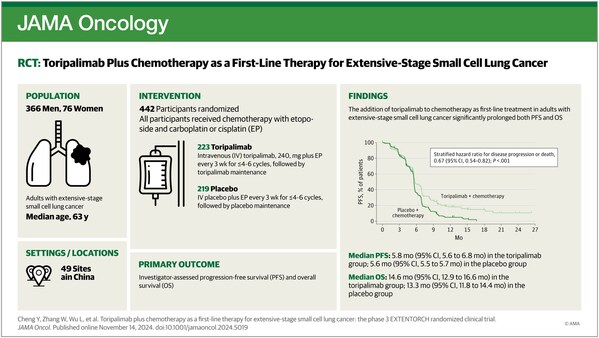
EXTENTORCH研究(NCT04012606)是一项多中心、随机、双盲、安慰剂对照的III期临床研究,旨在比较特瑞普利单抗或安慰剂联合依托泊苷及铂类一线治疗ES-SCLC的有效性和安全性。
EXTENTORCH研究主要研究者,
吉林省肿瘤医院程颖教授
表示:"EXTENTORCH研究作为ES-SCLC领域全球首个成功达到预设双主要研究终点阳性结果的抗PD-1单抗的Ⅲ期临床研究,是ES-SCLC治疗的又一次关键突破。 试验组1年PFS率提升近4倍,所有亚组患者均有获益,主要终点之一的OS取得阳性结果,成功通过了临床‘金标准’的考核,为患者带来确切生存获益。本次EXTENTORCH研究见刊不仅公布了特瑞普利单抗联合化疗一线治疗ES-SCLC的疗效数据,更重要的是,这项研究进行了分子层面的探索,对筛选接受免疫治疗的患者具有重要的指导意义。"
2023年5月,EXTENTORCH研究主要终点无进展生存期(PFS)和总生存期(OS)均达到方案预设的优效边界,特瑞普利单抗由此成为
全球首个
在ES-SCLC一线治疗III期研究中取得预设双重主要终点阳性结果的PD-1抑制剂。
2024年6月,基于该研究的积极结果,
特瑞普利单抗获国家药品监督管理局(
NMPA)正式批准联合依托泊苷和铂类用于ES-SCLC一线治疗
,并获中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)两大指南推荐为ES-SCLC一线治疗
优选方案
,为中国ES-SCLC患者提供了治疗新选择。
此前,EXTENTORCH研究以口头报告的形式在2023年ESMO大会上首次公布了研究数据,此次全文发表于国际期刊,彰显了国际学者对这项研究及特瑞普利单抗的肯定,结果显示:
与单纯化疗相比,
特瑞普利单抗联合化疗显著改善患者
PFS和OS,将疾病进展或死亡风险降低33%
(HR=0.67;95% CI, 0.54-0.82),
死亡风险降低了
20%
(HR=0.80;95% CI, 0.65-0.98)。亚组分析显示,
所有关键亚组均显示出一致的
PFS和OS获益。
生物标志物探索分析显示,在特瑞普利单抗联合化疗组中,具有
低肿瘤内异质性
(ITH),
HLA-A11
+
HLA-B62
-
单倍型
,
KMT2D 和COL4A4
野生型
,或
CTNNA2/SCN4A
序列变异的患者的临床获益更明显
。
特瑞普利单抗联合化疗的安全性良好,
未发现新的安全信号
。两组在治疗期间出现的不良事件(TEAE,99.5%vs100%)和≥3级TEAE(89.6%vs89.4%)的发生率相似。
君实生物总经理兼首席执行官邹建军博士
表示: “此次EXTENTORCH的重磅研究成果获得《美国医学会杂志·肿瘤学》发表,体现了国际学术界对以特瑞普利单抗为代表的免疫治疗在ES-SCLC患者一线治疗中的价值认可。肺癌一直是公司重点关注的疾病领域,截至目前,特瑞普利单抗已成功获批包括非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)和小细胞肺癌(SCLC)在内的3项适应症,覆盖了早中期(围手术期)至晚期人群,管线内也还有其他产品正处于攻关阶段,我们会积极推进相关工作,期待能为全球肺癌患者带来更多更优的创新方案。"
1. 本材料旨在传递前沿信息,无意向您做任何产品的推广,不作为临床用药指导。
2. 若您想了解具体疾病诊疗信息,请遵从医疗卫生专业人士的意见与指导。
关于
EXTENTORCH研究
EXTENTORCH研究(NCT04012606)是一项多中心、随机、双盲、安慰剂对照的III期临床研究,旨在比较特瑞普利单抗或安慰剂联合依托泊苷及铂类一线治疗ES-SCLC的有效性和安全性。研究纳入既往未接受系统治疗的ES-SCLC患者,以1:1的比例随机接受特瑞普利单抗(240mg, Q3W)或安慰剂联合依托泊苷(100mg/m
2
, Q3W)和铂类(顺铂 75 mg/m
2
或卡铂 AUC 5 mg/mL/min, Q3W)治疗4~6个周期,之后接受特瑞普利单抗或安慰剂维持治疗,直至疾病进展、出现不可耐受的毒性或完成2年治疗。研究分层因素包括性别和基线ECOG体能状况评分。主要终点为研究者根据RECIST v1.1评估的PFS和OS。次要终点包括盲态独立中心审查(BICR)评估的PFS、客观缓解率(ORR)、疾病控制率(DCR)、疾病缓解率(DOR)和安全性等。探索性终点包括PD-L1的表达、肿瘤突变负荷(TMB)和其他基于测序的与临床疗效相关的生物标志物。
自2019年9月至2021年5月,研究共纳入442例ES-SCLC患者,随机分配至特瑞普利单抗联合化疗组(n=223)或安慰剂联合化疗组(n=219)。该研究由程颖教授担任主要研究者,在全国49家临床中心联合开展。
关于特瑞普利单抗注射液(拓益
®
)
特瑞普利单抗注射液(拓益
®
)作为我国批准上市的首个国产以PD-1为靶点的单抗药物,获得国家科技重大专项项目支持,并荣膺国家专利领域最高奖项"中国专利金奖"。
特瑞普利单抗至今已在全球(包括中国、美国、东南亚及欧洲等地)开展了覆盖超过15个适应症的40多项由公司发起的临床研究。正在进行或已完成的关键注册临床研究在多个瘤种范围内评估特瑞普利单抗的安全性及疗效,包括肺癌、鼻咽癌、食管癌、胃癌、膀胱癌、乳腺癌、肝癌、肾癌及皮肤癌等。
截至目前,特瑞普利单抗已在中国内地获批10项适应症:用于既往接受全身系统治疗失败的不可切除或转移性黑色素瘤的治疗(2018年12月);用于既往接受过二线及以上系统治疗失败的复发/转移性鼻咽癌患者的治疗(2021年2月);用于含铂化疗失败包括新辅助或辅助化疗12个月内进展的局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌的治疗(2021年4月);联合顺铂和吉西他滨用于局部复发或转移性鼻咽癌患者的一线治疗(2021年11月);联合紫杉醇和顺铂用于不可切除局部晚期/复发或远处转移性食管鳞癌患者的一线治疗(2022年5月);联合培美曲塞和铂类用于表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)基因突变阴性和间变性淋巴瘤激酶(ALK)阴性、不可手术切除的局部晚期或转移性非鳞状非小细胞肺癌的一线治疗(2022年9月);联合化疗围手术期治疗,继之本品单药作为辅助治疗,用于可切除IIIA-IIIB期非小细胞肺癌的成人患者(2023年12月);联合阿昔替尼用于中高危的不可切除或转移性肾细胞癌患者的一线治疗(2024年4月);联合依托泊苷和铂类用于广泛期小细胞肺癌一线治疗(2024年6月);联合注射用紫杉醇(白蛋白结合型)用于经充分验证的检测评估PD-L1阳性(CPS≥1)的复发或转移性三阴性乳腺癌的一线治疗(2024年6月)。2020年12月,特瑞普利单抗首次通过国家医保谈判,目前已有6项获批适应症纳入《国家医保目录(2023年)》,是目录中唯一用于治疗黑色素瘤的抗PD-1单抗药物。2024年10月,特瑞普利单抗用于复发/转移性鼻咽癌治疗的适应症在中国香港获批。
在国际化布局方面,特瑞普利单抗已作为首款鼻咽癌药物在美国和印度获批上市,其用于晚期鼻咽癌和食管鳞癌的一线治疗获得欧盟委员会批准上市。此外,英国药品和保健品管理局(MHRA)受理了特瑞普利单抗联合顺铂和吉西他滨用于局部复发或转移性鼻咽癌患者的一线治疗以及联合紫杉醇和顺铂用于不可切除局部晚期/复发或转移性食管鳞癌患者的一线治疗的上市许可申请,澳大利亚药品管理局(TGA)和新加坡卫生科学局(HSA)分别受理了特瑞普利单抗联合顺铂/吉西他滨作为转移性或复发性局部晚期鼻咽癌成人患者的一线治疗,以及作为单药治疗既往含铂治疗过程中或治疗后疾病进展的复发性、不可切除或转移性鼻咽癌的成人患者的上市许可申请。
关于君实生物
君实生物(688180.SH, 1877.HK)成立于2012年12月,是一家以创新为驱动,致力于创新疗法的发现、开发和商业化的生物制药公司。依托全球一体化源头创新研发能力,公司已构建起涵盖超过50款创新药物的多层次产品管线,覆盖恶性肿瘤、自身免疫、慢性代谢类、神经系统、感染性疾病五大治疗领域,已有5款产品在国内或海外上市,包括我国首个自主研发、在中美欧等地超过30个国家和地区获批上市的PD-1抑制剂特瑞普利单抗(拓益
®
),临床开发阶段的药物超过30款。疫情期间,君实生物还参与开发了埃特司韦单抗、民得维
®
等多款预防和治疗新冠的创新药物,积极承担本土创新药企的责任。
君实生物以"用世界一流、值得信赖的创新药普惠患者"为使命,立足中国,布局全球。目前,公司在全球拥有约2500名员工,分布在美国旧金山和马里兰,中国上海、苏州、北京、广州等。
官方网站:
www.junshipharma.com
官方微信:君实生物
CSCO会议临床3期临床结果免疫疗法上市后研究
2022-11-30
·药通社
注:本文不构成任何投资意见和建议,以官方/公司公告为准;本文仅作医疗健康相关药物介绍,非治疗方案推荐(若涉及),不代表平台立场。任何文章转载需得到授权。海洋生物独特的生活环境赋予了海洋天然产物的复杂多样性、结构新颖性、生物活性多元性和作用机制独特性等特点,因此,海洋天然产物是重要药物先导物和具有新生物作用机制药物的主要来源,芋螺多肽——是一种来自海洋天然抗皱活性成分。芋螺(Cone snail, Conus),又称鸡心螺,属于海洋腹足纲芋螺总科(Conoidean)超家族芋螺科(Conidae),该家族还包括塔螺科(Turridae)和笋螺科(Terebridae)等有毒软体动物,全球约有800种芋螺,主要分布于热带或亚热带海域中岩石丰富的浅海域和珊瑚礁从的沙质底部。这些捕食性螺类拥有特殊且复杂的摄食行为,无论是食虫类,食螺类还是食鱼类,它们已进化出一套特殊的捕食装置(如下图),通过快速伸出特殊针状的齿舌,向猎物和掠食者皮下注射入使其麻痹或不停抽搐的分泌物完成捕食和御敌。芋螺使用的分泌物是一种非常复杂的混合物,由100到1,000种不同的生物活性成分组成,其组成因物种而异。通过高效液相色谱和质谱技术等,预测在芋螺资源库中约有70,000种具有药理活性的物质。这些活性成分包括小分子物质、多肽和酶等,其中的多肽类物质被统称为芋螺多肽。芋螺多肽(conopeptide)通常是由7-46个氨基酸构成分子量小的多肽,富含二硫键。其作用靶点通常为钙,钠,钾离子通道,烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,去甲肾上腺素转运蛋白,N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体和神经降压素受体等。因此芋螺毒素可被开发为相应受体的特异性分子探针,成为研究受体相关机体活动(如学习、记忆、兴奋产生等)和疾病的重要工具,并有望开发成为药物,可能潜在的用于治疗癫痫,阿尔茨海默症,多发性硬化症,糖尿病性神经病变,带状疱疹,帕金森综合症,癌症和神经保护或心脏保护等。2004年12月,美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)批准首个芋螺多肽药物Ziconotide(Prialt@),以鞘内靶向注射给药方式,代替吗啡用于治疗严重的慢性难治性疼痛和用于预防罹患艾滋病或阿片类药物耐受的癌症患者的中风和难治性疼痛的治疗, 由于它可以阻断哺乳动物疼痛感受神经元中的N-型钙离子通道,所以在吗啡效果不佳或不活跃的情况下,它具有强大的抗伤害感受作用,使其成为最佳的鞘内镇痛药物。此外,Ziconotide具有极好的安全性,不具有成瘾性低免疫原性,也没有炎症,神经毒性,致突变性,致畸性或致癌性等副作用。研究表明,女性25岁以后,皮肤中胶原蛋白的含量会逐渐减少,伴随着的色斑、皱纹等一系列老化现象也会越来越明显,随着人们物质生活的提高,对抗衰老、皮肤保养等也越来越看重。目前,除皱的一些有效方法是采用医美手段,比如注射肉毒毒素等。但医美手段通常需要持续进行,且容易引起副作用,比如面瘫、肌肉僵硬、疼痛等。因此,寻找安全性更高的替代方式变得越来越重要。皮肤皱纹是皮肤亚健康的表症,皱纹的产生有很多原因,主要分成内部因素及外部因素。外部因素包括紫外线、烟雾、吸烟、不良生活习惯等。内部因素包括皮肤的自然衰老和肌肉的过度收缩。随着年龄增长皮肤弹性降低,厚度变薄,皮脂分泌减少,表皮通透屏障功能降低及角质层含水量明显减少,皮肤表皮层和真皮层的结构、胶原蛋白的类型和含量均有发生变化,从而形成皱纹。肌肉的过度收缩,也会导致皮肤结构的变化,产生皱纹,如面部的鱼尾纹。而皮肤肌肉的收缩是由神经元发送的动作电位沿神经原纤维传播至其在肌纤维上的终端NMJ处,这引起神经肌肉接头(NMS)的突触前膜向突触间隙中释放神经递质Ach, ACh与突触后膜的肌肉型nAChR结合,并激活受体开放通道, Na内流,引起肌纤维内Na浓度升高,并在细胞膜上使动作电位沿着肌纤维膜纵向传导。动作电位使肌细胞膜去极化,引起Ca2+从肌质网释放。钙离子直接发起肌肉收缩过程。若能阻断NMS处的动作电位的传导过程,就能阻止肌肉的收缩作用,从而减少皮肤皱纹形成。芋螺多肽可以结合m-nAchR,阻断乙酰胆碱与m-nAchR结合,还可以特异性地阻断电压门控钠离子通道,使钠离子内流受阻,导致肌肉动作电位不能形成,表情肌得以放松,从而有效地预防和减少皱纹,可作为抗皱产品中的活性成分。24名志愿者,要求半边面部用含有3% 芋螺多肽配方,使用2小时和8小时测量数据。通过边缘投影分析的体积。将处理结束时得到的体积与初始值进行比较。结果表明,使用8小时后,每一位志愿者的鱼尾纹临床效果都有显著改善。44位自愿者(41至55岁间),选择自愿者标准: 在眼角处有细纹和皱纹(Bazin分级级别2或3),每天使用两次,共28天含3% 芋螺多肽精华,当笑的时候,使用arruther's动态纹分级法进行评估,结果表明芋螺多肽具有明显的细纹改善作用。芋螺多肽相对分子质量更小、结构更稳定、作用效果更强、更易于合成。因而芋螺多肽在开发为抗皱产品方面更有优势。芋螺多肽肽,其通过目标性的阻断电压依赖型钠离子通道,特别是阻断Nav1.4通道来阻断神经肌肉的电流传导,达到有效放松肌肉,淡化皱纹的效果。由于其直接作用于钠离子通道,作用效果迅速,30分钟即可起效。芋螺多肽是高度折叠的胜肽,强力穿透,高稳定性,目标性的针对肌肉达到放松的作用。芋螺多肽通过目标性的阻断电压依赖性钠离子通道,特别是阻断NAv1.4通道来阻断神经肌肉的电流传导,达到有效放松肌肉,瞬间淡化皱纹的效果。如果您有兴趣获取有关芋螺多肽的更详细技术资料,可联系江苏吉泰肽业有限公司。2022.12.01—02 • 中国上海中国化学制药CMC创新峰会展位号:32号》点击查看会议详情《
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用